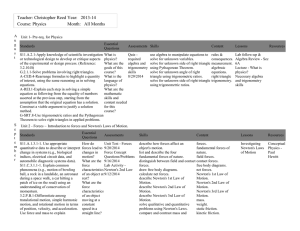
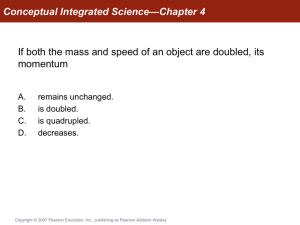
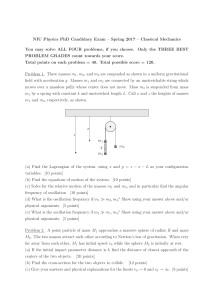
to this worksheet as nicely formatted
... 79 A car exerts a force of 10,000 N while driving on a horizontal stretch of road. How much work is done when the car travels 100 m? 80 A bucket is lifted out of a well by a 200 N force. If the well is 30 m deep, then how much work is done in lifting the bucket? 81 A 60,000 kg jet exerts a force of ...
... 79 A car exerts a force of 10,000 N while driving on a horizontal stretch of road. How much work is done when the car travels 100 m? 80 A bucket is lifted out of a well by a 200 N force. If the well is 30 m deep, then how much work is done in lifting the bucket? 81 A 60,000 kg jet exerts a force of ...
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum
... .22 caliber long rifle can fire a 30 g bullet at about 500 m/s. Design a ballistic pendulum that could measure the speed of such a bullet. In particular, be sure to give the mass and moment of inertia of the ballistic pendulum, its length, and through what angle the pendulum would move after impact. ...
... .22 caliber long rifle can fire a 30 g bullet at about 500 m/s. Design a ballistic pendulum that could measure the speed of such a bullet. In particular, be sure to give the mass and moment of inertia of the ballistic pendulum, its length, and through what angle the pendulum would move after impact. ...
AP Physics C - Mechanics Spring and a Block
... equilibrium point. This can be a slow oscillation - like the earth orbiting the sun, returning to its starting place once a year. Or very rapid oscillations such as alternating current or electric and magnetic fields. Simple harmonic motion is a periodic motion where there is a force that acts to re ...
... equilibrium point. This can be a slow oscillation - like the earth orbiting the sun, returning to its starting place once a year. Or very rapid oscillations such as alternating current or electric and magnetic fields. Simple harmonic motion is a periodic motion where there is a force that acts to re ...
Form A
... E) The force of the earth on the spaceship and the force of the spaceship on the earth cancel because they are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. F) The location of the spaceship is equidistant between the earth and the moon G) The earth's gravitation force is balanced by the centrifugal ...
... E) The force of the earth on the spaceship and the force of the spaceship on the earth cancel because they are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. F) The location of the spaceship is equidistant between the earth and the moon G) The earth's gravitation force is balanced by the centrifugal ...
Chapter 10
... Example 10.2 The Speed of a Falling Rock ASSESS The figure below shows energy bar charts for Amber and Bill. despite their disagreement over the value of Ug, Amber and Bill arrive at the same value for vf and their Kf bars are the same height. You can place the origin of your coordinate system, and ...
... Example 10.2 The Speed of a Falling Rock ASSESS The figure below shows energy bar charts for Amber and Bill. despite their disagreement over the value of Ug, Amber and Bill arrive at the same value for vf and their Kf bars are the same height. You can place the origin of your coordinate system, and ...
Energy HD APP WOWatch Teacher
... This app explores several forms of energy with videos and fun facts. We will explore the major types of energy: potential energy and kinetic energy. Potential energy is stored energy that is ready to use. Kinetic energy is energy of motion. It is not just ready; it’s already on the move. We will als ...
... This app explores several forms of energy with videos and fun facts. We will explore the major types of energy: potential energy and kinetic energy. Potential energy is stored energy that is ready to use. Kinetic energy is energy of motion. It is not just ready; it’s already on the move. We will als ...
Physics as Spacetime Geometry
... space), which as such would be absolute (the same for all observers). As a space constitutes a class of simultaneous events (the space points at a given moment), a single (absolute) space implies absolute simultaneity and therefore absolute time as well. Hence a three-dimensional world allows only a ...
... space), which as such would be absolute (the same for all observers). As a space constitutes a class of simultaneous events (the space points at a given moment), a single (absolute) space implies absolute simultaneity and therefore absolute time as well. Hence a three-dimensional world allows only a ...
Chapter 8 Gravitational Attraction and Unification of Forces
... There are several steps involved, and it is probably desirable to begin with a brief review. Recall that we are dealing with dipole waves in spacetime which modulate both the rate of time and volume. There are two ways that we can express the amplitude of the dipole in spacetime: ...
... There are several steps involved, and it is probably desirable to begin with a brief review. Recall that we are dealing with dipole waves in spacetime which modulate both the rate of time and volume. There are two ways that we can express the amplitude of the dipole in spacetime: ...