Part I
... • To a high degree of accuracy diatomic molecules can be described using the rigid rotor – harmonic oscillator approximation • With this approximation, in addition to the translational, electronic, and nuclear energies, the molecule has two additional energies • Rotational (rigid rotor): rotary moti ...
... • To a high degree of accuracy diatomic molecules can be described using the rigid rotor – harmonic oscillator approximation • With this approximation, in addition to the translational, electronic, and nuclear energies, the molecule has two additional energies • Rotational (rigid rotor): rotary moti ...
The Chemical Context of Life Chapter 2 Notes
... Neutrons (0), Electrons (-) Protons and Neutrons have a mass of 1 dalton. Electrons have no mass ...
... Neutrons (0), Electrons (-) Protons and Neutrons have a mass of 1 dalton. Electrons have no mass ...
Chemistry Ch 4
... great, it could orbit a nucleus millions of times in 1 second! (He used algebraic methods and the equations of Einstein, Planck, and the speed of a wave to figure) So, how could we possibly know where an electron is in an atom? ...
... great, it could orbit a nucleus millions of times in 1 second! (He used algebraic methods and the equations of Einstein, Planck, and the speed of a wave to figure) So, how could we possibly know where an electron is in an atom? ...
Chemistry (CP) Final Exam Study Guide 1
... ____ 7. a physical blend of two or more components ____ 8. part of a sample having uniform composition and properties ____ 9. not uniform in composition ____ 10. a substance formed in a chemical reaction ____ 11. starting substance in a chemical reaction Match each item with the correct statement be ...
... ____ 7. a physical blend of two or more components ____ 8. part of a sample having uniform composition and properties ____ 9. not uniform in composition ____ 10. a substance formed in a chemical reaction ____ 11. starting substance in a chemical reaction Match each item with the correct statement be ...
Introduction to quantum spin systems
... classes for antiferromagnetic (J > 0) Heisenberg (AFH) Hamiltonian (7) in one-dimensional models (chains). It has been conjectured by Haldane that an integer spin AFH chain is gapful and its correlation functions decay exponentialy versus distance, while the half-integer ones are gapless with algebr ...
... classes for antiferromagnetic (J > 0) Heisenberg (AFH) Hamiltonian (7) in one-dimensional models (chains). It has been conjectured by Haldane that an integer spin AFH chain is gapful and its correlation functions decay exponentialy versus distance, while the half-integer ones are gapless with algebr ...
No Slide Title
... review of the Schrödinger equation and the Born postulate (PDF) review of the Schrödinger equation and the Born postulate (HTML) review of Schrödinger equation and Born postulate (PowerPoint **, ...
... review of the Schrödinger equation and the Born postulate (PDF) review of the Schrödinger equation and the Born postulate (HTML) review of Schrödinger equation and Born postulate (PowerPoint **, ...
Monday, Oct. 2, 2006
... • Orbits and energy levels an electron can occupy are labeled by – Principle quantum number: n • n can only be integer ...
... • Orbits and energy levels an electron can occupy are labeled by – Principle quantum number: n • n can only be integer ...
EMR and the Bohr Model of the Atom
... effective nuclear charge & distance of electron from nucleus. • Increasing effective charge or decreasing distance from nucleus increases attraction between electron & nucleus – more difficult to remove an electron so ionization energy increases. (Both happen when move across row) • As we move down ...
... effective nuclear charge & distance of electron from nucleus. • Increasing effective charge or decreasing distance from nucleus increases attraction between electron & nucleus – more difficult to remove an electron so ionization energy increases. (Both happen when move across row) • As we move down ...
Review for Chapter 3: Atoms, Electrons and Periodic Trends Text
... 4c) Einstein supported Planck’s idea that energy had particle-like properties and was quantized, so energy came in certain amounts. Einstein found that light (a form of energy) is also quantized and suggested that the packages of energy were actually photons (particles) of light. 4d) Heisenberg stat ...
... 4c) Einstein supported Planck’s idea that energy had particle-like properties and was quantized, so energy came in certain amounts. Einstein found that light (a form of energy) is also quantized and suggested that the packages of energy were actually photons (particles) of light. 4d) Heisenberg stat ...
Equation Chapter 1 Section 1 Tips for Studying: Take responsibility
... the penstock it loses gravitational potential energy but gains kinetic energy as it increases speed. 4. As water reaches the turbines, its kinetic energy pushes the blades of the turbines. The kinetic energy of the water is converted to kinetic energy of the turbines. 5. The turbines turn a coil of ...
... the penstock it loses gravitational potential energy but gains kinetic energy as it increases speed. 4. As water reaches the turbines, its kinetic energy pushes the blades of the turbines. The kinetic energy of the water is converted to kinetic energy of the turbines. 5. The turbines turn a coil of ...
elastic - NUCLEAR REACTIONS VIDEO Project
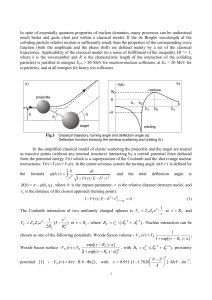
... where k (b, r ) k 1 V (r ) / E b 2 / r 2 is the local wavenumber, r0 (b) is the turning point of the trajectory with the impact parameter b (l 1 / 2) / k . In the general case there are several complex solutions of Eq. (1) for the turning points. Imaginary part of r0 (b) arises due to a po ...
... where k (b, r ) k 1 V (r ) / E b 2 / r 2 is the local wavenumber, r0 (b) is the turning point of the trajectory with the impact parameter b (l 1 / 2) / k . In the general case there are several complex solutions of Eq. (1) for the turning points. Imaginary part of r0 (b) arises due to a po ...