* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2 revision questions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
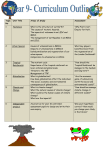
Unit 2 – Hostile World: Hazards Revision Questions and Case Studies MAKE SURE YOU CAN ANSWER ALL OF THESE QUESTIONS USING KEY WORDS AND CASE STUDIES IN YOUR ANSWERS WHERE YOU CAN What are the causes and effects of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions and how do people prepare for and respond to them? 1. What are the primary and secondary effects of earthquakes? 2. What are the primary and secondary effects of volcanic eruptions? 3. How might the effects of volcanic eruptions and earthquakes vary between an LEDC and an MEDC? Use examples to explain your answer. 4. What are the causes of earthquakes? (ie how and why do they happen?) 5. What are the causes of volcanic eruptions? (ie how and why do they happen?) 6. Where do earthquakes and volcanoes occur? 7. Why do earthquakes and volcanoes occur along plate boundaries? 8. Explain the 4 different types of plate boundary. Make sure you can create a diagram of each (include constructive, destructive, conservative, collisions). 9. Why do people live in areas at risk from earthquakes and volcanoes? 10. What are some of the advantages of living in an area which is at risk of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions (include geothermal energy, tourism and fertile soils as a starting point)? 11. Explain why some people choose to stay in, or are unable to move away from an area at risk from earthquakes and volcanic eruptions (use case study examples to back you up). 12. Describe the range of ways in which the damaging effects of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions can be reduced. 13. Why do LEDC’s and MEDC’s use different strategies to reduce the effects of earthquakes and volcanoes? What different strategies do they use? 14. What can be done in the short term (over a short space of time) to respond to an earthquake or volcano? 15. What can be done in the long term (over a short space of time) to respond to an earthquake or volcano? 16. What can be done to predict and prepare for earthquakes and volcanoes? 17. Why can some countries be better prepared than others? What are the causes and effects of tropical storms and how do people prepare for and respond to them? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the primary and secondary effects of tropical storms? Why do the effects of tropical storms vary between LEDC’s and MEDC’s? Use case study examples. What causes a tropical storm? Where do tropical storms occur? How do tropical storms form? (make sure you can include diagrams) What can be done to reduce the effects of tropical storms? (include a range of strategies and examples – the use of GIS (geographical information systems), education programmes etc) 7. Why can some countries prepare better for tropical storms than others? 8. Why would some people think that tropical storms could happen more and in different locations in the future? 9. How could climate change influence the pattern of tropical storms in the future? What are the causes and effects of wildfires and how do people prepare for and respond to them? 1. Describe the primary and secondary effects of wildfires (make sure you know how both people and the environment are impacted). 2. What are the natural causes of wildfires? 3. What are the human causes of wildfires? 4. Using an example, explain whether wildfires are a natural thing or not. 5. Describe a range of strategies which can be used to reduce the effects of wildfires (include evacuation, education and the role of emergency services)? 6. Why do some people think that wildfires could happen more often and in more places in the future? (include the effects of increasing numbers of people living in and using semi-arid (dry) areas, increased frequency of drought due to climate change) 7. Why should areas which are prone to wildfires be protected? Case studies for this unit – you can of course have extra examples, these are the main ones we have studied: Case study Mount St Helens Tunurahua volcano in Ecaudor (in the text book, we focussed on Mt St Helens in lesson time) Yogyakarta earthquake, Java (Indonesia) Haiti earthquake San Francisco Earthquake Java volcano Mount Etna Montserrat Mount Merapi (Indonesia) Hurricane Hanna, Haiti Hurricane Katrina Hurricane Katrina Bangladesh California wildfires Smokey Bear California wildfires Used for... Volcanic eruption primary and secondary effects(MEDC) Volcanic eruption primary and secondary effects(LEDC) Earthquake primary and secondary effects (LEDC) Earthquake primary and secondary effects (LEDC) Earthquake primary and secondary effects (MEDC) Evacuation plan Building volcano defences (rock walls to divert lava, helicopters dropping water etc) Evacuation plan Evacuation plan Primary and secondary effects of tropical storms (LEDC) Primary and secondary effects of tropical storms (MEDC) Preparing for a tropical storm MEDC (range of strategies) Preparing for a tropical storm LEDC (range of strategies) Effects of wildfires (MEDC) Wildfire education programme The future of wildfires and climate change