The Physics of Superheroes by James Kakalios - crespiphysics
... P80 size of atom determined by: 1) mass of electron 2) charge of electron 3) # of protons in nucleus 4) Planck’s constant, h -these are all constants, so you can’t change the size of an atom P81 2nd option to shrink-remove atoms -to go from 6 ft to 6 inches (and corresponding reduction in width and ...
... P80 size of atom determined by: 1) mass of electron 2) charge of electron 3) # of protons in nucleus 4) Planck’s constant, h -these are all constants, so you can’t change the size of an atom P81 2nd option to shrink-remove atoms -to go from 6 ft to 6 inches (and corresponding reduction in width and ...
Review - Mr MAC's Physics
... pendulum using the equipment provided. The photo-gates must be set up in “gate” mode this time. The width of the pendulum bob is an important number. To get it accurately, use the caliper. Turn in just your data, calculations, and result. Clearly show the speed you predict for the pendulum bob from ...
... pendulum using the equipment provided. The photo-gates must be set up in “gate” mode this time. The width of the pendulum bob is an important number. To get it accurately, use the caliper. Turn in just your data, calculations, and result. Clearly show the speed you predict for the pendulum bob from ...
- Philsci
... conclude that a condition rg R cannot be physically realized. It follows from (1.11) that the proper mass exponentially approaches a zero limit at rg /r , therefore, a sphere with rg R cannot be formed. The difference of (1.25) from (1.11) is because the gravitational dynamic force acquires ...
... conclude that a condition rg R cannot be physically realized. It follows from (1.11) that the proper mass exponentially approaches a zero limit at rg /r , therefore, a sphere with rg R cannot be formed. The difference of (1.25) from (1.11) is because the gravitational dynamic force acquires ...
PERFORMANCE STANDARDS IS 3
... 14. Know that every object exerts gravitational force on every other object, and how this force depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between them. 15. Know that when one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force of equal magnitude and in the opposite ...
... 14. Know that every object exerts gravitational force on every other object, and how this force depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between them. 15. Know that when one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force of equal magnitude and in the opposite ...
How do we describe motion?
... How do gravity and energy together explain orbits? • Orbits cannot change spontaneously. • An object’s orbit can only change if it somehow gains or loses orbital energy = ...
... How do gravity and energy together explain orbits? • Orbits cannot change spontaneously. • An object’s orbit can only change if it somehow gains or loses orbital energy = ...
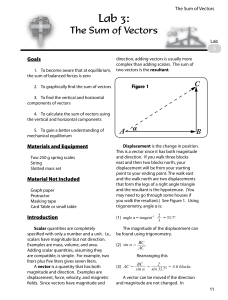
Scalars and vectors
... length of the arrow indicates the magnitude, and the direction the direction! ...
... length of the arrow indicates the magnitude, and the direction the direction! ...
Energy - Team841
... 1. Cash in your wallet 3. A Bank Account 2. Gold or Silver Coins 4. Traveler’s Check ...
... 1. Cash in your wallet 3. A Bank Account 2. Gold or Silver Coins 4. Traveler’s Check ...
Document
... This simple pendulum consists of a small bob of mass m suspended by a massless cord of length l. The bob is released (without a push) at t = 0, where the cord makes an angle θ = θ0 to the vertical. (a) Describe the motion of the bob in terms of kinetic energy and potential energy. Then determine the ...
... This simple pendulum consists of a small bob of mass m suspended by a massless cord of length l. The bob is released (without a push) at t = 0, where the cord makes an angle θ = θ0 to the vertical. (a) Describe the motion of the bob in terms of kinetic energy and potential energy. Then determine the ...
chapter11
... A non-zero torque produces a change in the angular momentum The result of the change in angular momentum is a precession about the z axis The direction of the angular momentum is changing The precessional motion is the motion of the symmetry axis about the vertical The precession is usually slow rel ...
... A non-zero torque produces a change in the angular momentum The result of the change in angular momentum is a precession about the z axis The direction of the angular momentum is changing The precessional motion is the motion of the symmetry axis about the vertical The precession is usually slow rel ...
HP Unit 3 - student handout
... Newton’s First Law of Motion Newton’s 1st Law is often called the law of inertia. ...
... Newton’s First Law of Motion Newton’s 1st Law is often called the law of inertia. ...
NCEA Level 3 Physics (91524) 2016 Assessment Schedule
... Correct angle for t = 0.25 s. OR Correct value for angular frequency. OR Use of suitable equation ...
... Correct angle for t = 0.25 s. OR Correct value for angular frequency. OR Use of suitable equation ...
advanced placement chemistry
... B. What term in the distance formula does the lower rectangular area of the graph represent? C. What term in the distance formula does the upper triangular area of the graph represent? D. Using the knowledge that the area under the velocity-time graph is the objects total displacement (Δx), use Geom ...
... B. What term in the distance formula does the lower rectangular area of the graph represent? C. What term in the distance formula does the upper triangular area of the graph represent? D. Using the knowledge that the area under the velocity-time graph is the objects total displacement (Δx), use Geom ...