Slide 1
... The electric field accelerates the electron, but only until the electron collides with a “scattering center.” Then the electron’s velocity is randomized and the acceleration begins again. Some predictions based on this model are off by a factor or 10 or so, but with the inclusion of some quantum mec ...
... The electric field accelerates the electron, but only until the electron collides with a “scattering center.” Then the electron’s velocity is randomized and the acceleration begins again. Some predictions based on this model are off by a factor or 10 or so, but with the inclusion of some quantum mec ...
2000 - Year 11
... (b) What is the total kinetic energy of the trolley and the block after the collision? [1] (c) When the block fell into the trolley its vertical velocity was 5.0 m/s. Why was it not necessary to take this into account when finding the answer to part (a)? [1] 21. This question refers to the diagram b ...
... (b) What is the total kinetic energy of the trolley and the block after the collision? [1] (c) When the block fell into the trolley its vertical velocity was 5.0 m/s. Why was it not necessary to take this into account when finding the answer to part (a)? [1] 21. This question refers to the diagram b ...
Earth Science Pages 190-196
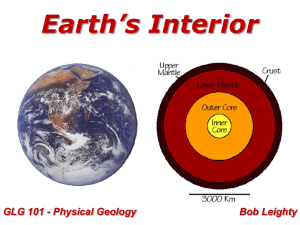
... iron, calcium, and magnesium, which form minerals that are denser than those in the continental crust. 5. The crust is less than 1% of the Earth’s mass…100km thick ...
... iron, calcium, and magnesium, which form minerals that are denser than those in the continental crust. 5. The crust is less than 1% of the Earth’s mass…100km thick ...
BACKGROUND - Exploration Works
... are on plates moving on the earth’s mantle. The movement is caused by the mantle’s high temperature causing its layer to be somewhat fluid. Background for the Advanced Lesson Geologists have distinguished three main internal subdivisions of the Earth, based on the behavior of seismic waves and labor ...
... are on plates moving on the earth’s mantle. The movement is caused by the mantle’s high temperature causing its layer to be somewhat fluid. Background for the Advanced Lesson Geologists have distinguished three main internal subdivisions of the Earth, based on the behavior of seismic waves and labor ...
Edible Tectonics
... observations and phenomena. It explains, for example, the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes throughout the world. It also explains how many of Earth’s surface features- such as mountain ranges, ocean trenches, and fault lines- were formed. To understand plate tectonics remember that the lith ...
... observations and phenomena. It explains, for example, the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes throughout the world. It also explains how many of Earth’s surface features- such as mountain ranges, ocean trenches, and fault lines- were formed. To understand plate tectonics remember that the lith ...
A. Compression - mccullochscience
... ____ 17.) This graph illustrates the fact that… A. as you move deeper into the Earth, pressure decreases. B. as you move deeper into the Earth, pressure increases. C. as you move deeper into the Earth, temperature increases. ____ 18.) Which of the following would be an appropriate title for the grap ...
... ____ 17.) This graph illustrates the fact that… A. as you move deeper into the Earth, pressure decreases. B. as you move deeper into the Earth, pressure increases. C. as you move deeper into the Earth, temperature increases. ____ 18.) Which of the following would be an appropriate title for the grap ...
Experiment 1G Uniform Circular Motion
... (3) Calculate the following using data from Parts I and II and fill out Table A: TABLE A: CHANGING THE RADIUS Source of Data ...
... (3) Calculate the following using data from Parts I and II and fill out Table A: TABLE A: CHANGING THE RADIUS Source of Data ...
Blaine Smit Assignment 1.3 Definitions
... plastic lower mantle. This convection within the mantle causes the rigid plates to move around like slow moving ice on water. Tectonic activity results from the movement of these rigid plates relative to each other and the consequent forces that act on them, which cause deformation of the plates. Th ...
... plastic lower mantle. This convection within the mantle causes the rigid plates to move around like slow moving ice on water. Tectonic activity results from the movement of these rigid plates relative to each other and the consequent forces that act on them, which cause deformation of the plates. Th ...
Suggestions for obtaining UC "d" lab status - H
... Cosmic expansion and the Big Bang Theory. Dark matter and dark energy. Physics applications: wave and particle properties of electromagnetic radiation, Doppler effect and red shift, wave refraction and reflection, gravitation, general relativity, nuclear reactions, conservation of energy, energy con ...
... Cosmic expansion and the Big Bang Theory. Dark matter and dark energy. Physics applications: wave and particle properties of electromagnetic radiation, Doppler effect and red shift, wave refraction and reflection, gravitation, general relativity, nuclear reactions, conservation of energy, energy con ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... body mass is above them. Consider hanging by your hands from a 100 m high diving board. Gravity pull down on you and stretches your body.You feel most stretching in your arms, because most body mass is below them. Let go of the 100 m high diving board. While gravity accelerates you downward, what do ...
... body mass is above them. Consider hanging by your hands from a 100 m high diving board. Gravity pull down on you and stretches your body.You feel most stretching in your arms, because most body mass is below them. Let go of the 100 m high diving board. While gravity accelerates you downward, what do ...
6th Grade Science Syllabus
... different types of rock 5-6 Sessions Earth History Understand how fossils Investigation 6 and other evidence are It’s About Time used to document life and environmental changes over time 2-3 Sessions Earth History Understand how fossils Investigation 7 and other evidence are Fossils and Time used to ...
... different types of rock 5-6 Sessions Earth History Understand how fossils Investigation 6 and other evidence are It’s About Time used to document life and environmental changes over time 2-3 Sessions Earth History Understand how fossils Investigation 7 and other evidence are Fossils and Time used to ...
10-3 Directed Reading
... 24. Ice covered most of Earth when all the continents were located near ______________________________________________________________ . 25. What caused Earth’s temperatures to change and its ice sheet to melt? _______________________________________________________________ 26. What happens to popul ...
... 24. Ice covered most of Earth when all the continents were located near ______________________________________________________________ . 25. What caused Earth’s temperatures to change and its ice sheet to melt? _______________________________________________________________ 26. What happens to popul ...
GS 388 handout: Gravity Anomalies: brief summary 1 1. Observed
... generally a measurement of the difference between the gravity at the point of observation and the gravity at one of the bench marks in a world-wide or national gravity network. These benchmarks have been tied (again, by a measurement of relative gravity with a geodetic gravimeter to cover a large ra ...
... generally a measurement of the difference between the gravity at the point of observation and the gravity at one of the bench marks in a world-wide or national gravity network. These benchmarks have been tied (again, by a measurement of relative gravity with a geodetic gravimeter to cover a large ra ...
Document
... 24. Ice covered most of Earth when all the continents were located near ______________________________________________________________ . 25. What caused Earth’s temperatures to change and its ice sheet to melt? _______________________________________________________________ 26. What happens to popul ...
... 24. Ice covered most of Earth when all the continents were located near ______________________________________________________________ . 25. What caused Earth’s temperatures to change and its ice sheet to melt? _______________________________________________________________ 26. What happens to popul ...
S11 NSCI 342 Packet General Info
... temperature, and color. c. how to use astronomical units and light years as measures of distance between the sun, stars, and Earth. d. stars are the source of light for all bright objects in outer space. The moon and planets shine by reflected sunlight, not by their own light. e. the appearance, gen ...
... temperature, and color. c. how to use astronomical units and light years as measures of distance between the sun, stars, and Earth. d. stars are the source of light for all bright objects in outer space. The moon and planets shine by reflected sunlight, not by their own light. e. the appearance, gen ...
Lesson 1 - Plate Tectonics
... nails — so don’t worry, we’re not about to be jolted off the surface of the crust. ...
... nails — so don’t worry, we’re not about to be jolted off the surface of the crust. ...
Schiehallion experiment

The Schiehallion experiment was an 18th-century experiment to determine the mean density of the Earth. Funded by a grant from the Royal Society, it was conducted in the summer of 1774 around the Scottish mountain of Schiehallion, Perthshire. The experiment involved measuring the tiny deflection of a pendulum due to the gravitational attraction of a nearby mountain. Schiehallion was considered the ideal location after a search for candidate mountains, thanks to its isolation and almost symmetrical shape. One of the triggers for the experiment were anomalies noted during the survey of the Mason–Dixon Line.The experiment had previously been considered, but rejected, by Isaac Newton as a practical demonstration of his theory of gravitation. However, a team of scientists, notably Nevil Maskelyne, the Astronomer Royal, were convinced that the effect would be detectable and undertook to conduct the experiment. The deflection angle depended on the relative densities and volumes of the Earth and the mountain: if the density and volume of Schiehallion could be ascertained, then so could the density of the Earth. Once this was known, then this would in turn yield approximate values for those of the other planets, their moons, and the Sun, previously known only in terms of their relative ratios. As an additional benefit, the concept of contour lines, devised to simplify the process of surveying the mountain, later became a standard technique in cartography.