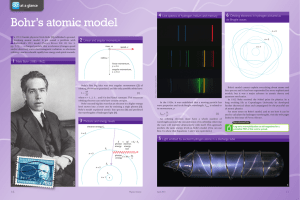
Final Exam Review
... 1. What is density? How is density calculated? 2. What are the steps of the scientific method? 3. What is a quantum of energy? 4. What is matter? 5. What is the difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures? 6. What are the contributions of Bohr, Heisenberg, Dalton, Thompson, & Rutherfor ...
... 1. What is density? How is density calculated? 2. What are the steps of the scientific method? 3. What is a quantum of energy? 4. What is matter? 5. What is the difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures? 6. What are the contributions of Bohr, Heisenberg, Dalton, Thompson, & Rutherfor ...
Chem20u2(5.2) - Mr. Searcy Chemistry 20
... Unit II: Atoms and Elements 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom Pgs. 127-134 I. The learning objectives for this section are: 1. Define and give an example of: ground state, quantum mechanical model of the atom, atomic orbital, principal energy level, energy sublevel. 2. Summarize the contributions made ...
... Unit II: Atoms and Elements 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom Pgs. 127-134 I. The learning objectives for this section are: 1. Define and give an example of: ground state, quantum mechanical model of the atom, atomic orbital, principal energy level, energy sublevel. 2. Summarize the contributions made ...
Chemistry I – Semester I Final Review
... - write electron configurations and orbital filling diagrams (including energy level, sublevels, and orbitals for any element) - recognize the difference between excited state and ground state configuration and everyday applications (fireworks, neon light) - understand the periodic properties due to ...
... - write electron configurations and orbital filling diagrams (including energy level, sublevels, and orbitals for any element) - recognize the difference between excited state and ground state configuration and everyday applications (fireworks, neon light) - understand the periodic properties due to ...
Chapt7
... related to spatial orientation of orbitals within a given subshell possible values of ml = - l, ..... 0, ....., + l the number of ml values = number of orbitals within a subshell e.g., within a subshell having l = 2, there are 5 orbitals corresponding to the 5 possible values of ml ( - 2, -1, 0, +1, ...
... related to spatial orientation of orbitals within a given subshell possible values of ml = - l, ..... 0, ....., + l the number of ml values = number of orbitals within a subshell e.g., within a subshell having l = 2, there are 5 orbitals corresponding to the 5 possible values of ml ( - 2, -1, 0, +1, ...
Chapter 2 Part 1 ppt
... Electrons - energy can be measured very accurately, therefore cannot know position (x) with any certainty • Probability of finding an electron at any position (electron density = probability) • Both Schrodinger and Heisenberg proposed ways to treat electrons as waves, Schrodinger’s math was easier ...
... Electrons - energy can be measured very accurately, therefore cannot know position (x) with any certainty • Probability of finding an electron at any position (electron density = probability) • Both Schrodinger and Heisenberg proposed ways to treat electrons as waves, Schrodinger’s math was easier ...
November 18
... What is Fire? Excited electrons when energy is added release light when they return to their original state Know your flame test colors Bohr’s model of atom, Heisenberg uncertainty principle, Quantum, Schrodinger Chapter 5 Mendeleev, Moseley Know group names, especially alkali metals and Noble gases ...
... What is Fire? Excited electrons when energy is added release light when they return to their original state Know your flame test colors Bohr’s model of atom, Heisenberg uncertainty principle, Quantum, Schrodinger Chapter 5 Mendeleev, Moseley Know group names, especially alkali metals and Noble gases ...
Chapter 4 Test Question Topics
... 1- Know the definitions of the ground state and the excited states of an atom. 2- What must occur for an atom to move from the ground to the excited state or from the excited to the ground state? 3- Know the definitions of an electron cloud and an atomic nucleus. 4- What determines the size and shap ...
... 1- Know the definitions of the ground state and the excited states of an atom. 2- What must occur for an atom to move from the ground to the excited state or from the excited to the ground state? 3- Know the definitions of an electron cloud and an atomic nucleus. 4- What determines the size and shap ...
Arrangement of Electrons In Atoms
... Principle Quantum Numbers • Symbolized by n • Value of n are positive integers (1,2,3 etc) • As n increases, so does its energy and distance from nucleus • More than one e- can have the same n value • Also called shells or main energy level • Total number of orbitals in a shell = n2 ...
... Principle Quantum Numbers • Symbolized by n • Value of n are positive integers (1,2,3 etc) • As n increases, so does its energy and distance from nucleus • More than one e- can have the same n value • Also called shells or main energy level • Total number of orbitals in a shell = n2 ...
Honors Chemistry Name_________________________________
... neutral atom in long form and short form. Write the electron configuration of an ion in long and short form. Relate the position of an atom on the periodic table and its predicted electron configuration. Identify the number of valence electrons in a given atom or ion. Explain the similaritie ...
... neutral atom in long form and short form. Write the electron configuration of an ion in long and short form. Relate the position of an atom on the periodic table and its predicted electron configuration. Identify the number of valence electrons in a given atom or ion. Explain the similaritie ...
Exam #2 Answers to Definitions (Problem #1)
... a) Born-Oppenheimer approximation assumes that the nuclei are stationary, and that electron motion can be treated separately. Fixed bond distances and bond angles are assumed, and a Hamiltonian operator is written for electronic motion only. b) LCAO-MO method for constucting approximate molecular el ...
... a) Born-Oppenheimer approximation assumes that the nuclei are stationary, and that electron motion can be treated separately. Fixed bond distances and bond angles are assumed, and a Hamiltonian operator is written for electronic motion only. b) LCAO-MO method for constucting approximate molecular el ...
Chemistry CPA Activity Sheet Week of November 18, 2013 Unit
... Discuss the dual wave-particle nature of light. Discuss the significance of the photoelectric effect and the line-emission spectrum of hydrogen to the development of the atomic model. Discuss Louis de Broglie’s role in the development of the quantum model of the atom. Explain how the Heisenberg unce ...
... Discuss the dual wave-particle nature of light. Discuss the significance of the photoelectric effect and the line-emission spectrum of hydrogen to the development of the atomic model. Discuss Louis de Broglie’s role in the development of the quantum model of the atom. Explain how the Heisenberg unce ...
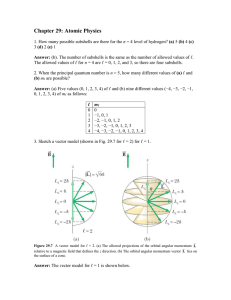
3. Represents an atom that has four valence electrons.
... (I) Only orbits of specific radii, corresponding to certain definite energies, are permitted for electrons in an atom. (II) An electron in a permitted orbit has a specific energy and is an "allowed" energy state. (III) Energy is only emitted or absorbed by an electron as it moves from one allowed en ...
... (I) Only orbits of specific radii, corresponding to certain definite energies, are permitted for electrons in an atom. (II) An electron in a permitted orbit has a specific energy and is an "allowed" energy state. (III) Energy is only emitted or absorbed by an electron as it moves from one allowed en ...
Chemistry 354 - Homework Set IV
... combustion of a single molecule of sucrose; the distance from sideline to sideline on a football field; the time required for an electron to make one circuit of the nucleus in the Bohr atom; the mass of a hydrogen atom; the mass of Haystacks Calhoun (erstwhile professional wrestler); the distance be ...
... combustion of a single molecule of sucrose; the distance from sideline to sideline on a football field; the time required for an electron to make one circuit of the nucleus in the Bohr atom; the mass of a hydrogen atom; the mass of Haystacks Calhoun (erstwhile professional wrestler); the distance be ...