Functional Form of the Imaginary Part of the Atomic Polarizability
... where G′ (E0 ) = [1/(H0 − E0 )′ ] is the reduced Green function. Written in this form, the terms correspond to the entries in Fig. 1, (a) and (b), and the last term to the sum of (c) and (d), while the photon loop involves a photon in the mode k λ. The propagator denominators in Fig. 1(a) in the “ou ...
... where G′ (E0 ) = [1/(H0 − E0 )′ ] is the reduced Green function. Written in this form, the terms correspond to the entries in Fig. 1, (a) and (b), and the last term to the sum of (c) and (d), while the photon loop involves a photon in the mode k λ. The propagator denominators in Fig. 1(a) in the “ou ...
ppt
... OAKLAND, Calif., Jan. 12 — A fleeting, ultradense state of matter, comparable in some respects to a bizarre kind of subatomic pudding, has been discovered deep within the core of ordinary gold atoms, scientists from Brookhaven National Laboratory said at a conference ...
... OAKLAND, Calif., Jan. 12 — A fleeting, ultradense state of matter, comparable in some respects to a bizarre kind of subatomic pudding, has been discovered deep within the core of ordinary gold atoms, scientists from Brookhaven National Laboratory said at a conference ...
Frustration-driven multi magnon condensates and their excitations Current trends in frustrated magnetism
... remains the the possibility of a spin-liquid phase at S ! 1=2 as derotation symmetryresults, is preserved. ...
... remains the the possibility of a spin-liquid phase at S ! 1=2 as derotation symmetryresults, is preserved. ...
Applied Gauge/Gravity Duality from Supergravity to Superconductivity Francesco Aprile
... the microscopic information is not important and short distances degrees of freedom can be integrated out. Then, according to the Wilsonian renormalization group flow, the resulting theory will be described only by a finite number of relevant and marginal terms [4]. The idea of integrating out micro ...
... the microscopic information is not important and short distances degrees of freedom can be integrated out. Then, according to the Wilsonian renormalization group flow, the resulting theory will be described only by a finite number of relevant and marginal terms [4]. The idea of integrating out micro ...
Introduction to Renormalization Group Alex Kovner Valparaiso, December 12-14, 2013
... FIND A GIVEN FIELD CONFIGURATION φ(x) at time t. THERE IS STILL SCHROEDINGER EQUATION, BUT IT IS MUCH LESS USEFUL Ψ[φ] contains too much information, even knowing Ψ it is still hard work to get this information out. USUALLY WE ARE CONTENT WITH LESS. AS PARTICLE PHYSICISTS WE WANT SCATTERING AMPLITUD ...
... FIND A GIVEN FIELD CONFIGURATION φ(x) at time t. THERE IS STILL SCHROEDINGER EQUATION, BUT IT IS MUCH LESS USEFUL Ψ[φ] contains too much information, even knowing Ψ it is still hard work to get this information out. USUALLY WE ARE CONTENT WITH LESS. AS PARTICLE PHYSICISTS WE WANT SCATTERING AMPLITUD ...
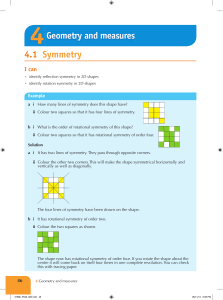
4.1 Symmetry Geometry and measures
... The area of the bottom rectangle is 4 × 5 = 20 m2. The total area is 33 + 20 = 53 m2. The sides are in metres (m) so the area is in square metres (m2). b There are two missing lengths. The right-hand side is 3 + 4 = 7 m. The other missing length is 11 - 5 = 6 m. The perimeter is the total length ro ...
... The area of the bottom rectangle is 4 × 5 = 20 m2. The total area is 33 + 20 = 53 m2. The sides are in metres (m) so the area is in square metres (m2). b There are two missing lengths. The right-hand side is 3 + 4 = 7 m. The other missing length is 11 - 5 = 6 m. The perimeter is the total length ro ...
Escher`s Tessellations: The Symmetry of Wallpaper Patterns III
... The series in blue results from doing a vertical reflection followed by a 90 degree rotation. The series in red results from performing the two isometries in the opposite order. Since the results are different, the order in which isometries are performed matters. Symmetry III ...
... The series in blue results from doing a vertical reflection followed by a 90 degree rotation. The series in red results from performing the two isometries in the opposite order. Since the results are different, the order in which isometries are performed matters. Symmetry III ...
arXiv:0906.1334v1 [cond-mat.supr
... theoretical physics aiming at the understanding of dynamics of such systems which are exposed to strong time-dependent external fields [2, 3, 4, 5]. Fundamental informations regarding high-temperature superconductors can be obtained from the high frequency electrodynamic response. Informations invol ...
... theoretical physics aiming at the understanding of dynamics of such systems which are exposed to strong time-dependent external fields [2, 3, 4, 5]. Fundamental informations regarding high-temperature superconductors can be obtained from the high frequency electrodynamic response. Informations invol ...
Manifestly Covariant Functional Measures for Quantum Field Theory
... In the conventional approach to deriving the functional integral representation of the partition function in quantum field theory, one discretizes time into slices spaced a constant distance apart in coordinate time. When quantum field theory is formulated in a curved spacetime background, the measu ...
... In the conventional approach to deriving the functional integral representation of the partition function in quantum field theory, one discretizes time into slices spaced a constant distance apart in coordinate time. When quantum field theory is formulated in a curved spacetime background, the measu ...
Paper
... condensate. Depending on the momentum transfer, both the phonon regime as well as the free-particle regime could be explored. In the second set of studies, the cigarshaped condensate was exposed to a single off-resonant laser beam and highly directional scattering of light and atoms was observed. Th ...
... condensate. Depending on the momentum transfer, both the phonon regime as well as the free-particle regime could be explored. In the second set of studies, the cigarshaped condensate was exposed to a single off-resonant laser beam and highly directional scattering of light and atoms was observed. Th ...
Effects of thermal and quantum fluctuations on the phase diagram of
... Since the first experimental realization of a BoseEinstein condensate with spin degrees of freedom (spinor BEC) in 1998 [1, 2], many interesting phenomena have been investigated. Due to the competition between the interatomic interactions and the coupling of atoms to an external magnetic field [3, 4 ...
... Since the first experimental realization of a BoseEinstein condensate with spin degrees of freedom (spinor BEC) in 1998 [1, 2], many interesting phenomena have been investigated. Due to the competition between the interatomic interactions and the coupling of atoms to an external magnetic field [3, 4 ...
Title First Name Last
... (LFQ) of constrained dynamical systems. Study of canonical structure, constrained dynamics, operator solutions and Hamiltonian, path Integral and BRST quantization of field theories, string theories and D-brane actions using the Dirac's relativistic IF and LF dynamics and construction and quantizati ...
... (LFQ) of constrained dynamical systems. Study of canonical structure, constrained dynamics, operator solutions and Hamiltonian, path Integral and BRST quantization of field theories, string theories and D-brane actions using the Dirac's relativistic IF and LF dynamics and construction and quantizati ...
The Hadronic Spectrum of a Holographic Dual of QCD Abstract
... will be described in a simplified model based on a “hard-wall” approximation where the metric factor e2A(z) is a step function. This provides an analog of the MIT bag model where quarks are permanently confined inside a finite region of space [17]. However, unlike bag models, the truncated boundary ...
... will be described in a simplified model based on a “hard-wall” approximation where the metric factor e2A(z) is a step function. This provides an analog of the MIT bag model where quarks are permanently confined inside a finite region of space [17]. However, unlike bag models, the truncated boundary ...
Algebraic approach to interacting quantum systems
... of complex phenomena exhibited by Nature exceeds our ability to explain them, in part, because the whole is not necessarily the sum of its parts [1] and thus typical perturbation-like-theory arguments or standard mathematical techniques are not appropriate to disentangle its mysteries. In this paper ...
... of complex phenomena exhibited by Nature exceeds our ability to explain them, in part, because the whole is not necessarily the sum of its parts [1] and thus typical perturbation-like-theory arguments or standard mathematical techniques are not appropriate to disentangle its mysteries. In this paper ...
the PDF - JILA - University of Colorado Boulder
... major goal of current research at this interface between condensed matter and atomic physics is to emulate the Heisenberg and t-J models, which are believed to underlie certain quantum magnetic materials [2] and hightemperature superconductors [3], respectively. However, in the ultracold atom realiz ...
... major goal of current research at this interface between condensed matter and atomic physics is to emulate the Heisenberg and t-J models, which are believed to underlie certain quantum magnetic materials [2] and hightemperature superconductors [3], respectively. However, in the ultracold atom realiz ...
Simply Symmetric
... obviously no need to prove that it has opposite sides equal and parallel, because it then inherits those properties from the parallelogram. However, if need be, one can also easily derive these properties of a rectangle from its symmetry definition above. For example, it’s easy to see by reflection ...
... obviously no need to prove that it has opposite sides equal and parallel, because it then inherits those properties from the parallelogram. However, if need be, one can also easily derive these properties of a rectangle from its symmetry definition above. For example, it’s easy to see by reflection ...
pptx version - Physics Department, Princeton University
... In 1926, Fock noted that gauge invariance of the electromagnetic potentials in Schrödinger’s equation requires local phase invariance of the wavefunction . V. Fock, Z. Phys. 39, 226 (1926) In 1954, Yang and Mills inverted this to argue that local phase invariance requires “charged” particles to int ...
... In 1926, Fock noted that gauge invariance of the electromagnetic potentials in Schrödinger’s equation requires local phase invariance of the wavefunction . V. Fock, Z. Phys. 39, 226 (1926) In 1954, Yang and Mills inverted this to argue that local phase invariance requires “charged” particles to int ...
Spin-current and other unusual phases in magnetized triangular lattice antiferromagnets
... a “critical” spin-liquid antiferromagnet at 3 magnetization from a dual vortex perspective, and indeed find which is obtained by putting singlets on all diagonal J phase described by quantum electrodynamics in !2 + 1"-dimensions with an emergent SU!6" symmetry. bonds. This eigenstate isAthe ground s ...
... a “critical” spin-liquid antiferromagnet at 3 magnetization from a dual vortex perspective, and indeed find which is obtained by putting singlets on all diagonal J phase described by quantum electrodynamics in !2 + 1"-dimensions with an emergent SU!6" symmetry. bonds. This eigenstate isAthe ground s ...
Topological search for the production of neutralinos and
... ah University of Victoria, Department of Physics, P 0 Box 3055, Victoria BC V8W 3P6. Canada a’ University of British Columbia, Department of Physics, Vancouver BC V6T 121, Canada ad University of Alberta, Department of Physics, Edmonton AB T6G 2J1, Canada ae Duke University, Department of Physics, D ...
... ah University of Victoria, Department of Physics, P 0 Box 3055, Victoria BC V8W 3P6. Canada a’ University of British Columbia, Department of Physics, Vancouver BC V6T 121, Canada ad University of Alberta, Department of Physics, Edmonton AB T6G 2J1, Canada ae Duke University, Department of Physics, D ...
Poincaré group
... and by equating Eq. (B.8) with T (1, 0) we can read off the inverse element: T −1 (Λ, a) = T (Λ−1 , −Λ−1 a) . ...
... and by equating Eq. (B.8) with T (1, 0) we can read off the inverse element: T −1 (Λ, a) = T (Λ−1 , −Λ−1 a) . ...
Weakton Model of Elementary Particles and Decay Mechanisms
... This phenomena is called quark confinement, which can be very well explained using the three levels of strong interaction potentials derived using a unified field theory developed recently in [7, 8]; see discussions in Section 3.4. The quantum numbers of quarks include the mass m, the charge Q, the ...
... This phenomena is called quark confinement, which can be very well explained using the three levels of strong interaction potentials derived using a unified field theory developed recently in [7, 8]; see discussions in Section 3.4. The quantum numbers of quarks include the mass m, the charge Q, the ...
Shining Light on Modifications of Gravity
... The second term in equation (1.1) is the disformal term. On its own, when A ≡ const, this term is not problematic for fifth force experiments because as we will see a scalar field that couples to matter in this way is not sourced by a static non-relativistic mass distribution. All of the objects use ...
... The second term in equation (1.1) is the disformal term. On its own, when A ≡ const, this term is not problematic for fifth force experiments because as we will see a scalar field that couples to matter in this way is not sourced by a static non-relativistic mass distribution. All of the objects use ...
Fiber Bundles and Quantum Theory
... 90-degree rotation of the neutron spin vector. The half-angle relation continues. When the physical spin vector has rotated 180 degrees, it points down. The spin-down probability amplitude is +1 and the spin-up probability is 0. The corresponding point in the neutron-state space is 90 degrees from t ...
... 90-degree rotation of the neutron spin vector. The half-angle relation continues. When the physical spin vector has rotated 180 degrees, it points down. The spin-down probability amplitude is +1 and the spin-up probability is 0. The corresponding point in the neutron-state space is 90 degrees from t ...
Phase transition of Light - Universiteit van Amsterdam
... quantized wave-modes. To quantize the electromagnetic field each mode of the electromagnetic field is associated by a simple quantum harmonic oscillator. So for each mode - analogue to the quantum harmonic oscillator - the formalism of ladder operators and number states can be applied. The electroma ...
... quantized wave-modes. To quantize the electromagnetic field each mode of the electromagnetic field is associated by a simple quantum harmonic oscillator. So for each mode - analogue to the quantum harmonic oscillator - the formalism of ladder operators and number states can be applied. The electroma ...