E5668: Spin precession due to spin-orbit interaction
... An electron, with mass M , charge e and gyromagnetic constant g, launched with energy E in a one dimensional conductor, in the direction of the X axis. The conductor passes through capacitor plates of length L. The capacitor creates an electric field E in the Y direction. Likewise, there’s a magneti ...
... An electron, with mass M , charge e and gyromagnetic constant g, launched with energy E in a one dimensional conductor, in the direction of the X axis. The conductor passes through capacitor plates of length L. The capacitor creates an electric field E in the Y direction. Likewise, there’s a magneti ...
Microsoft Word - ANL_form6
... plateaus of fluid 3 He with two, three and six-site exchanges on kagome chain at low temperatures. A multi-dimensional mapping deduced to study the maximum Lyapunov exponent near plateaus and one can show that the location of plateaus on the maximal Lyapunov exponent is the same for magnetization. T ...
... plateaus of fluid 3 He with two, three and six-site exchanges on kagome chain at low temperatures. A multi-dimensional mapping deduced to study the maximum Lyapunov exponent near plateaus and one can show that the location of plateaus on the maximal Lyapunov exponent is the same for magnetization. T ...
The Two Characteristics of Superconductivity
... cooper pair at absolute zero is about 3kbTC , where kb is Boltzmann constant, TC is critical temperature Cooper pairs do not obey Fermi-Dirac statistics. They are bosons. BCS theory presently fails to explain superconductivity of high temperature super conductors Summary of Superconductor Proper ...
... cooper pair at absolute zero is about 3kbTC , where kb is Boltzmann constant, TC is critical temperature Cooper pairs do not obey Fermi-Dirac statistics. They are bosons. BCS theory presently fails to explain superconductivity of high temperature super conductors Summary of Superconductor Proper ...
8. Superfluid to Mott-insulator transition
... In order to find energies and eigenstates for a given k, the equation system (*) has to be solved for all k ∈ [k+nk0] . Note: |k> is not an eigenstate of the Hamiltonian. ...
... In order to find energies and eigenstates for a given k, the equation system (*) has to be solved for all k ∈ [k+nk0] . Note: |k> is not an eigenstate of the Hamiltonian. ...
Effective lattice models for two-dimensional
... fluctuations are less strongly coupled. We integrate out the n fluctuations in Sf (Eqn 4) by a ‘high-temperature’ expansion and sum over vµ (subject to the constraint 4µ vµ = m) in a Debye-Huckel approximation [18]. This can be shown to yield [16] an effective Coulombic interaction ∼ N mı̄ m̄ /(e2 ...
... fluctuations are less strongly coupled. We integrate out the n fluctuations in Sf (Eqn 4) by a ‘high-temperature’ expansion and sum over vµ (subject to the constraint 4µ vµ = m) in a Debye-Huckel approximation [18]. This can be shown to yield [16] an effective Coulombic interaction ∼ N mı̄ m̄ /(e2 ...
Frustrated Magnetism in Vanadium Oxides
... In magnetically frustrated compounds the pairwise exchange interactions of spins cannot all be minimized simultaneously in any microscopic moment configuration. This may arise already in the case of nearest neighbor (n.n.) interactions when the lattice has the property of geometric frustration like, ...
... In magnetically frustrated compounds the pairwise exchange interactions of spins cannot all be minimized simultaneously in any microscopic moment configuration. This may arise already in the case of nearest neighbor (n.n.) interactions when the lattice has the property of geometric frustration like, ...
Clément Hongler Spring 2016 Lecture Series EPFL
... Quantum Field Theory. In two dimensions, this convergence resulted in the most beautiful chapters of mathematical physics: Conformal Field Theory (CFT) reveals deep structures that allow for extremely precise investigations, yielding in particular nonperturbative descriptions with exact formulae. Th ...
... Quantum Field Theory. In two dimensions, this convergence resulted in the most beautiful chapters of mathematical physics: Conformal Field Theory (CFT) reveals deep structures that allow for extremely precise investigations, yielding in particular nonperturbative descriptions with exact formulae. Th ...
Damage spreading on the 3-12 lattice with competing Glauber and
... a continuous flux of energy and this has been proved to be of great importance in describing the time evolution of many dynamical systems. Although the concept of DS was introduced in the context of biologically motivated systems by Kuffman in 1969 [4], now it has been proved to be a useful techniqu ...
... a continuous flux of energy and this has been proved to be of great importance in describing the time evolution of many dynamical systems. Although the concept of DS was introduced in the context of biologically motivated systems by Kuffman in 1969 [4], now it has been proved to be a useful techniqu ...
1.1 Construction of two band models
... This recover the Hamiltonian for the two band model except that we need to redefine the Pauli matrices and neglect the identity matrix term. One can further show that in the above limit, the contribution from the orbital can be included in the second order perturbation theory, which is not essential ...
... This recover the Hamiltonian for the two band model except that we need to redefine the Pauli matrices and neglect the identity matrix term. One can further show that in the above limit, the contribution from the orbital can be included in the second order perturbation theory, which is not essential ...
Simulations of Quantum Spin Systems in the Valence Bond Basis
... • Spans the singlet space (generalizations for triplets, etc) ...
... • Spans the singlet space (generalizations for triplets, etc) ...
Spin-Separation in Cyclotron Motion.
... There has been much interest, and theoretical discussion, about the possibility to use spin-orbit coupling to separate the trajectories of carriers of different spin in a two-dimensional semiconductor structure, without the use of a strong magnetic field. Rokhinson et al. have been able to achieve s ...
... There has been much interest, and theoretical discussion, about the possibility to use spin-orbit coupling to separate the trajectories of carriers of different spin in a two-dimensional semiconductor structure, without the use of a strong magnetic field. Rokhinson et al. have been able to achieve s ...
Physics (Paper- V) - BackBenchersCafe.com
... Answer any four of the following questions: (a) Distinguish Lagrangian, Hamiltonian and. Newtonian formulations from each other, explaining the advantages and disadvantages of each. (b) What is coriolis force? Discuss the effects of this force in some natural phenomena. (c) Prove the formula S=k In ...
... Answer any four of the following questions: (a) Distinguish Lagrangian, Hamiltonian and. Newtonian formulations from each other, explaining the advantages and disadvantages of each. (b) What is coriolis force? Discuss the effects of this force in some natural phenomena. (c) Prove the formula S=k In ...
Ginzburg-Landau theory Free energy Ginzburg
... At certain thickness the transition order changes ...
... At certain thickness the transition order changes ...
Deconfined Quantum Criticality
... The modern theory of phase transition have been developed largely due to the LandauGinzburg framework combined with the Wilson’s renormalization idea. In this framework, the high energy modes are integrated out to be absorbed into the effective relevant parameters. By this mechanism, long wavelength ...
... The modern theory of phase transition have been developed largely due to the LandauGinzburg framework combined with the Wilson’s renormalization idea. In this framework, the high energy modes are integrated out to be absorbed into the effective relevant parameters. By this mechanism, long wavelength ...
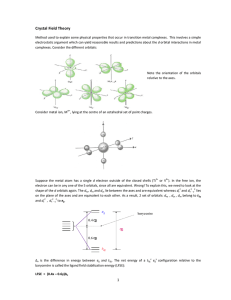
Crystal Field Theory
... Method used to explain some physical properties that occur in transition metal complexes. This involves a simple electrostatic argument which can yield reasonable results and predictions about the d orbital interactions in metal complexes. Consider the different orbitals: ...
... Method used to explain some physical properties that occur in transition metal complexes. This involves a simple electrostatic argument which can yield reasonable results and predictions about the d orbital interactions in metal complexes. Consider the different orbitals: ...
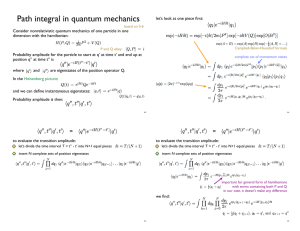
Path integral in quantum mechanics
... we repeat everything we did for the path integral in QM but now for fields; we divide space and time into small segments; take a field in each segment to be constant; the differences between fields in neighboring segments become derivatives; use the trick: multiplying by is equivalent to replacing w ...
... we repeat everything we did for the path integral in QM but now for fields; we divide space and time into small segments; take a field in each segment to be constant; the differences between fields in neighboring segments become derivatives; use the trick: multiplying by is equivalent to replacing w ...
Large N quantum system
... • Problem Infinite number of solutions. • f like a Nambu-Goldstone boson. • Fix: Remember that the symmetry is also explicitly broken (like the pion mass). ...
... • Problem Infinite number of solutions. • f like a Nambu-Goldstone boson. • Fix: Remember that the symmetry is also explicitly broken (like the pion mass). ...
Quantum Effects in Spin Ice 1. Thermodynamic properties of
... quantum systems which exhibit exotic properties such as emergent hidden or topological order, quantum entanglement or fractionalized excitations has made the study of quantum spin liquids and the so-called “spin ice” materials an area of considerable activity over the last decade. This has also coin ...
... quantum systems which exhibit exotic properties such as emergent hidden or topological order, quantum entanglement or fractionalized excitations has made the study of quantum spin liquids and the so-called “spin ice” materials an area of considerable activity over the last decade. This has also coin ...
Poster
... It may be useful to help students to recall on the concept of resonance before the experiment/demonstration. To equip students about gyroscopic precession (if it is not covered before) teachers may want to use the bicycle wheel on turntable demonstration. Electron spin has no classical equivalent. T ...
... It may be useful to help students to recall on the concept of resonance before the experiment/demonstration. To equip students about gyroscopic precession (if it is not covered before) teachers may want to use the bicycle wheel on turntable demonstration. Electron spin has no classical equivalent. T ...
Gautam Menon
... small, NMR only probes the sample surface. Often the surface has many imperfections, so strong vortex-line pinning and a disordered vortex lattice • The penetration depth of the RF field also limits the range over which the vortex lattice can be sampled. Plus additional sources of broadening. ...
... small, NMR only probes the sample surface. Often the surface has many imperfections, so strong vortex-line pinning and a disordered vortex lattice • The penetration depth of the RF field also limits the range over which the vortex lattice can be sampled. Plus additional sources of broadening. ...
Fall 2011 CHEM 760: Introductory Quantum Chemistry Homework 9
... this hypothetical universe. The spin portion of your wave function should be in terms of the spin functions (ms = 1), (ms = 1), and (ms = -1). b) For each of the trial functions you wrote down above, what is the value of the projection of the total spin angular momentum vector onto the z-axis, ...
... this hypothetical universe. The spin portion of your wave function should be in terms of the spin functions (ms = 1), (ms = 1), and (ms = -1). b) For each of the trial functions you wrote down above, what is the value of the projection of the total spin angular momentum vector onto the z-axis, ...