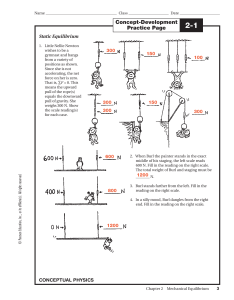
Chapter Assessment f
... rock. The rock has kinetic and potential energy as it flies through the air. When it hits the wall, the inelastic collision causes most of the mechanical energy to be converted to thermal and sound energy and to do work breaking apart the wall structure. Some of the mechan ical energy appears in the ...
... rock. The rock has kinetic and potential energy as it flies through the air. When it hits the wall, the inelastic collision causes most of the mechanical energy to be converted to thermal and sound energy and to do work breaking apart the wall structure. Some of the mechan ical energy appears in the ...
Welcome to Physics I !!!
... • Cross products are messy…why would we ever use them, instead of the simpler L I RF • Because the cross product allows us to determine the angular momentum of, or torque on, objects which are not necessarily moving with constant, or even circular motion! ...
... • Cross products are messy…why would we ever use them, instead of the simpler L I RF • Because the cross product allows us to determine the angular momentum of, or torque on, objects which are not necessarily moving with constant, or even circular motion! ...
Chapter 2. Conservation of Energy
... (c) The net force on each block is zero, since their acceleration is also zero. It follows that the total work on each block must be zero. 2. (Prob. 6.19 in Young and Freedman.) Use the work-energy theorem to work these problems. Neglect air resistance in all cases. (a) A branch falls from a 95-m ta ...
... (c) The net force on each block is zero, since their acceleration is also zero. It follows that the total work on each block must be zero. 2. (Prob. 6.19 in Young and Freedman.) Use the work-energy theorem to work these problems. Neglect air resistance in all cases. (a) A branch falls from a 95-m ta ...
... This value is the net work done on the package. The person actually does more work than this, because friction opposes the motion. Friction does negative work and removes some of the energy the person expends and converts it to thermal energy. The net work equals the sum of the work done by each ind ...
biomechanics2008
... Using this concept, explain why: a. The white ball in pool slows down after impacting the black. Some of the momentum of the white ball is passed on to the black ball. b. When suddenly braking in a car, your body moves forward (thankfully you are wearing a seatbelt). The momentum of the car is tran ...
... Using this concept, explain why: a. The white ball in pool slows down after impacting the black. Some of the momentum of the white ball is passed on to the black ball. b. When suddenly braking in a car, your body moves forward (thankfully you are wearing a seatbelt). The momentum of the car is tran ...
Chapter 4 Kinetics of a particle
... Therefore, any path Fc dr is a function of initial and end points only, It is defined as the change of potential energy, P.E. P.E. between two points is equal to the work done by an external force against the field of a conservative force for bringing the particle from the starting point ...
... Therefore, any path Fc dr is a function of initial and end points only, It is defined as the change of potential energy, P.E. P.E. between two points is equal to the work done by an external force against the field of a conservative force for bringing the particle from the starting point ...
Slide 1
... You’ll notice as you pull the spring, that the further you extend the spring, then the greater the force that you have to exert in order to extend it even further. As long as the spring is not streched beyond a certain extension, called elastic limit, the force is directly proportional to the ex ...
... You’ll notice as you pull the spring, that the further you extend the spring, then the greater the force that you have to exert in order to extend it even further. As long as the spring is not streched beyond a certain extension, called elastic limit, the force is directly proportional to the ex ...













![Introduction to Potential Energy Chapter 7 [ Edit ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001806152_1-56e31e3a0f500f873edd7dba09c21af1-300x300.png)