Seciton 7-1 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Two integers from 1 to 10 are randomly selected. The same number may be chosen twice. What is the probability that both numbers are less than 9? ...
... Two integers from 1 to 10 are randomly selected. The same number may be chosen twice. What is the probability that both numbers are less than 9? ...
Introduction to probability
... (3) You throw a dice twice (the first dice is, say, red and the second one is yellow). What is the sample space here? What is the probability that the sum of the face values is equal to 7? To 6? To 5? To 12? Note: the probability of the sum of the face values being equal to 7 is 1/ 6 , while the pro ...
... (3) You throw a dice twice (the first dice is, say, red and the second one is yellow). What is the sample space here? What is the probability that the sum of the face values is equal to 7? To 6? To 5? To 12? Note: the probability of the sum of the face values being equal to 7 is 1/ 6 , while the pro ...
Probability Notes
... A random number generator on a computer selects three integers from 1 to 20. What is the probability that all three numbers are less than or equal to 5? The probability of selecting a number from 1 to 5 is: ...
... A random number generator on a computer selects three integers from 1 to 20. What is the probability that all three numbers are less than or equal to 5? The probability of selecting a number from 1 to 5 is: ...
Recitation 11 Supplementary Exercises
... First Note: To be a pro in probability theory, you need to do a lot of problems. The more you expose yourself to problems, the easier you are able to interpret them. Some of the following exercises are from the textbook, but I recommend that you do the remaining exercies in the book as well, especia ...
... First Note: To be a pro in probability theory, you need to do a lot of problems. The more you expose yourself to problems, the easier you are able to interpret them. Some of the following exercises are from the textbook, but I recommend that you do the remaining exercies in the book as well, especia ...
Addition and Multiplication Principles of Counting
... To find the number of codes, find the sum of the numbers of possibilities for 1-letter codes, 2-letter codes and 3letter codes. 1-letter: 26 choices for each letter and 10 choices for each digit. So 26•10•10 = ...
... To find the number of codes, find the sum of the numbers of possibilities for 1-letter codes, 2-letter codes and 3letter codes. 1-letter: 26 choices for each letter and 10 choices for each digit. So 26•10•10 = ...
Probability of Simple Events
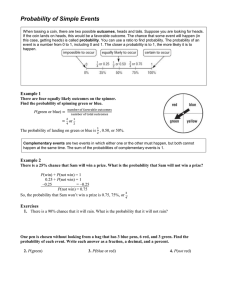
... Probability of Simple Events When tossing a coin, there are two possible outcomes, heads and tails. Suppose you are looking for heads. If the coin lands on heads, this would be a favorable outcome. The chance that some event will happen (in this case, getting heads) is called probability. You can us ...
... Probability of Simple Events When tossing a coin, there are two possible outcomes, heads and tails. Suppose you are looking for heads. If the coin lands on heads, this would be a favorable outcome. The chance that some event will happen (in this case, getting heads) is called probability. You can us ...
P( number greater than 5)
... Based on the P(students identifying the Da Vinci) = 20% from the previous question, how many of the 250 students would be able to identify the Da Vinci? ...
... Based on the P(students identifying the Da Vinci) = 20% from the previous question, how many of the 250 students would be able to identify the Da Vinci? ...
Stat 414.2 - Penn State Department of Statistics
... Schaum's Outline Series has 2 study guides with many worked out programs that may be useful for those requiring extra practice: Probability Calculus Prerequisites: Math 230 or Math 231 Learning Outcomes: Probability theory is used in almost all disciplines in the physical, biological and social scie ...
... Schaum's Outline Series has 2 study guides with many worked out programs that may be useful for those requiring extra practice: Probability Calculus Prerequisites: Math 230 or Math 231 Learning Outcomes: Probability theory is used in almost all disciplines in the physical, biological and social scie ...
Chapter 5: Regression - Tench's Homepage / FrontPage
... event has occurred. This idea is the key to many applications of probability. When we are trying to find the probability that one event will happen under the condition that some other event is already known to have occurred, we are trying to determine a conditional probability. The probability that ...
... event has occurred. This idea is the key to many applications of probability. When we are trying to find the probability that one event will happen under the condition that some other event is already known to have occurred, we are trying to determine a conditional probability. The probability that ...
barnfm10e_ppt_7_1
... • Example: Probability of a sum of 7 when two dice are rolled. First we must calculate the number of events of the sample space. From our previous example, we know that there are 36 possible sums that can occur when two dice are rolled. Of these 36 possibilities, how many ways can a sum of seven occ ...
... • Example: Probability of a sum of 7 when two dice are rolled. First we must calculate the number of events of the sample space. From our previous example, we know that there are 36 possible sums that can occur when two dice are rolled. Of these 36 possibilities, how many ways can a sum of seven occ ...
Ars Conjectandi

Ars Conjectandi (Latin for The Art of Conjecturing) is a book on combinatorics and mathematical probability written by Jakob Bernoulli and published in 1713, eight years after his death, by his nephew, Niklaus Bernoulli. The seminal work consolidated, apart from many combinatorial topics, many central ideas in probability theory, such as the very first version of the law of large numbers: indeed, it is widely regarded as the founding work of that subject. It also addressed problems that today are classified in the twelvefold way, and added to the subjects; consequently, it has been dubbed an important historical landmark in not only probability but all combinatorics by a plethora of mathematical historians. The importance of this early work had a large impact on both contemporary and later mathematicians; for example, Abraham de Moivre.Bernoulli wrote the text between 1684 and 1689, including the work of mathematicians such as Christiaan Huygens, Gerolamo Cardano, Pierre de Fermat, and Blaise Pascal. He incorporated fundamental combinatorial topics such as his theory of permutations and combinations—the aforementioned problems from the twelvefold way—as well as those more distantly connected to the burgeoning subject: the derivation and properties of the eponymous Bernoulli numbers, for instance. Core topics from probability, such as expected value, were also a significant portion of this important work.