list of abstracts - Faculdade de Ciências
... Based on a family of indefinite unitary representations of the diffeomorphism group of an oriented smooth 4-manifold, a manifestly covariant 4dimensional and non-perturbative algebraic quantum field theory formulation of gravity is exhibited. More precisely among the bounded linear operators acting ...
... Based on a family of indefinite unitary representations of the diffeomorphism group of an oriented smooth 4-manifold, a manifestly covariant 4dimensional and non-perturbative algebraic quantum field theory formulation of gravity is exhibited. More precisely among the bounded linear operators acting ...
128 KB
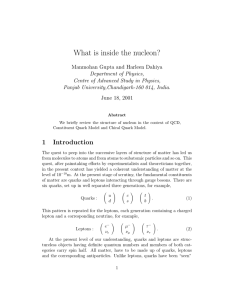
... were able to calculate the total spin content of the proton carried by the quarks. To everyone’s amazement, they came up with an answer that was close to zero… Was there a problem with the theory, the experiment or both? Both the SLAC and CERN data now essentially agree, indicating that only about 3 ...
... were able to calculate the total spin content of the proton carried by the quarks. To everyone’s amazement, they came up with an answer that was close to zero… Was there a problem with the theory, the experiment or both? Both the SLAC and CERN data now essentially agree, indicating that only about 3 ...
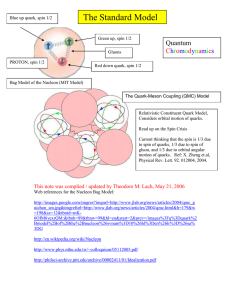
Field and gauge theories
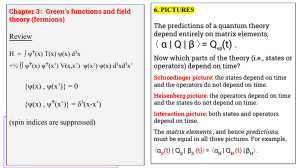
... This process conserves energy, but also gives us a way to measure ABSOLUTE potential, forbidden by gauge invariance If gauge symmetry holds and energy is conserved, charge is conserved ...
... This process conserves energy, but also gives us a way to measure ABSOLUTE potential, forbidden by gauge invariance If gauge symmetry holds and energy is conserved, charge is conserved ...
PROBset3_2015 - University of Toronto, Particle Physics and
... uu in the K p 0 0 . This is an example of the colour force conserving strangeness, or quark flavour. Also note that the weak interaction can change an s quark into a u quark or an s into a u . This is an example of the weak force not conserving quark flavour. In each of these quark flow diagra ...
... uu in the K p 0 0 . This is an example of the colour force conserving strangeness, or quark flavour. Also note that the weak interaction can change an s quark into a u quark or an s into a u . This is an example of the weak force not conserving quark flavour. In each of these quark flow diagra ...
Many-Body Coulomb Gauge Exotic and Charmed Hybrids
... models, have been an elusive, yet signature prediction of Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD). It was therefore quite natural that the recent observation by the E852 collaboration [1] of two exotic J P C = 1−+ states with masses 1.4 and 1.6 GeV would attract widespread interest. Since these states have iso ...
... models, have been an elusive, yet signature prediction of Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD). It was therefore quite natural that the recent observation by the E852 collaboration [1] of two exotic J P C = 1−+ states with masses 1.4 and 1.6 GeV would attract widespread interest. Since these states have iso ...
20070822140014201
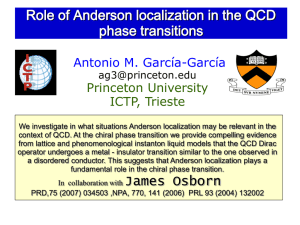
... At which temperature does the transition occur ? What is the nature of transition ? ...
... At which temperature does the transition occur ? What is the nature of transition ? ...
Milikan`s Oil Drop Experiment
... the changes in the charge were always a multiple of –1.6x10-19 C. The changes were caused by one or more electrons being added to or removed from the drops. He concluded that the smallest change in charge that could occur was the amount of charge of one electron. Therefore, Milikan said that each el ...
... the changes in the charge were always a multiple of –1.6x10-19 C. The changes were caused by one or more electrons being added to or removed from the drops. He concluded that the smallest change in charge that could occur was the amount of charge of one electron. Therefore, Milikan said that each el ...