Hearing Loss Prevention
... sounds). If the hair cells are damaged, the sound cannot reach the brain and we cannot recognize the sounds. Hair cells will not regenerate; therefore, they cannot be reproduced or repaired. Did you know noise is a common cause of hearing loss? ...
... sounds). If the hair cells are damaged, the sound cannot reach the brain and we cannot recognize the sounds. Hair cells will not regenerate; therefore, they cannot be reproduced or repaired. Did you know noise is a common cause of hearing loss? ...
Presentation
... a- deafness that occurs when something interferes with the conduction of sound vibrations to the fluids of the inner ear. ...
... a- deafness that occurs when something interferes with the conduction of sound vibrations to the fluids of the inner ear. ...
Outer Ear
... All these structures of the ear must work well for normal hearing. Damage to any of them, through illness or injury, may cause hearing loss. Total hearing loss is called deafness. Most adults experience at least some hearing loss as they get older. The most common cause is exposure to loud sounds, w ...
... All these structures of the ear must work well for normal hearing. Damage to any of them, through illness or injury, may cause hearing loss. Total hearing loss is called deafness. Most adults experience at least some hearing loss as they get older. The most common cause is exposure to loud sounds, w ...
Hearing Impairment
... The cochlea is the end organ of hearing and is shaped like a snail shell with 2.5 turns. Inside, 2 membranes longitudinally divide the cochlea into 3 sections: the scala tympani, the scala vestibuli, and the scala media. All 3 are filled with fluid of various ion concentrations (similar to intracell ...
... The cochlea is the end organ of hearing and is shaped like a snail shell with 2.5 turns. Inside, 2 membranes longitudinally divide the cochlea into 3 sections: the scala tympani, the scala vestibuli, and the scala media. All 3 are filled with fluid of various ion concentrations (similar to intracell ...
Selective Inner Hair Cell Loss in Premature Infants and Cochlea
... Figure Legend: Photomicrographs illustrating expected selective outer hair cell (OHC) loss (long arrows) in 2 patients. Short arrows in both parts indicate stereocilia on inner hair cells. A, All 3 OHC rows are missing in this section from the basal turn of patient 1, a full-term baby who failed the ...
... Figure Legend: Photomicrographs illustrating expected selective outer hair cell (OHC) loss (long arrows) in 2 patients. Short arrows in both parts indicate stereocilia on inner hair cells. A, All 3 OHC rows are missing in this section from the basal turn of patient 1, a full-term baby who failed the ...
Senses Other Than Vision Hearing (Audition) Transmission of
... • The chemical senses are so called because they are based on the chemical properties of the materials being sensed. • Two senses fall into this category: – Smell – Taste ...
... • The chemical senses are so called because they are based on the chemical properties of the materials being sensed. • Two senses fall into this category: – Smell – Taste ...
Chapter 2 Physiological correlates of hearing impairment
... temporal resolution and speech perception (Moore, 1995; Florentine et al., 1993; Holube, 1993; Glasberg and Moore, 1989; Festen and Plomp, 1983; Moore, 1983) even when compared at the same sensation level (SL) with normal subjects. Usually, large intersubject variability is seen in the results of di ...
... temporal resolution and speech perception (Moore, 1995; Florentine et al., 1993; Holube, 1993; Glasberg and Moore, 1989; Festen and Plomp, 1983; Moore, 1983) even when compared at the same sensation level (SL) with normal subjects. Usually, large intersubject variability is seen in the results of di ...
The Ear and Hearing - Bishop Amat Memorial High School
... The Ear... Acoustic energy, in the form of sound waves, is channeled into the ear canal by the pinna. Sound waves strike the tympanic membrane, causing it to vibrate like a drum, and changing it into mechanical energy. The malleus, which is attached to the tympanic membrane, starts the ossicles into ...
... The Ear... Acoustic energy, in the form of sound waves, is channeled into the ear canal by the pinna. Sound waves strike the tympanic membrane, causing it to vibrate like a drum, and changing it into mechanical energy. The malleus, which is attached to the tympanic membrane, starts the ossicles into ...
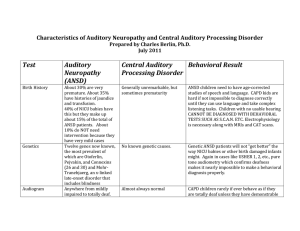
Characteristics of Auditory Neuropathy and Central Auditory
... abnormal tympanograms that require medical or surgical attention. The reflexes assess the lower brainstem’s integrity along with inner hair cells. CAPD patients should not have elevated middle ear muscle reflex thresholds and should always be between 75 and 95 dB. The site of lesion in ANSD starts a ...
... abnormal tympanograms that require medical or surgical attention. The reflexes assess the lower brainstem’s integrity along with inner hair cells. CAPD patients should not have elevated middle ear muscle reflex thresholds and should always be between 75 and 95 dB. The site of lesion in ANSD starts a ...
Inner-Ear Function - Cutis Laxa Research Study
... • How an audiologist measures integrity of function (is it working?) – Middle ear – tympanometry (ME pressure) – Inner ear – otoacoustic emissions (outer hair cells) ...
... • How an audiologist measures integrity of function (is it working?) – Middle ear – tympanometry (ME pressure) – Inner ear – otoacoustic emissions (outer hair cells) ...
File
... temporary or permanent, depending on the intensity and duration of the exposure. Although a person’s hearing may recover from temporary, slight damage to the hair cells, the complete loss of hair cells is irreversible in humans. ...
... temporary or permanent, depending on the intensity and duration of the exposure. Although a person’s hearing may recover from temporary, slight damage to the hair cells, the complete loss of hair cells is irreversible in humans. ...
7/29/2015 Proposal of Auditory Neuropathy Auditory Neuropathy
... — Central auditory pathway in the brainstem ...
... — Central auditory pathway in the brainstem ...
Transcripts/2_4 2
... a sensory stimulus: Modality (today talking about sound), Intensity (usually encoded in the number/frequency of action potentials), Duration (can be measured with sound by how long cells are stimulated), Location (interesting for auditory because we have mechanisms to detect the direction of sound w ...
... a sensory stimulus: Modality (today talking about sound), Intensity (usually encoded in the number/frequency of action potentials), Duration (can be measured with sound by how long cells are stimulated), Location (interesting for auditory because we have mechanisms to detect the direction of sound w ...
Cochlear duct
... Sounds set up vibrations in air that beat against the eardrum that pushes a chain of tiny bones that press fluid in the internal ear against membranes that set up shearing forces that pull on the tiny hair cells that stimulate nearby neurons that give rise to the impulses that travel to the brain – ...
... Sounds set up vibrations in air that beat against the eardrum that pushes a chain of tiny bones that press fluid in the internal ear against membranes that set up shearing forces that pull on the tiny hair cells that stimulate nearby neurons that give rise to the impulses that travel to the brain – ...
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. Noise
... the tiny hair cells in our cochlea can become disorganized and damaged from too much and too harsh of vibrations. Once the hair cells break, they will NEVER grow back, this causes hearing loss. To treat NIHL visit an audiologist. From David J. Lim. Functional Structure of the Organ of Corti: A Revie ...
... the tiny hair cells in our cochlea can become disorganized and damaged from too much and too harsh of vibrations. Once the hair cells break, they will NEVER grow back, this causes hearing loss. To treat NIHL visit an audiologist. From David J. Lim. Functional Structure of the Organ of Corti: A Revie ...
Olivocochlear system

The olivocochlear system is a component of the auditory system involved with the descending control of the cochlea. Its nerve fibres, the olivocochlear bundle (OCB), form part of the vestibulocochlear nerve (VIIIth cranial nerve, also known as the auditory-vestibular nerve), and project from the superior olivary complex in the brainstem (pons) to the cochlea.