Energy
... Work is a scalar quantity. It depends only on the components of the force and distance that are in the same direction. The units in which work is measured are the units of force times the units of distance, newton-meters (N . m). This unit could be called a newton-meter, but it is given the name jou ...
... Work is a scalar quantity. It depends only on the components of the force and distance that are in the same direction. The units in which work is measured are the units of force times the units of distance, newton-meters (N . m). This unit could be called a newton-meter, but it is given the name jou ...
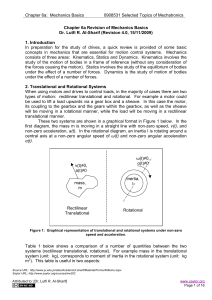
Revision of Mechanics Basics
... In many mechanical systems the concept of dead load and live load exists. Dead load is always present in the system and does not provide any useful contribution. An example of this is the mass of the car that transports passengers. In each journey we move the mass of the whole vehicle back and forth ...
... In many mechanical systems the concept of dead load and live load exists. Dead load is always present in the system and does not provide any useful contribution. An example of this is the mass of the car that transports passengers. In each journey we move the mass of the whole vehicle back and forth ...
Chapter 6, Week 6.
... Equation 6.10 says that the local acceleration of gravity, g, near the Earth’s surface is known at a given value. We will use the standard approximation of g as an appropriate value for this problem. Equation 6.11 says that there is no heat transfer between the cart and it surroundings. As is clear ...
... Equation 6.10 says that the local acceleration of gravity, g, near the Earth’s surface is known at a given value. We will use the standard approximation of g as an appropriate value for this problem. Equation 6.11 says that there is no heat transfer between the cart and it surroundings. As is clear ...
Patterns of Motion
... If you now apply a greater force on the pedals the extra force you apply is unbalanced by friction and air resistance. Hence there will be a net force greater than zero, and you will accelerate. You will accelerate during, and only during, the time that the (unbalanced) net force is greater than ze ...
... If you now apply a greater force on the pedals the extra force you apply is unbalanced by friction and air resistance. Hence there will be a net force greater than zero, and you will accelerate. You will accelerate during, and only during, the time that the (unbalanced) net force is greater than ze ...
force and acceleration
... This is constant acceleration. ,/ Galileo defined the rate of change of velocity as acceleration :* ...
... This is constant acceleration. ,/ Galileo defined the rate of change of velocity as acceleration :* ...
Whoosh!
... Look at the balls being juggled in Figure 11–5. If you consider the system to be only one ball, then it has several external forces exerted on it. The force of the juggler’s hand does work, giving the ball its original kinetic energy. After the ball leaves his hand, only the force of gravity acts on ...
... Look at the balls being juggled in Figure 11–5. If you consider the system to be only one ball, then it has several external forces exerted on it. The force of the juggler’s hand does work, giving the ball its original kinetic energy. After the ball leaves his hand, only the force of gravity acts on ...
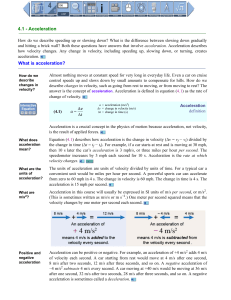
4.1 - Acceleration What is acceleration?
... The car in the diagram below has an initial upward velocity of −1 m/s. The constant downward acceleration adds +0.5 m/s to the velocity every second. The car’s velocity starts negative then becomes 0.5 m/s more positive each second until v = 0. At the car’s highest point its velocity is zero. After ...
... The car in the diagram below has an initial upward velocity of −1 m/s. The constant downward acceleration adds +0.5 m/s to the velocity every second. The car’s velocity starts negative then becomes 0.5 m/s more positive each second until v = 0. At the car’s highest point its velocity is zero. After ...
Newtonian Mechanics
... book known as Principia. The full Latin title of the book1 may be translated into English as Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy. The theory that the planets (including Earth) revolve around the sun was published by Nicolaus Copernicus in 1543. This was a revolutionary idea! The picture of ...
... book known as Principia. The full Latin title of the book1 may be translated into English as Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy. The theory that the planets (including Earth) revolve around the sun was published by Nicolaus Copernicus in 1543. This was a revolutionary idea! The picture of ...
High School - Iredell
... I will show how to use different frames of reference to describe an objects current position. ...
... I will show how to use different frames of reference to describe an objects current position. ...
Newton`s Laws of. Motion
... of a reference frame, that is, a choice of spatial origin and axes to label positions as in Figure 1.1 and a choice of temporal origin to measure times. The difference between two frames may be quite minor. For instance, they may differ only in their choice of the origin of time — what one frame lab ...
... of a reference frame, that is, a choice of spatial origin and axes to label positions as in Figure 1.1 and a choice of temporal origin to measure times. The difference between two frames may be quite minor. For instance, they may differ only in their choice of the origin of time — what one frame lab ...
Ch17 Oscillations
... 11.6 cm from equilibrium and released. Take time t=0 when the block is released, the horizontal surface is frictionless. (a) What is the total energy? (b) What is the maximum speed of the block? (c) What is the maximum acceleration? (d) What is the position, velocity, and acceleration at t=0.215s? ...
... 11.6 cm from equilibrium and released. Take time t=0 when the block is released, the horizontal surface is frictionless. (a) What is the total energy? (b) What is the maximum speed of the block? (c) What is the maximum acceleration? (d) What is the position, velocity, and acceleration at t=0.215s? ...
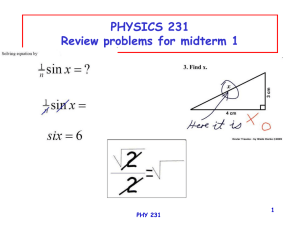
PHYSICS 231 Review problems for midterm 1 1 PHY 231
... force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the speed (not a vector, just a positive number) increases. So answer c is correct. PHY 231 ...
... force is slowing it down. This goes on until it reaches the highest point, where the velocity/speed equals zero. The ball than moves down: the velocity becomes negative, but the speed (not a vector, just a positive number) increases. So answer c is correct. PHY 231 ...
Lecture notes for Physics 10154: General Physics I
... the equation match. It is important to remember that the “=” symbol has a very specific meaning in mathematics and physics. It means that whatever is on either side of this sign is exactly the same thing even though it may look a little different on either side. If both sides must be the same, then ...
... the equation match. It is important to remember that the “=” symbol has a very specific meaning in mathematics and physics. It means that whatever is on either side of this sign is exactly the same thing even though it may look a little different on either side. If both sides must be the same, then ...