Plate Tectonics presentation
... • This upper mantle is less dense than the mantle underneath, so it is able to “float” on the mantle below. • The mantle just below the lithosphere is called the asthenosphere. • The asthenosphere has a plastic like consistency, and it carries the lithosphere. ...
... • This upper mantle is less dense than the mantle underneath, so it is able to “float” on the mantle below. • The mantle just below the lithosphere is called the asthenosphere. • The asthenosphere has a plastic like consistency, and it carries the lithosphere. ...
Lithosphere - paulding.k12.ga.us
... • This upper mantle is less dense than the mantle underneath, so it is able to “float” on the mantle below. • The mantle just below the lithosphere is called the asthenosphere. • The asthenosphere has a plastic like consistency, and it carries the lithosphere. ...
... • This upper mantle is less dense than the mantle underneath, so it is able to “float” on the mantle below. • The mantle just below the lithosphere is called the asthenosphere. • The asthenosphere has a plastic like consistency, and it carries the lithosphere. ...
High Spirits 3: Towards CLIL
... The crust is very thin and it consists of large, thin pieces of rock, called plates. These plates are constantly moving, and they lie on the hotter, softer material under them, called the mantle. There are 16 main plates. Volcanoes usually form when the plates push against or pull away from each oth ...
... The crust is very thin and it consists of large, thin pieces of rock, called plates. These plates are constantly moving, and they lie on the hotter, softer material under them, called the mantle. There are 16 main plates. Volcanoes usually form when the plates push against or pull away from each oth ...
- Astarte Resources
... in the middle of a plate where volcanic activity takes place. 13. Yellowstone National Park is famous for its low-level volcanic activity. 14. The Hawaiian Islands are volcanic formed one a�er the other as the Pacific Plate inched its way north over a fixed hot spot. Chapter 2: Types of Volcanoes 15. ...
... in the middle of a plate where volcanic activity takes place. 13. Yellowstone National Park is famous for its low-level volcanic activity. 14. The Hawaiian Islands are volcanic formed one a�er the other as the Pacific Plate inched its way north over a fixed hot spot. Chapter 2: Types of Volcanoes 15. ...
EarthComm_c2s1_136-147
... A volcano is a vent or fissure in Earth’s crust that allows magma, gases, and ash to escape from below the surface. Magma is the molten rock material generated within Earth. When the molten rock comes out of a volcano, it is called lava. Geologists have known for a long time that there are many volc ...
... A volcano is a vent or fissure in Earth’s crust that allows magma, gases, and ash to escape from below the surface. Magma is the molten rock material generated within Earth. When the molten rock comes out of a volcano, it is called lava. Geologists have known for a long time that there are many volc ...
Earthquake risk - EdCommunity
... risk or low risk for an earthquake or a volcanic crust is composed of several tectonic plates eruption. Name five high-risk cities and five that are always on the move. The effects low-risk cities. Remember to turn layers on of movement are most noticeable at the and off and move them around as need ...
... risk or low risk for an earthquake or a volcanic crust is composed of several tectonic plates eruption. Name five high-risk cities and five that are always on the move. The effects low-risk cities. Remember to turn layers on of movement are most noticeable at the and off and move them around as need ...
Geoscience 10: Geology of The National Parks Unit 3 - e
... Towers of rising rock from very deep (often core-mantle boundary) feed “hot spots”; Plates drift over the top, and hot spots occasionally punch through to make lines of volcanoes, which often are oceanic islands (seamounts); Hotspots from mantle, basaltic, very similar to sea floor; A new hotspot lo ...
... Towers of rising rock from very deep (often core-mantle boundary) feed “hot spots”; Plates drift over the top, and hot spots occasionally punch through to make lines of volcanoes, which often are oceanic islands (seamounts); Hotspots from mantle, basaltic, very similar to sea floor; A new hotspot lo ...
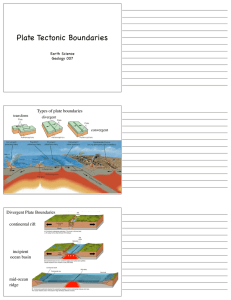
Plate Tectonic Boundaries
... Tectonic plates sideswipe each other Shallow earthquakes horizontal displacement of the crust over great distances ...
... Tectonic plates sideswipe each other Shallow earthquakes horizontal displacement of the crust over great distances ...
Chapter 12 - Mr. Goodenough
... move together are called convergent plate boundaries. They include areas where an oceanic plate slides below a continental plate as in Figure 7, and where one oceanic plate slides below another oceanic plate. The Andes in South America began forming when an oceanic plate started sliding below a cont ...
... move together are called convergent plate boundaries. They include areas where an oceanic plate slides below a continental plate as in Figure 7, and where one oceanic plate slides below another oceanic plate. The Andes in South America began forming when an oceanic plate started sliding below a cont ...
Unit 2 revision questions
... (include geothermal energy, tourism and fertile soils as a starting point)? 11. Explain why some people choose to stay in, or are unable to move away from an area at risk from earthquakes and volcanic eruptions (use case study examples to back you up). 12. Describe the range of ways in which the dam ...
... (include geothermal energy, tourism and fertile soils as a starting point)? 11. Explain why some people choose to stay in, or are unable to move away from an area at risk from earthquakes and volcanic eruptions (use case study examples to back you up). 12. Describe the range of ways in which the dam ...
How*s Earth*s Plates Move
... She IS trying, so give her credit. Don’t copy this: this ISN’T notes! ...
... She IS trying, so give her credit. Don’t copy this: this ISN’T notes! ...
Notes #5 Plate tectonics
... * earthquakes occur as plates spread apart *Rift Zone- is a feature of some volcanoes, especially shield volcanoes, in which a linear series of fissures in the volcanic edifice allows lava to be erupted from the volcano's flank instead of from its summit ...
... * earthquakes occur as plates spread apart *Rift Zone- is a feature of some volcanoes, especially shield volcanoes, in which a linear series of fissures in the volcanic edifice allows lava to be erupted from the volcano's flank instead of from its summit ...
Breanna
... The recent earthquakes that have occurred are in Chili, Alaska, Japan, Indonesia, Mexico, Papa New Guinea, Pacific and Atlantic Ocean, and Tonga. These areas are near subduction zones or slip-strike areas. In some areas earthquakes are to happen more in particular locations depending on how much tim ...
... The recent earthquakes that have occurred are in Chili, Alaska, Japan, Indonesia, Mexico, Papa New Guinea, Pacific and Atlantic Ocean, and Tonga. These areas are near subduction zones or slip-strike areas. In some areas earthquakes are to happen more in particular locations depending on how much tim ...
Enquiry 1: How do volcanoes affect the lives of people on Hiemaey?
... Resource 1. Ask the pupils to describe the walk they think Saethor and Tiry do every day? Encourage speculation and reasoning based on evidence they can see. What is it that they have walked up? Possibly a hill or a mountain. What does the ground appear to be made of? To focus the thinking of pupils ...
... Resource 1. Ask the pupils to describe the walk they think Saethor and Tiry do every day? Encourage speculation and reasoning based on evidence they can see. What is it that they have walked up? Possibly a hill or a mountain. What does the ground appear to be made of? To focus the thinking of pupils ...
Planet Earth
... • The crust is the cool, hard surface of the mantle. – ocean - more dense, basalt rock – continents - less dense, granite rock ...
... • The crust is the cool, hard surface of the mantle. – ocean - more dense, basalt rock – continents - less dense, granite rock ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.