Ch 15-16 DNA and RNA
... New complementary nucleotides link to the exposed bases on the separated strands. A new complementary strand is built along each ‘old’ strand. ...
... New complementary nucleotides link to the exposed bases on the separated strands. A new complementary strand is built along each ‘old’ strand. ...
Genetic_Meiosis Review_15
... Base substitution: occurs when one base is switched out with another base SUBSTITUTION (one base is substituted for another) If a substitution changes the amino acid, it’s called a MISSENSE mutation If a substitution does not change the amino acid, it’s called a SILENT mutation If a substi ...
... Base substitution: occurs when one base is switched out with another base SUBSTITUTION (one base is substituted for another) If a substitution changes the amino acid, it’s called a MISSENSE mutation If a substitution does not change the amino acid, it’s called a SILENT mutation If a substi ...
Short Questions
... Explain each of the underlined terms. 39. Explain the following terms which are used in genetics: homozygous, recessive, phenotype 40. For hair colour black (B) is dominant over brown (b). Seán is heterozygous (Bb) and Máire is homozygous (bb). 1. What colour is Seán’s hair? 2. What colour is Máire’ ...
... Explain each of the underlined terms. 39. Explain the following terms which are used in genetics: homozygous, recessive, phenotype 40. For hair colour black (B) is dominant over brown (b). Seán is heterozygous (Bb) and Máire is homozygous (bb). 1. What colour is Seán’s hair? 2. What colour is Máire’ ...
Recombinant DNA Technology (b)
... (ii) Recognition sites for restriction endonuclease (iii)Presence of at least two markers with recognition site being present in one of the two markers (iv)Relaxed replication control so that the recombinant plasmid is capable of forming several copies. A plasmid containing resistance to an antibiot ...
... (ii) Recognition sites for restriction endonuclease (iii)Presence of at least two markers with recognition site being present in one of the two markers (iv)Relaxed replication control so that the recombinant plasmid is capable of forming several copies. A plasmid containing resistance to an antibiot ...
DNA Worksheet
... Does one enzyme speed up a number of different reactions or just one type? ________. ...
... Does one enzyme speed up a number of different reactions or just one type? ________. ...
DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis Pre-Test
... a. attaches to mRNA and reads it three bases at a time. b. attaches to DNA and breaks it apart for transcription to occur c. attaches to DNA and breaks it apart to make replication occur d. attaches the correct bases to the DNA strand to replicate DNA 21. ________ This the DNA strand ATCTTCGTCAT, wh ...
... a. attaches to mRNA and reads it three bases at a time. b. attaches to DNA and breaks it apart for transcription to occur c. attaches to DNA and breaks it apart to make replication occur d. attaches the correct bases to the DNA strand to replicate DNA 21. ________ This the DNA strand ATCTTCGTCAT, wh ...
Asbury Park School District
... All living organisms contain DNA. Some fruits are especially suited for DNA extractions due to their multiple sets of chromosomes. Strawberries are octoploid, which means they have 8 copies of each chromosome (human body cells are diploid; they contain two copies of each chromosomes). Students will ...
... All living organisms contain DNA. Some fruits are especially suited for DNA extractions due to their multiple sets of chromosomes. Strawberries are octoploid, which means they have 8 copies of each chromosome (human body cells are diploid; they contain two copies of each chromosomes). Students will ...
Genome Editing Slides
... • Discovered as what prokaryotes have as an immune system • Pallindromic Repeats of 20-40 bases, separated by short sequences that turn out to be leftover from bacterial viruses that had previously infected the cell – Pallindromic DNA, when transcribed make RNA’s that can base pair with themselves t ...
... • Discovered as what prokaryotes have as an immune system • Pallindromic Repeats of 20-40 bases, separated by short sequences that turn out to be leftover from bacterial viruses that had previously infected the cell – Pallindromic DNA, when transcribed make RNA’s that can base pair with themselves t ...
Timeline Code DNAi Site Guide
... Production Problem Making insulin with recombinant DNA technology Players Herbert Boyer, David Goeddel, Walter Gilbert Pieces of the puzzle Synthetic insulin, Synthesizing the DNA, Isolating the DNA, The P4 facility Putting it together Synthetic insulin was made using recombinant DNA. ...
... Production Problem Making insulin with recombinant DNA technology Players Herbert Boyer, David Goeddel, Walter Gilbert Pieces of the puzzle Synthetic insulin, Synthesizing the DNA, Isolating the DNA, The P4 facility Putting it together Synthetic insulin was made using recombinant DNA. ...
Lesson 3.2 Reducing Cancer Risk
... and/or radiation therapy expect during treatment? • Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to kill, prevent the spreading, slow growth, and treat symptoms of cancer. • The side effects are different for everyone, but typical side effects are hair loss, anemia and symptoms that occur with anemia, increased ...
... and/or radiation therapy expect during treatment? • Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to kill, prevent the spreading, slow growth, and treat symptoms of cancer. • The side effects are different for everyone, but typical side effects are hair loss, anemia and symptoms that occur with anemia, increased ...
RNA
... Point Mutations: Insertions and Deletions Insertion mutation: when a single extra base is added into the code Deletion mutation: when a single base is removed from the code ...
... Point Mutations: Insertions and Deletions Insertion mutation: when a single extra base is added into the code Deletion mutation: when a single base is removed from the code ...
101 -- 2006
... f) translocation __ 78. Which of the following is always fatal in humans? a) polyploid c) inversion e) inversion b) monosomy d) deletion f) translocation __ 79. Which of the following contains the normal amount of genetic material? a) polyploid b) monosomy c) inversion d) deletion e) inversion __ 80 ...
... f) translocation __ 78. Which of the following is always fatal in humans? a) polyploid c) inversion e) inversion b) monosomy d) deletion f) translocation __ 79. Which of the following contains the normal amount of genetic material? a) polyploid b) monosomy c) inversion d) deletion e) inversion __ 80 ...
BDOL Interactive Chalkboard
... Mutations in body cells • What happens if powerful radiation, such as gamma radiation, hits the DNA of a nonreproductive cell, a cell of the body such as in skin, muscle, or bone? • If the cell’s DNA is changed, this mutation would not be passed on to offspring. ...
... Mutations in body cells • What happens if powerful radiation, such as gamma radiation, hits the DNA of a nonreproductive cell, a cell of the body such as in skin, muscle, or bone? • If the cell’s DNA is changed, this mutation would not be passed on to offspring. ...
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndromes: Are we there yet?
... 1. Ohio Cancer Incidence Surveillance System, Ohio Department of Health, 2011 2. Anderson MR et al. Cancer 2008;113:484-489. 3. Myers ER et al. Evidence Report Technology Assessment 2006 full report 1-145. 4. Cancer Research UK. http://info.cancerresearchuk.org/cancerstats/types/ovary/survival/index ...
... 1. Ohio Cancer Incidence Surveillance System, Ohio Department of Health, 2011 2. Anderson MR et al. Cancer 2008;113:484-489. 3. Myers ER et al. Evidence Report Technology Assessment 2006 full report 1-145. 4. Cancer Research UK. http://info.cancerresearchuk.org/cancerstats/types/ovary/survival/index ...
Document
... 4. In the chemical analysis of the DNA from different species, the work of Chargaff indicated that the amount of adenine equaled the amount of thymine and that the amount of cytosine equaled the amount of guanine. 5. In the early 1950s, Linus Pauling proposed that regions of proteins can fold into a ...
... 4. In the chemical analysis of the DNA from different species, the work of Chargaff indicated that the amount of adenine equaled the amount of thymine and that the amount of cytosine equaled the amount of guanine. 5. In the early 1950s, Linus Pauling proposed that regions of proteins can fold into a ...
S1.A hypothetical sequence at the beginning of an mRNA molecule
... 4. In the chemical analysis of the DNA from different species, the work of Chargaff indicated that the amount of adenine equaled the amount of thymine and that the amount of cytosine equaled the amount of guanine. 5. In the early 1950s, Linus Pauling proposed that regions of proteins can fold into a ...
... 4. In the chemical analysis of the DNA from different species, the work of Chargaff indicated that the amount of adenine equaled the amount of thymine and that the amount of cytosine equaled the amount of guanine. 5. In the early 1950s, Linus Pauling proposed that regions of proteins can fold into a ...
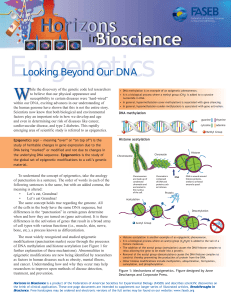
Looking Beyond Our DNA - Federation of American Societies for
... In addition to the epigenetic changes that occur throughout a person’s lifetime, researchers are also beginning to understand how the fetal environment can alter the epigenome and affect gene expression well into adulthood. To further explore this process, Randy Jirtle, PhD, and his colleagues at Du ...
... In addition to the epigenetic changes that occur throughout a person’s lifetime, researchers are also beginning to understand how the fetal environment can alter the epigenome and affect gene expression well into adulthood. To further explore this process, Randy Jirtle, PhD, and his colleagues at Du ...
國立彰化師範大學100 學年度碩士班招生考試試題
... (C) inability to synthesize a primer for the last Okazaki fragment made so that it can fully replicate its template DNA (D) inability to ligate the last Okazaki fragment to the one immediately preceding it 8. The spontaneous loss of a purine (guanine or adenine) from cellular DNA is repaired by (A) ...
... (C) inability to synthesize a primer for the last Okazaki fragment made so that it can fully replicate its template DNA (D) inability to ligate the last Okazaki fragment to the one immediately preceding it 8. The spontaneous loss of a purine (guanine or adenine) from cellular DNA is repaired by (A) ...
Chapter 12 Molecular Genetics
... cigarette smoke, and many others Affect DNA by changing chemical nature of the bases May resemble nucleotides and bond in place of the DNA nucleotides preventing DNA replication ...
... cigarette smoke, and many others Affect DNA by changing chemical nature of the bases May resemble nucleotides and bond in place of the DNA nucleotides preventing DNA replication ...
Modern Genetics Notes
... funny name, is the TATA box (named for its sequences of alternating adenine and thymine), which helps RNA polymerase bind to the promoter. ...
... funny name, is the TATA box (named for its sequences of alternating adenine and thymine), which helps RNA polymerase bind to the promoter. ...
Quick Reference Sheet
... Simple dominance, monohybrid cross Incomplete dominance Dihybrid cross ...
... Simple dominance, monohybrid cross Incomplete dominance Dihybrid cross ...
Topic 7: Mendelian and Human Genetics Uncover Inheritance
... Simple dominance, monohybrid cross Incomplete dominance Dihybrid cross ...
... Simple dominance, monohybrid cross Incomplete dominance Dihybrid cross ...
Topic 7: Mendelian and Human Genetics
... Simple dominance, monohybrid cross Incomplete dominance Dihybrid cross ...
... Simple dominance, monohybrid cross Incomplete dominance Dihybrid cross ...
Genetics Review: What is genetics? Genetics is what makes me
... Phenotype: a manifestation of genes. Appearance of organism due to traits expressed by a particular genotype. Genotype: the genetic makeup that is controlled by an organism’s alleles. Locus: the physical location of a gene on a chromosome. ...
... Phenotype: a manifestation of genes. Appearance of organism due to traits expressed by a particular genotype. Genotype: the genetic makeup that is controlled by an organism’s alleles. Locus: the physical location of a gene on a chromosome. ...
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called ""spontaneous mutations"" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination.