Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with th ...
... the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with th ...
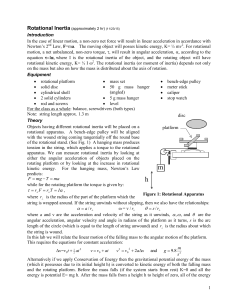
Rotational Inertia
... Determining Rotational Inertia of an Object Added to the Platform Now you will add various objects onto the platform and determine their rotational inertia. If the new object has rotational inertia I then the total rotational inertia of both the platform and the object on top of it is Itotal = I0 + ...
... Determining Rotational Inertia of an Object Added to the Platform Now you will add various objects onto the platform and determine their rotational inertia. If the new object has rotational inertia I then the total rotational inertia of both the platform and the object on top of it is Itotal = I0 + ...
Unit 2 Section 4 Notes Newton`s Laws of Motion
... stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an outside force. In other words, the net force acting on the object is zero. Example: A book sliding on any surface will eventually come to a stop due to friction. If it weren’t for friction, the book would continue to s ...
... stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an outside force. In other words, the net force acting on the object is zero. Example: A book sliding on any surface will eventually come to a stop due to friction. If it weren’t for friction, the book would continue to s ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... acting on a 4500 kg spacecraft when it is 3 Earth radii from the Earth’s center? ...
... acting on a 4500 kg spacecraft when it is 3 Earth radii from the Earth’s center? ...
PHYSICS 151 – Notes for Online Lecture #15
... W = F cos θ x = 1312.5 J = 1300 J So although the person applies the same amount of force each time, less work is done in the case where the force is applied at an angle. There are other forces acting on this box, including the normal force and gravity. Do they do any work on the box as it moves acr ...
... W = F cos θ x = 1312.5 J = 1300 J So although the person applies the same amount of force each time, less work is done in the case where the force is applied at an angle. There are other forces acting on this box, including the normal force and gravity. Do they do any work on the box as it moves acr ...
1 CHAPTER 22 DIMENSIONS 22.1 Mass, Length and Time Any
... momentum J. We might then say that the dimensions of area could be expressed as E −2 V 2 J 2 . (Verify this!) While agreeing that such a system might be possible, you might feel that it would be totally absurd and there is no point in reading further. But stop! Such a system is not only possible, bu ...
... momentum J. We might then say that the dimensions of area could be expressed as E −2 V 2 J 2 . (Verify this!) While agreeing that such a system might be possible, you might feel that it would be totally absurd and there is no point in reading further. But stop! Such a system is not only possible, bu ...
Simple Harmonic Motion
... The total energy of the undamped oscillating system is A a maximum at an extreme position of the mass. B a maximum at the mean position of the mass. C a minimum at the mean position of the mass. D the same at all positions of the mass. (Total for Question = 1 mark) ...
... The total energy of the undamped oscillating system is A a maximum at an extreme position of the mass. B a maximum at the mean position of the mass. C a minimum at the mean position of the mass. D the same at all positions of the mass. (Total for Question = 1 mark) ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • A car will tend to either keep standing still or keep moving in a straight line at the same speed unless some unbalanced force makes it do otherwise. • Examples of unbalanced forces are air r ...
... to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. • A car will tend to either keep standing still or keep moving in a straight line at the same speed unless some unbalanced force makes it do otherwise. • Examples of unbalanced forces are air r ...
AP Physics 1 Circular Motion Multiple
... 10. A heavy (2.0 kg) point-like object rests 2.0m from the center of a rough turntable as the turntable rotates. The period of the turntable's rotation is 5.0 seconds. The coefficient of static friction is 0.80. What is the magnitude of the force of friction acting on the object? (A) 19.6N ...
... 10. A heavy (2.0 kg) point-like object rests 2.0m from the center of a rough turntable as the turntable rotates. The period of the turntable's rotation is 5.0 seconds. The coefficient of static friction is 0.80. What is the magnitude of the force of friction acting on the object? (A) 19.6N ...
Course Title: Physical Science 9 A – Physics Highly Qualified
... amplitudes, and travel at different speeds. PS3E (9-12) Electromagnetic waves differ from physical waves because they do not require a medium and they all travel at the same speed in a vacuum. This is the maximum speed that any object or wave can travel. Forms of electromagnetic waves include X-ra ...
... amplitudes, and travel at different speeds. PS3E (9-12) Electromagnetic waves differ from physical waves because they do not require a medium and they all travel at the same speed in a vacuum. This is the maximum speed that any object or wave can travel. Forms of electromagnetic waves include X-ra ...