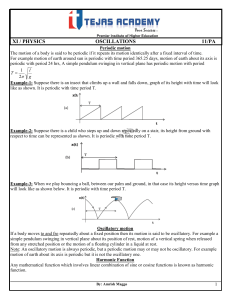
Lecture 1
... and it slides down the incline where the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.3. It hits a spring with a spring constant of 500 N/m. While it is being acted upon by the spring, assume it is on a frictionless surface. a) How far does the block go up the plane on the rebound from the spring? b) How fa ...
... and it slides down the incline where the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.3. It hits a spring with a spring constant of 500 N/m. While it is being acted upon by the spring, assume it is on a frictionless surface. a) How far does the block go up the plane on the rebound from the spring? b) How fa ...
Ch. 4 Energy - WordPress.com
... potential energy, the GPE of an object can be increased by increasing its height above the ground. • If two objects are at the same height, then the object with the larger mass has more gravitational potential energy. ...
... potential energy, the GPE of an object can be increased by increasing its height above the ground. • If two objects are at the same height, then the object with the larger mass has more gravitational potential energy. ...
6. The Impulse-Momentum Change Theorem
... First, observe that the answers in the table above reveal that the third and fourth columns are always equal; that is, the impulse is always equal to the momentum change. Observe also that the if any two of the first three columns are known, then the remaining column can be computed. This is true be ...
... First, observe that the answers in the table above reveal that the third and fourth columns are always equal; that is, the impulse is always equal to the momentum change. Observe also that the if any two of the first three columns are known, then the remaining column can be computed. This is true be ...
Experimental determination of natural frequency and damping ratio
... If excitation is harmonic, the system is forced to vibrate at excitation frequency. If the frequency of excitation coincides with one of the natural frequencies of the system, a condition of resonance is encountered and dangerously large oscillations may result, which results in failure of major str ...
... If excitation is harmonic, the system is forced to vibrate at excitation frequency. If the frequency of excitation coincides with one of the natural frequencies of the system, a condition of resonance is encountered and dangerously large oscillations may result, which results in failure of major str ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
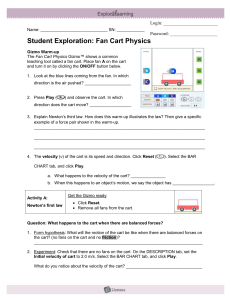
... 3. Explain Newton’s third law. How does this warm-up illustrates the law? Then give a specific example of a force pair shown in the warm-up. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
... 3. Explain Newton’s third law. How does this warm-up illustrates the law? Then give a specific example of a force pair shown in the warm-up. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ _________ ...
Chapter 10 Rotational Motion
... • An object that is rotating has rotational kinetic energy. If it is translating as well, the translational kinetic energy must be added to the rotational to find the total kinetic energy. • Angular momentum is • If the net torque on an object is zero, its angular momentum does not change. ...
... • An object that is rotating has rotational kinetic energy. If it is translating as well, the translational kinetic energy must be added to the rotational to find the total kinetic energy. • Angular momentum is • If the net torque on an object is zero, its angular momentum does not change. ...
Momentum and Its Conservation
... Conservation of Momentum Momentum in a Closed, Isolated System Systems can contain any number of objects, and the objects can stick together or come apart in a collision. Under these conditions, the law of conservation of momentum states that the momentum of any closed, isolated system does not chan ...
... Conservation of Momentum Momentum in a Closed, Isolated System Systems can contain any number of objects, and the objects can stick together or come apart in a collision. Under these conditions, the law of conservation of momentum states that the momentum of any closed, isolated system does not chan ...
PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 1
... force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the speed (not a vector, just a positive number) increases. So answer c is correct. PHY 231 ...
... force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the speed (not a vector, just a positive number) increases. So answer c is correct. PHY 231 ...
Lecture 12
... – The work done by the object (on something else) on a given path is equivalent to the work done by the something else on the object on its return trip. – This means that the net work done on the object over the closed loop is zero, which means, from the workenergy theorem, that the change in energy ...
... – The work done by the object (on something else) on a given path is equivalent to the work done by the something else on the object on its return trip. – This means that the net work done on the object over the closed loop is zero, which means, from the workenergy theorem, that the change in energy ...
What is energy? - Horace Mann Webmail
... potential energy, the GPE of an object can be increased by increasing its height above the ground. • If two objects are at the same height, then the object with the larger mass has more gravitational potential energy. ...
... potential energy, the GPE of an object can be increased by increasing its height above the ground. • If two objects are at the same height, then the object with the larger mass has more gravitational potential energy. ...
Dynamical relations in the system of two objects with internal
... principle, if interaction between them is known. On the other hand, Bertrand sets up an inverse problem of determining interaction with respect to known trajectories of motion of bodies ( [2]). As it is known, according to the Bertrand’s theorem only two types of central potentials, of Coulomb and h ...
... principle, if interaction between them is known. On the other hand, Bertrand sets up an inverse problem of determining interaction with respect to known trajectories of motion of bodies ( [2]). As it is known, according to the Bertrand’s theorem only two types of central potentials, of Coulomb and h ...
Seesaws 9 Balanced Seesaw
... Why does the seesaw need a pivot? Why does a lone rider plummet to the ground? Why do the riders’ weights and positions matter? Why does distance from the pivot affect speed? ...
... Why does the seesaw need a pivot? Why does a lone rider plummet to the ground? Why do the riders’ weights and positions matter? Why does distance from the pivot affect speed? ...