Noise Induced Hearing Loss
... our ability to hear higher frequency sounds. If NIHL spreads to frequencies where human speech occurs (500-3000 Hz) , understanding speech will be difficult. ...
... our ability to hear higher frequency sounds. If NIHL spreads to frequencies where human speech occurs (500-3000 Hz) , understanding speech will be difficult. ...
Noise Induced Hearing Loss (NIHL)
... hear are at safe levels that do not affect our hearing. However, when we are exposed to harmful noise - loud sounds that last a long time or extremely loud sounds – hair cells in our inner ear can be damaged. These small sensitive structures make hearing possible by converting sound energy into elec ...
... hear are at safe levels that do not affect our hearing. However, when we are exposed to harmful noise - loud sounds that last a long time or extremely loud sounds – hair cells in our inner ear can be damaged. These small sensitive structures make hearing possible by converting sound energy into elec ...
Hearin
... • Reflexive motor commands issued by vestibular nuclei are distributed to motor nuclei for cranial nerves involved with eye, head, and neck movements • Automatic movements of eye that occur in response to sensations of motion • directed by the superior colliculi of the mesencephalon (in an attempt t ...
... • Reflexive motor commands issued by vestibular nuclei are distributed to motor nuclei for cranial nerves involved with eye, head, and neck movements • Automatic movements of eye that occur in response to sensations of motion • directed by the superior colliculi of the mesencephalon (in an attempt t ...
Spatial Hearing
... The goal is to assess their abilities to localize sounds in space and to communicate under acoustically adverse conditions. The information is needed , among other reasons, to decide if hearings aids should be applied to them – and, if yes, which kind of these? Outline a battery of perceptual tests ...
... The goal is to assess their abilities to localize sounds in space and to communicate under acoustically adverse conditions. The information is needed , among other reasons, to decide if hearings aids should be applied to them – and, if yes, which kind of these? Outline a battery of perceptual tests ...
A Guide to Hearing Protection
... As sound enters the outer ear, it is channeled down the ear canal until it reaches the ear drum. The ear drum, a thin membrane stretched over a tube, is moved by the sound waves. When the sound vibrations reach the coiled, liquid-filled tube called the cochlea, thousands of hair cells in the cochlea ...
... As sound enters the outer ear, it is channeled down the ear canal until it reaches the ear drum. The ear drum, a thin membrane stretched over a tube, is moved by the sound waves. When the sound vibrations reach the coiled, liquid-filled tube called the cochlea, thousands of hair cells in the cochlea ...
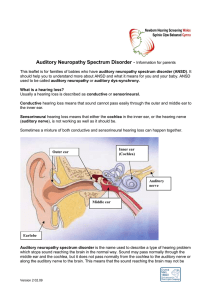
Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder
... baby is very young. If the tests show the cochlea is working well but the auditory nerve is not working as it should be, then ANSD could be the cause. In some babies, this pattern of test results can happen if the development of the auditory nerve is delayed. This is often the case with babies who a ...
... baby is very young. If the tests show the cochlea is working well but the auditory nerve is not working as it should be, then ANSD could be the cause. In some babies, this pattern of test results can happen if the development of the auditory nerve is delayed. This is often the case with babies who a ...
Hearing Physiology
... • Base of hair cell in contact with auditory nerve end • Outer hair cell primarily responsive to lateral shear • Inner hair cells, do not drag against tectorial ...
... • Base of hair cell in contact with auditory nerve end • Outer hair cell primarily responsive to lateral shear • Inner hair cells, do not drag against tectorial ...
Auditory processing disorder Auditory process disorder
... carried through the ear to the brain. The ear consists of three parts, the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. Sound waves enter the ear canal and cause the eardrum to vibrate. The sound then passes through the middle ear via the three small bones of hearing (ossicles) on to the inner ear, ...
... carried through the ear to the brain. The ear consists of three parts, the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. Sound waves enter the ear canal and cause the eardrum to vibrate. The sound then passes through the middle ear via the three small bones of hearing (ossicles) on to the inner ear, ...
Hearing Loss Following Microvascular Decompression for
... Patients with HFHL often have deficiencies in high ...
... Patients with HFHL often have deficiencies in high ...
6 Classifications of Presbycusis
... *Loss of 50% of cochlear neurons, greater in the elderly over 80 years of age = 15,000 from 30,000 as a young adult Most consistent pathological change in older ear Associated with poorer than expected word recognition ...
... *Loss of 50% of cochlear neurons, greater in the elderly over 80 years of age = 15,000 from 30,000 as a young adult Most consistent pathological change in older ear Associated with poorer than expected word recognition ...
How Hearing Works File
... frequent intermarriage among deaf people, Bell cautioned that the incidence of deafness could rise until there was a separate race of deaf people. Although his ideas on eugenics are not credited now, he was responsible for many changes made to education of the deaf. Deafness is the most common inher ...
... frequent intermarriage among deaf people, Bell cautioned that the incidence of deafness could rise until there was a separate race of deaf people. Although his ideas on eugenics are not credited now, he was responsible for many changes made to education of the deaf. Deafness is the most common inher ...
Rotational acceleration
... NOTE: It is important to understand that the maculae is responsible for the change in acceleration only. Because the hair cell can adapt it quickly ...
... NOTE: It is important to understand that the maculae is responsible for the change in acceleration only. Because the hair cell can adapt it quickly ...
Olivocochlear system

The olivocochlear system is a component of the auditory system involved with the descending control of the cochlea. Its nerve fibres, the olivocochlear bundle (OCB), form part of the vestibulocochlear nerve (VIIIth cranial nerve, also known as the auditory-vestibular nerve), and project from the superior olivary complex in the brainstem (pons) to the cochlea.