Supplment to Chapter 24: Energy Levels of a Free
... This is (24.1). The energy levels of a free relativistic fermion can be understood in much the same way. Interacting relativistic particles can be created and destroyed — a process which is most efficiently described in terms of quantum field theory. But it is possible to think of a free relativisti ...
... This is (24.1). The energy levels of a free relativistic fermion can be understood in much the same way. Interacting relativistic particles can be created and destroyed — a process which is most efficiently described in terms of quantum field theory. But it is possible to think of a free relativisti ...
Writing Equations
... Writing Equations Write Equations Writing equations is one strategy for solving problems. You can use a variable to represent an unspecified number or measure referred to in a problem. Then you can write a verbal expression as an algebraic expression. ...
... Writing Equations Write Equations Writing equations is one strategy for solving problems. You can use a variable to represent an unspecified number or measure referred to in a problem. Then you can write a verbal expression as an algebraic expression. ...
Lecture 12
... collisions (to be defined below) that lead to the approach to equilibrium, and not in the properties of that equilibrium (such as the equation of state, compressibility etc.). In some cases (e.g. Fermi liquid theory) it is useful to take other effects of the interactions into account in a mean field ...
... collisions (to be defined below) that lead to the approach to equilibrium, and not in the properties of that equilibrium (such as the equation of state, compressibility etc.). In some cases (e.g. Fermi liquid theory) it is useful to take other effects of the interactions into account in a mean field ...
Part 3 - MGNet
... In gas dynamics an ideal gas satisfies the law r = nT, where r is the pressure of the gas. For the isentropic case T(n) = T0n2/3 and using the diffusion matrix above, the electron current density is rewritten as: ...
... In gas dynamics an ideal gas satisfies the law r = nT, where r is the pressure of the gas. For the isentropic case T(n) = T0n2/3 and using the diffusion matrix above, the electron current density is rewritten as: ...
Problem set 7
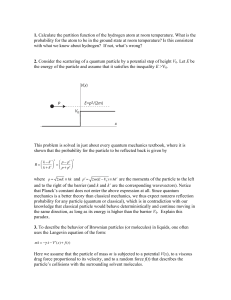
... Quantum Mechanics 3, Spring 2012 CMI Problem set 7 Due by beginning of class on Monday Mar 5, 2012 BCH formula for x and p , SHO 1. Consider the function f (t) = etA Be−tA where A, B are a pair of operators (e.g. position and momentum or creation and annihilation operators etc.). t is a parameter wh ...
... Quantum Mechanics 3, Spring 2012 CMI Problem set 7 Due by beginning of class on Monday Mar 5, 2012 BCH formula for x and p , SHO 1. Consider the function f (t) = etA Be−tA where A, B are a pair of operators (e.g. position and momentum or creation and annihilation operators etc.). t is a parameter wh ...






![3 — Blackbody Radiation [Revision : 1.5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005908504_1-5005bdffc2e5f9c6e0687c31f49c7e9d-300x300.png)