quantum field theory in curved spacetime
... not wrong in a technical mathematical sense. It simply provides a grossly inadequate founqation for the theory. Here are just some of the situations in which it fails: 1. There may be no Killing vector at all, timelike or spacelike. This is the generic situation. How to deal with it is unkown, excep ...
... not wrong in a technical mathematical sense. It simply provides a grossly inadequate founqation for the theory. Here are just some of the situations in which it fails: 1. There may be no Killing vector at all, timelike or spacelike. This is the generic situation. How to deal with it is unkown, excep ...
Fractionalization in an easy-axis Kagome antiferromagnet
... Typically single strength vortices condense, but one can also imagine insulating states which result from a condensation of composites made from N v vortices.12 Such insulators are necessarily fractionalized since they support deconfined 共but gapped兲 charge excitations with ‘‘boson charge’’ Q ⫽S z ⫽ ...
... Typically single strength vortices condense, but one can also imagine insulating states which result from a condensation of composites made from N v vortices.12 Such insulators are necessarily fractionalized since they support deconfined 共but gapped兲 charge excitations with ‘‘boson charge’’ Q ⫽S z ⫽ ...
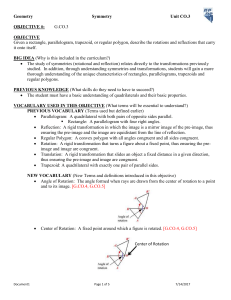
Geometry Symmetry Unit CO.3 OBJECTIVE #: G.CO.3 OBJECTIVE
... its image. These facts are not new, but will now be used to solidify relationships later. Reflectional symmetry is when a figure in the plane is mapped onto itself by a line of reflection. Rotational symmetry is when a figure in the plane is mapped onto itself by a rotation between 0° and 360°. Revi ...
... its image. These facts are not new, but will now be used to solidify relationships later. Reflectional symmetry is when a figure in the plane is mapped onto itself by a line of reflection. Rotational symmetry is when a figure in the plane is mapped onto itself by a rotation between 0° and 360°. Revi ...
An introduction to topological phases of electrons
... there are two paths γ1 , γ2 that have different integrals but the same endpoints. Form a new path γ so that, as t goes from 0 to 12 , γ1 is traced, and then as t goes from 21 to 1, γ2 is traced opposite its original direction (now you can see why piecewise smooth paths are needed if one wants to be ...
... there are two paths γ1 , γ2 that have different integrals but the same endpoints. Form a new path γ so that, as t goes from 0 to 12 , γ1 is traced, and then as t goes from 21 to 1, γ2 is traced opposite its original direction (now you can see why piecewise smooth paths are needed if one wants to be ...
Inverse magnetic catalysis in QCD and holography
... Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD) is the theory describing the strong interactions. Developed in the mid-twentieth century, it describes hadrons in terms of smaller constituent particles called quarks and gluons. Mathematically, it is a Yang-Mills (YM) theory based on the Lie group SU (3), where 3 is the ...
... Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD) is the theory describing the strong interactions. Developed in the mid-twentieth century, it describes hadrons in terms of smaller constituent particles called quarks and gluons. Mathematically, it is a Yang-Mills (YM) theory based on the Lie group SU (3), where 3 is the ...
CMP3 Grade 7
... have vertical lines of symmetry through the middle. Ohio’s flag does not have a horizontal line of symmetry because the stars don’t all match up. New Mexico’s flag has a horizontal line of symmetry. b. The circle in the Ohio flag, the stars in ...
... have vertical lines of symmetry through the middle. Ohio’s flag does not have a horizontal line of symmetry because the stars don’t all match up. New Mexico’s flag has a horizontal line of symmetry. b. The circle in the Ohio flag, the stars in ...
A C E
... the middle. Ohio’s flag does not have a horizontal line of symmetry because the stars don’t all match up. New Mexico’s flag has a horizontal line of symmetry. b. The circle in the Ohio flag, the stars in ...
... the middle. Ohio’s flag does not have a horizontal line of symmetry because the stars don’t all match up. New Mexico’s flag has a horizontal line of symmetry. b. The circle in the Ohio flag, the stars in ...
SAD ACE Inv.3 KEY - Issaquah Connect
... the middle. Ohio’s flag does not have a horizontal line of symmetry because the stars don’t all match up. New Mexico’s flag has a horizontal line of symmetry. b. The circle in the Ohio flag, the stars in ...
... the middle. Ohio’s flag does not have a horizontal line of symmetry because the stars don’t all match up. New Mexico’s flag has a horizontal line of symmetry. b. The circle in the Ohio flag, the stars in ...
Overview of Neutrino Physics Issues and Opportunities Andr´ e de Gouvˆ
... Why don’t we just enhance the fermion sector of the theory? One may argue that it is trivial and simpler to just add LYukawa = −yiα Li HN α + H.c., and neutrinos get a mass like all other fermions: miα = yiα v • Data requires y < 10−12 . Why so small? • Neutrinos are Dirac fermions. B − L exactly co ...
... Why don’t we just enhance the fermion sector of the theory? One may argue that it is trivial and simpler to just add LYukawa = −yiα Li HN α + H.c., and neutrinos get a mass like all other fermions: miα = yiα v • Data requires y < 10−12 . Why so small? • Neutrinos are Dirac fermions. B − L exactly co ...
Anisotropic pyrochlores and the global phase diagram of the checkerboard... Oleg A. Starykh, Akira Furusaki, and Leon Balents
... More recently, it was recognized that the situation becomes more interesting and less clearcut when the interchain interaction is strongly frustrated, as is the case for the crossed-chain model we investigate here. The effect of frustration is to reduce and, ultimately, nullify the effective interch ...
... More recently, it was recognized that the situation becomes more interesting and less clearcut when the interchain interaction is strongly frustrated, as is the case for the crossed-chain model we investigate here. The effect of frustration is to reduce and, ultimately, nullify the effective interch ...
Paired states of fermions in two dimensions with breaking of parity
... mode physics, from those connected with topological effects, quasiparticle zero modes and Hall-type responses for unbroken symmetries. In this paper we will make extensive use of the methods for BCS paired states, and consider the transitions between the weak and strong coupling regimes in two dimen ...
... mode physics, from those connected with topological effects, quasiparticle zero modes and Hall-type responses for unbroken symmetries. In this paper we will make extensive use of the methods for BCS paired states, and consider the transitions between the weak and strong coupling regimes in two dimen ...
What is inside the nucleon?
... From the above expression, one can find out that α has the value 1/137 at energies which are not large compared with the electron mass, however at LEP energies (101 GeV), it takes a value closer to 1/128. In contrast to the electromagnetic interactions, which is an Abelian gauge theory, the coupling ...
... From the above expression, one can find out that α has the value 1/137 at energies which are not large compared with the electron mass, however at LEP energies (101 GeV), it takes a value closer to 1/128. In contrast to the electromagnetic interactions, which is an Abelian gauge theory, the coupling ...
2 + 1 dimensional gravity as an exactly soluble system
... run into when the vierbein and spin connection are independent variables is that discussed in ref. [10]. We will see later that this is one type of singularity that we will definitely have to allow.) Much of the interest in trying to quantize 2 + 1 dimensional gravity is precisely the question of wh ...
... run into when the vierbein and spin connection are independent variables is that discussed in ref. [10]. We will see later that this is one type of singularity that we will definitely have to allow.) Much of the interest in trying to quantize 2 + 1 dimensional gravity is precisely the question of wh ...
PHYS571: Lecture Notes Modern Atomic Physics
... Relaxation arises from the collection of weak and effectively random perturbations that practically every atomic oscillator is subject to. These perturbations are conventionally attributed to interaction with the “environment” or “reservoir”, which means any very large physical system coupled to a s ...
... Relaxation arises from the collection of weak and effectively random perturbations that practically every atomic oscillator is subject to. These perturbations are conventionally attributed to interaction with the “environment” or “reservoir”, which means any very large physical system coupled to a s ...
Slides - indico.jinr.ru – Indico
... upgrade works have been performed to enable effective operation of experiment at high luminosity 1–2×1034sm-2s-1 and nominal LHC energy up to 14 TeV Upgrade of ME1/1 is completed (produced and replaced electronics at 72 chambers of МЕ1/1). The trigger acceptance is extended from 2.1 up to 2.4. The ...
... upgrade works have been performed to enable effective operation of experiment at high luminosity 1–2×1034sm-2s-1 and nominal LHC energy up to 14 TeV Upgrade of ME1/1 is completed (produced and replaced electronics at 72 chambers of МЕ1/1). The trigger acceptance is extended from 2.1 up to 2.4. The ...
Monday, Nov. 27, 2006 - UTA High Energy Physics page.
... Red, blue or green Baryons and Mesons (the observed particles) are color charge neutral ...
... Red, blue or green Baryons and Mesons (the observed particles) are color charge neutral ...
Invariance Principles and Conservation Laws
... • Does an underlying long range field lead to this? – Equivalency of gravitational and intertial mass established at the 10-12 level – Since the nuclear binding energy differs with nuclei, the ratio of mass to number of nucleons is not constant, providing a potential source for a difference bet ...
... • Does an underlying long range field lead to this? – Equivalency of gravitational and intertial mass established at the 10-12 level – Since the nuclear binding energy differs with nuclei, the ratio of mass to number of nucleons is not constant, providing a potential source for a difference bet ...
Coherence of atomic matter-wave fields - IAP TU
... There is a fundamental distinction between the situation at hand and Glauber’s photodetection theory, because in the present case both the detected and detector fields consist of matter waves. There is a complete symmetry between these two fields so far, and their roles are interchangeable. In order ...
... There is a fundamental distinction between the situation at hand and Glauber’s photodetection theory, because in the present case both the detected and detector fields consist of matter waves. There is a complete symmetry between these two fields so far, and their roles are interchangeable. In order ...
String Backgrounds
... and deform at background. String theory contains quantum gravity. Large deformations away from at background represented by coherent states of ...
... and deform at background. String theory contains quantum gravity. Large deformations away from at background represented by coherent states of ...
Weak-Equivalence Principle Violation and Mass Change
... with neutral matter only due to the influence of the electromagnetic fields that can disturb the measurement. While such tests have achieved an Eötwash-factor sensitivity of 10−13 [1], only one test has been reported for the free-fall of an electron with its elementary charge at a sensitivity of on ...
... with neutral matter only due to the influence of the electromagnetic fields that can disturb the measurement. While such tests have achieved an Eötwash-factor sensitivity of 10−13 [1], only one test has been reported for the free-fall of an electron with its elementary charge at a sensitivity of on ...
neutrinos: mysterious particles with fascinating features, which led to
... that some nuclei change their spin by 1 unit under β-decay, so he specified that this new particle should carry spin 1/2, just like the electron; thus also angular momentum conservation is saved. To further conserve the electric charge, it must be electrically neutral, therefore he wanted to call i ...
... that some nuclei change their spin by 1 unit under β-decay, so he specified that this new particle should carry spin 1/2, just like the electron; thus also angular momentum conservation is saved. To further conserve the electric charge, it must be electrically neutral, therefore he wanted to call i ...
1999
... observing the ballistically expanding atoms after 35 ms of time-of-flight using resonant absorption imaging. After the expansion, the condensate and the recoiling atoms were fully separated (see figure). Phase-coherence of the matter-wave amplifier was demonstrated with an interferometric technique ...
... observing the ballistically expanding atoms after 35 ms of time-of-flight using resonant absorption imaging. After the expansion, the condensate and the recoiling atoms were fully separated (see figure). Phase-coherence of the matter-wave amplifier was demonstrated with an interferometric technique ...
SU(3) symmetry and Baryon wave functions
... There would be no way to distinguish between a proton and neutron (symmetry) – p and n have very similar masses – The nuclear force is charge-independent ...
... There would be no way to distinguish between a proton and neutron (symmetry) – p and n have very similar masses – The nuclear force is charge-independent ...
Landau Gauge Quark Propagator with External Magnetic Fields
... Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD) is a remarkable theory as it has founded the success of quantum field theory already long time ago, consolidating and deepening the significant insights into quantum physics that Quantum Electrodynamics (QED) had just given a few years before. The feature of asymptotic f ...
... Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD) is a remarkable theory as it has founded the success of quantum field theory already long time ago, consolidating and deepening the significant insights into quantum physics that Quantum Electrodynamics (QED) had just given a few years before. The feature of asymptotic f ...
or ppt
... site =>> if feasible, could be significantly cheaper than other futuristic HEP colliders. Can be an upgrade to any other collider scheme. ...
... site =>> if feasible, could be significantly cheaper than other futuristic HEP colliders. Can be an upgrade to any other collider scheme. ...