Physics and the Search for Ultimate BuildingBlocks
... theory incorporating both electromagnetism and the weak interaction. ...
... theory incorporating both electromagnetism and the weak interaction. ...
PPT
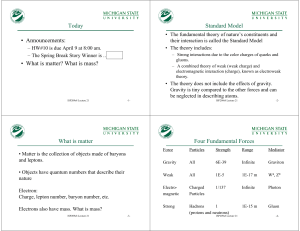
... • Some particles (e.g., quarks) participate in EM, but not weak interactions, and some (e.g., neutrinos) vice-versa. • But there are similarities. Within its short range, the weak interaction is actually the same strength as EM. It has been known since 1935 (Yukawa) that the shortrange forces are du ...
... • Some particles (e.g., quarks) participate in EM, but not weak interactions, and some (e.g., neutrinos) vice-versa. • But there are similarities. Within its short range, the weak interaction is actually the same strength as EM. It has been known since 1935 (Yukawa) that the shortrange forces are du ...
Strong Nuclear Interaction
... dimensions (of color, but abstractly, it’s all the same!). In fact, we need to worry about quantum mechanical phase also, so this is really the group SU(3) of rotations in three complex dimensions (but don’t worry about the “complex”). ...
... dimensions (of color, but abstractly, it’s all the same!). In fact, we need to worry about quantum mechanical phase also, so this is really the group SU(3) of rotations in three complex dimensions (but don’t worry about the “complex”). ...
Standard Model
... 1964 – Proposed by Murray Gell-Mann and George Zweig Initially only three flavours of quarks: up, down and strange A year later, another flavour was added: charm ...
... 1964 – Proposed by Murray Gell-Mann and George Zweig Initially only three flavours of quarks: up, down and strange A year later, another flavour was added: charm ...
Advances in Effective Field Theories
... and protons into nuclei and for the many facets of nuclei and dense matter in astrophysics. Combined with the electroweak interaction, it determines the properties of all nuclei in the nuclear chart in a similar way as quantum electrodynamics shapes the periodic table of elements. ...
... and protons into nuclei and for the many facets of nuclei and dense matter in astrophysics. Combined with the electroweak interaction, it determines the properties of all nuclei in the nuclear chart in a similar way as quantum electrodynamics shapes the periodic table of elements. ...
Intro to particle physics 1. Particles, Fields
... In QFT, interactions of particles are controlled by coupling of the field to the current interaction is determined by the form of the current, but current is determined by the symmetry by Noether's theorem, e.g. ...
... In QFT, interactions of particles are controlled by coupling of the field to the current interaction is determined by the form of the current, but current is determined by the symmetry by Noether's theorem, e.g. ...