time of completion
... 10. A uniform beam of mass m = 10.0 kg and length l = 2.00 m is hung from two cables, one at the end of the beam and the other 1.25 m of the way to the other end as shown below. A box of 20.0 kg mass stands at a distance of 0.75 m from the same end. Determine the magnitudes of the forces the cable e ...
... 10. A uniform beam of mass m = 10.0 kg and length l = 2.00 m is hung from two cables, one at the end of the beam and the other 1.25 m of the way to the other end as shown below. A box of 20.0 kg mass stands at a distance of 0.75 m from the same end. Determine the magnitudes of the forces the cable e ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... arguably the most important relationship in introductory physics, because it successfully describes how our everyday world works. It is not derived from basic principles, but stands on its own as a fundamental relationship between force, mass and acceleration. r r Rewriting it as a = Fnet m , one ca ...
... arguably the most important relationship in introductory physics, because it successfully describes how our everyday world works. It is not derived from basic principles, but stands on its own as a fundamental relationship between force, mass and acceleration. r r Rewriting it as a = Fnet m , one ca ...
12.2 Chemical Calculations
... be either a reactant or a product. In mass-mass calculations, the amount of a substance is determined by measuring its mass in grams. The mass can later be converted to moles by using the molar mass. Then use the molar mass to calculate the number of moles in that mass. Moles to mass (mass-mass, mas ...
... be either a reactant or a product. In mass-mass calculations, the amount of a substance is determined by measuring its mass in grams. The mass can later be converted to moles by using the molar mass. Then use the molar mass to calculate the number of moles in that mass. Moles to mass (mass-mass, mas ...
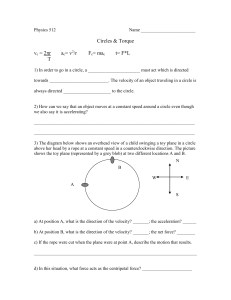
Physics 512 - Scarsdale Schools
... 4. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the object’s velocity is towards point A B C D 5. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the force acting on the object is towards A B C D 6.______ If the string breaks at this moment, the object would travel towards point A B C D 7. ______ If the sp ...
... 4. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the object’s velocity is towards point A B C D 5. ______ At the moment shown in the diagram, the force acting on the object is towards A B C D 6.______ If the string breaks at this moment, the object would travel towards point A B C D 7. ______ If the sp ...
Rotation Torque, Rolling, & Angular Momentum
... perpendicular to the baton and goes through it’s center. It spins at 3*pi rad-per-sec. He lets go of it quickly, without getting in its way or altering its rotation. He then quickly grabs the end of it and spins the baton about a new axis that is parallel to the old one, but that goes through the ro ...
... perpendicular to the baton and goes through it’s center. It spins at 3*pi rad-per-sec. He lets go of it quickly, without getting in its way or altering its rotation. He then quickly grabs the end of it and spins the baton about a new axis that is parallel to the old one, but that goes through the ro ...
ch05
... Newton’s laws fail in the following two circumstances: 1. When the speed of objects approaches (1% or more) the speed of light in vacuum (c = 8×108 m/s). In this case we must use Einstein’s special theory of relativity (1905). 2. When the objects under study become very small (e.g., electrons, atoms ...
... Newton’s laws fail in the following two circumstances: 1. When the speed of objects approaches (1% or more) the speed of light in vacuum (c = 8×108 m/s). In this case we must use Einstein’s special theory of relativity (1905). 2. When the objects under study become very small (e.g., electrons, atoms ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. When building soap box cars which race by
... Force needed is greater in (a), whereas the work and the final gravitational potential energy of the box (which increases by the amount of work done) are the same in the two cases, since they depend only on the height of the box. 17. You are riding on the edge of a spinning playground merry-go-round ...
... Force needed is greater in (a), whereas the work and the final gravitational potential energy of the box (which increases by the amount of work done) are the same in the two cases, since they depend only on the height of the box. 17. You are riding on the edge of a spinning playground merry-go-round ...
Document
... speed of 20 m/s. It rises to a maximum height of 18 m above the launch point. How much work is done by the dissipative (air) resistive force on the projectile during ...
... speed of 20 m/s. It rises to a maximum height of 18 m above the launch point. How much work is done by the dissipative (air) resistive force on the projectile during ...
2, 4, 6, 7, 12 / 3, 9, 15, 20, 26, 37, 41, 44, 47, 53, 60
... therefore, has zero acceleration. From Newton's second law, we know that the net external force on the sailboat must be zero. a. There is no work done on the sailboat by a zero net external force. b. Work is done by the individual forces that act on the boat; namely the wind that propels the boat fo ...
... therefore, has zero acceleration. From Newton's second law, we know that the net external force on the sailboat must be zero. a. There is no work done on the sailboat by a zero net external force. b. Work is done by the individual forces that act on the boat; namely the wind that propels the boat fo ...
Practice Exam
... (1) stronger and repulsive (2) weaker and repulsive (3) stronger and attractive (4) weaker and attractive 28 A balloon is rubbed against a student’s hair and then touched to a wall. The balloon “sticks” to the wall due to (1) electrostatic forces between the particles of the balloon (2) magnetic fo ...
... (1) stronger and repulsive (2) weaker and repulsive (3) stronger and attractive (4) weaker and attractive 28 A balloon is rubbed against a student’s hair and then touched to a wall. The balloon “sticks” to the wall due to (1) electrostatic forces between the particles of the balloon (2) magnetic fo ...
Circular Motion HW-4
... through 3/4 of a turn. Find the average frictional torque (net torque) exerted on the wheel given that it is a solid disk of radius 0.710 m and mass 6.40 kg. 4. A string of negligible mass is wound around a disk-shaped pulley of radius 0.121 m and mass 0.742 kg. Hanging from the string is a 2.85-kg ...
... through 3/4 of a turn. Find the average frictional torque (net torque) exerted on the wheel given that it is a solid disk of radius 0.710 m and mass 6.40 kg. 4. A string of negligible mass is wound around a disk-shaped pulley of radius 0.121 m and mass 0.742 kg. Hanging from the string is a 2.85-kg ...
Random Problems
... (b) If during the force of impact, Pete exerted a force of F on Repeat, what force did Repeat exert on Pete? According to Newton’s 3rd Law, for every force there is an equal but opposite force, therefore, Repeat exerted on force, F, on Pete. ...
... (b) If during the force of impact, Pete exerted a force of F on Repeat, what force did Repeat exert on Pete? According to Newton’s 3rd Law, for every force there is an equal but opposite force, therefore, Repeat exerted on force, F, on Pete. ...