NEWTON`S LAWS OF MOT ION, FRICTION
... Change of inertia (rest or motion) motion and direction (in case of motion) is only possible by an external force in an inertial frame of reference. Inertial frame of reference is the frame which is a non-accelerated accelerated frame. Earth is treated as inertial frame with some degree of approxima ...
... Change of inertia (rest or motion) motion and direction (in case of motion) is only possible by an external force in an inertial frame of reference. Inertial frame of reference is the frame which is a non-accelerated accelerated frame. Earth is treated as inertial frame with some degree of approxima ...
Chapter 9 Rotation
... reaches the bottom first. (b) The coin reaches the bottom first. (c) The coin and hoop arrive at the bottom simultaneously. (d) The race to the bottom depends on their relative masses. (e) The race to the bottom depends on their relative diameters. Picture the Problem The object moving the fastest w ...
... reaches the bottom first. (b) The coin reaches the bottom first. (c) The coin and hoop arrive at the bottom simultaneously. (d) The race to the bottom depends on their relative masses. (e) The race to the bottom depends on their relative diameters. Picture the Problem The object moving the fastest w ...
1101 Lab 8 - Oscillations
... stretch them enough so the cart oscillates smoothly. Find the most appropriate cart mass. Practice releasing the cart smoothly. How long does it take for the oscillations to stop? What effect will this have on your measured values compared to your predicted values? How can you affect this time? What ...
... stretch them enough so the cart oscillates smoothly. Find the most appropriate cart mass. Practice releasing the cart smoothly. How long does it take for the oscillations to stop? What effect will this have on your measured values compared to your predicted values? How can you affect this time? What ...
Physics Fall Semester Final Answer Section
... ____ 45. A net force of 6.8 N accelerates a 31 kg scooter across a level parking lot. What is the magnitude of the scooter’s acceleration? a. 0.22 m/s c. 3.2 m/s b. 0.69 m/s d. 4.6 m/s ____ 46. Whenever an object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force of the same magnitud ...
... ____ 45. A net force of 6.8 N accelerates a 31 kg scooter across a level parking lot. What is the magnitude of the scooter’s acceleration? a. 0.22 m/s c. 3.2 m/s b. 0.69 m/s d. 4.6 m/s ____ 46. Whenever an object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force of the same magnitud ...
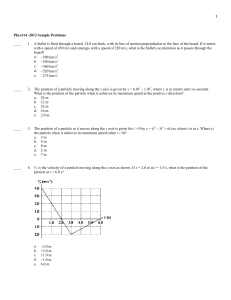
Phys114 -2013 Sample Problems ____ 1. A bullet is fired through a
... forces are applied separately to the two bodies. Jake says that equal forces applied for equal times do equal amounts of work on the two bodies. Jane says that the two forces do equal amounts of work only if the two bodies move equal distances in the direction of the forces. Which one, if either, is ...
... forces are applied separately to the two bodies. Jake says that equal forces applied for equal times do equal amounts of work on the two bodies. Jane says that the two forces do equal amounts of work only if the two bodies move equal distances in the direction of the forces. Which one, if either, is ...
Chapter 9 - Impulse and Momentum
... clay and a super-bouncy Superball next to your bed, both the same size and same mass. You’ve only time to throw one. Which will it be? Your life depends on making the right choice! ...
... clay and a super-bouncy Superball next to your bed, both the same size and same mass. You’ve only time to throw one. Which will it be? Your life depends on making the right choice! ...
Ch14 Homework Solutions
... Neglecting the mass of the spring results in your using a value for the mass of the oscillating system that is smaller than its actual value. Hence your calculated value for the period will be smaller than the actual period of the system. Because ω = k m , neglecting the mass of the spring will resu ...
... Neglecting the mass of the spring results in your using a value for the mass of the oscillating system that is smaller than its actual value. Hence your calculated value for the period will be smaller than the actual period of the system. Because ω = k m , neglecting the mass of the spring will resu ...
to apply the equation to the specific forces present on
... When more than one force acts on an object those forces must be added together as vectors. One implication of this is that forces that act in the same direction will add together, while forces that act in opposite directions will reduce each other. The critical determiner of how an object moves will ...
... When more than one force acts on an object those forces must be added together as vectors. One implication of this is that forces that act in the same direction will add together, while forces that act in opposite directions will reduce each other. The critical determiner of how an object moves will ...
Target – Conceptualise friction I can define friction. I can recognise
... A slippery substance known as a __________ stops surfaces _________ together. This makes friction ______er. A hovercraft puts a layer of ____ between two surfaces to make friction __________. Wheels, roller and spheres make the surfaces in contact ______er, so friction is ______. If friction is smal ...
... A slippery substance known as a __________ stops surfaces _________ together. This makes friction ______er. A hovercraft puts a layer of ____ between two surfaces to make friction __________. Wheels, roller and spheres make the surfaces in contact ______er, so friction is ______. If friction is smal ...
Engineering Mechanics
... Continuum mechanics is concerned with motion and deformation of material objects, called bodies, under the action of forces. If these objects are solid bodies, the respective subject area is termed solid mechanics, if they are fluids, it is fluid mechanics or fluid dynamics. The mathematical equatio ...
... Continuum mechanics is concerned with motion and deformation of material objects, called bodies, under the action of forces. If these objects are solid bodies, the respective subject area is termed solid mechanics, if they are fluids, it is fluid mechanics or fluid dynamics. The mathematical equatio ...
Mechanical oscillation, resonance
... 5. The phase constant (α) is a constant in the argument of the sine (or cosine) function used to describe the oscillatory motion: x = A sin(ω·t + α). It is determined by the initial state of the system. 6. A simple (or mathematical) pendulum consists of a point particle of mass m, swinging from a m ...
... 5. The phase constant (α) is a constant in the argument of the sine (or cosine) function used to describe the oscillatory motion: x = A sin(ω·t + α). It is determined by the initial state of the system. 6. A simple (or mathematical) pendulum consists of a point particle of mass m, swinging from a m ...