OPTICS14399
... with local baths having identical parameters. In case of classical noise, we consider a decoherence Hamiltonian which is invariant under swapping the first and second qubits. We find that as the system evolves in time, two of the three symmetric Bell states preserve their qubit exchange symmetry with ...
... with local baths having identical parameters. In case of classical noise, we consider a decoherence Hamiltonian which is invariant under swapping the first and second qubits. We find that as the system evolves in time, two of the three symmetric Bell states preserve their qubit exchange symmetry with ...
A n - USM
... ‘excited states’ as they must travel faster (at least according to the traffic rules). Cars travelling in the left lane are in the ``ground state’’ as they can move with a relaxingly lower speed. Cars in the excited states must finally resume to the ground state (i.e. back to the left lane) when the ...
... ‘excited states’ as they must travel faster (at least according to the traffic rules). Cars travelling in the left lane are in the ``ground state’’ as they can move with a relaxingly lower speed. Cars in the excited states must finally resume to the ground state (i.e. back to the left lane) when the ...
Aalborg Universitet Beyond the Modern Physics and Cosmological Equations
... analyzed. This review can be a step to combine general relativity and quantum mechanics. Zero-point energy, also called quantum vacuum zero-point energy, is the lowest possible energy that a quantum mechanical physical system may have; it is the energy of its ground state. All quantum mechanical sys ...
... analyzed. This review can be a step to combine general relativity and quantum mechanics. Zero-point energy, also called quantum vacuum zero-point energy, is the lowest possible energy that a quantum mechanical physical system may have; it is the energy of its ground state. All quantum mechanical sys ...
Heisenberg, Matrix Mechanics, and the Uncertainty Principle Genesis
... Box 3. Linear vector space The space in which the state of a quantum system “lives” is not to be confused with the three-dimensional physical space in which we live. To get the idea right, consider the simple example of a point particle that is free to move on a line. An observable in this case cou ...
... Box 3. Linear vector space The space in which the state of a quantum system “lives” is not to be confused with the three-dimensional physical space in which we live. To get the idea right, consider the simple example of a point particle that is free to move on a line. An observable in this case cou ...
High-Throughput Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay Performed
... the well. When the particles have bound to the magnet, they can be moved from one plate to another for washing and elution steps. The particles can be released from the magnetic head by lifting the magnet out of the tip comb and letting the particles to detach from the surface of the tip comb. ...
... the well. When the particles have bound to the magnet, they can be moved from one plate to another for washing and elution steps. The particles can be released from the magnetic head by lifting the magnet out of the tip comb and letting the particles to detach from the surface of the tip comb. ...
Physics Tutorial 19 Solutions
... interpretation. (Interested students can search along the lines of ‘many-world interpretation’ as well which speaks of parallel universes but this argument is not easy to understand, and it only receives active revival recently following some results in string theory.) Q15. (a)(i) Notice that if we ...
... interpretation. (Interested students can search along the lines of ‘many-world interpretation’ as well which speaks of parallel universes but this argument is not easy to understand, and it only receives active revival recently following some results in string theory.) Q15. (a)(i) Notice that if we ...
Here
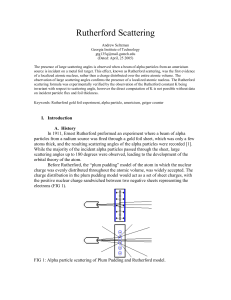
... They may be falling at different speeds or one may be falling the other rising as shown above. In either event, the particles collide. During the collision some of the charge on each particle is neutralized. Each particle is left with net charge following the collision. ...
... They may be falling at different speeds or one may be falling the other rising as shown above. In either event, the particles collide. During the collision some of the charge on each particle is neutralized. Each particle is left with net charge following the collision. ...