Dynamics Review Sheet Solutions
... is zero, the object will A. slow down and stop B. change the direction of its motion C. accelerate uniformly D. continue moving with constant velocity 15. As a ball falls, the action force is the pull of the earth’s mass on the ball. The reaction force is the A. air resistance acting against the bal ...
... is zero, the object will A. slow down and stop B. change the direction of its motion C. accelerate uniformly D. continue moving with constant velocity 15. As a ball falls, the action force is the pull of the earth’s mass on the ball. The reaction force is the A. air resistance acting against the bal ...
WORK AND ENERGY
... Remember in a system where only gravity is acting (like in a roller coaster), The potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and vice versa. ...
... Remember in a system where only gravity is acting (like in a roller coaster), The potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and vice versa. ...
The Gravitational Potential Energy will be at a maximum. The
... Consider a system where a ball attached to a spring is let go. How does the KE and PE change as it moves? ...
... Consider a system where a ball attached to a spring is let go. How does the KE and PE change as it moves? ...
Physics - Denton ISD
... b) What units does this equation give us? b) How much force is required to keep the object moving? c) What do these units combine to make? c) The rock’s tendency to do this is called… 5) If my crazy cousin Paco weighs 780 N here on Earth, what is his mass? ...
... b) What units does this equation give us? b) How much force is required to keep the object moving? c) What do these units combine to make? c) The rock’s tendency to do this is called… 5) If my crazy cousin Paco weighs 780 N here on Earth, what is his mass? ...
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE SYLLABUS FOR PHYS 2425
... Explain the difference between work, energy, and power. Calculate work done by a Spring System. Write the conservation of energy laws. Differentiate between potential and kinetic energy. Explain the meaning of conservative and non-conservative forces. Explain the quantization of energy. Work problem ...
... Explain the difference between work, energy, and power. Calculate work done by a Spring System. Write the conservation of energy laws. Differentiate between potential and kinetic energy. Explain the meaning of conservative and non-conservative forces. Explain the quantization of energy. Work problem ...
Solutions - faculty.ucmerced.edu
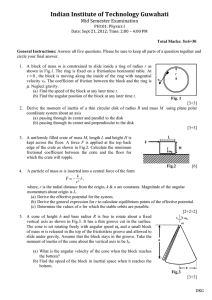
... (b) Find the amount the spring is stretched from its unstretched length when the object is in equilibrium. (c) Write expressions for the displacement x, the velocity vx , and the acceleration ax as functions of time. ...
... (b) Find the amount the spring is stretched from its unstretched length when the object is in equilibrium. (c) Write expressions for the displacement x, the velocity vx , and the acceleration ax as functions of time. ...
Examples of Lagrange`s Equations
... However, for angular coordinates we saw that the generalized force was the torque, and the generalized momentum was the angular momentum. In any case, when the generalized force is zero (i.e. the Lagrangian is independent of the generalized coordinate qi, then the generalized momentum is conserved. ...
... However, for angular coordinates we saw that the generalized force was the torque, and the generalized momentum was the angular momentum. In any case, when the generalized force is zero (i.e. the Lagrangian is independent of the generalized coordinate qi, then the generalized momentum is conserved. ...
01-4-momentum-with
... A constant force acts on a fan cart. If we double the mass of the cart (with the same force acting on the cart), has half the acceleration. Clearly the force on a cart changes the velocity of the cart. However, the rate that the velocity changes depends on the mass of the cart. Both mass and the vel ...
... A constant force acts on a fan cart. If we double the mass of the cart (with the same force acting on the cart), has half the acceleration. Clearly the force on a cart changes the velocity of the cart. However, the rate that the velocity changes depends on the mass of the cart. Both mass and the vel ...