Modern Physics
... e.g. Average A Level score is same for females as for males. Not an exact symmetry. ...
... e.g. Average A Level score is same for females as for males. Not an exact symmetry. ...
SpontaneouS Symmetry Breaking in particle phySicS
... early 1930s with the discovery of the neutron by Chadwick, the invention of the cyclotron by Lawrence, and the ‘invention’ of meson theory by Yukawa [1]. The appearance of an ever increasing array of new particles in the subsequent decades and advances in quantum field theory gradually led to our un ...
... early 1930s with the discovery of the neutron by Chadwick, the invention of the cyclotron by Lawrence, and the ‘invention’ of meson theory by Yukawa [1]. The appearance of an ever increasing array of new particles in the subsequent decades and advances in quantum field theory gradually led to our un ...
An Introduction to the Standard Model of Particle Physics
... Four types of interaction field, set out in Table 1.1., have been distinguished in Nature. On th scales of particle physics, gravitational forces are insignificant. The Standard Model excludes fro consideration the gravitational field. The quanta of the electromagnetic interaction field betwee elect ...
... Four types of interaction field, set out in Table 1.1., have been distinguished in Nature. On th scales of particle physics, gravitational forces are insignificant. The Standard Model excludes fro consideration the gravitational field. The quanta of the electromagnetic interaction field betwee elect ...
do physics online from quanta to quarks high
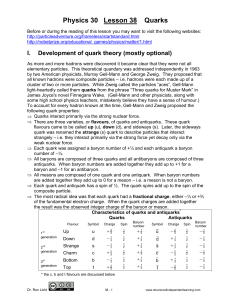
... Fermions are particles that obey the Pauli Exclusion Principle Two particles in a quantum system can’t occupy the same quantum state Fermions have a property called spin and the orientation of the spin together determines their behaviour in quantum systems, for example, in an external magnetic field ...
... Fermions are particles that obey the Pauli Exclusion Principle Two particles in a quantum system can’t occupy the same quantum state Fermions have a property called spin and the orientation of the spin together determines their behaviour in quantum systems, for example, in an external magnetic field ...
Document
... electromagnetic force by Glashow, Salam and Weinberg – who received the Nobel in 1979 • The weak force is carried by W and Z bosons of M~90 GeV • The massless photon is induced by the presence of a condensate of “Higgs” bosons, that spontaneously breaks the symmetry of the interaction ...
... electromagnetic force by Glashow, Salam and Weinberg – who received the Nobel in 1979 • The weak force is carried by W and Z bosons of M~90 GeV • The massless photon is induced by the presence of a condensate of “Higgs” bosons, that spontaneously breaks the symmetry of the interaction ...