Slide 1
... • Intrusive rocks cool slowly underground, allowing their crystals to grow large. Large crystals give intrusive rocks a coarse-grained texture. • Extrusive igneous rocks cool very quickly at the surface. Their crystals do not grow much before the rock cools. This gives extrusive rocks a finegrained ...
... • Intrusive rocks cool slowly underground, allowing their crystals to grow large. Large crystals give intrusive rocks a coarse-grained texture. • Extrusive igneous rocks cool very quickly at the surface. Their crystals do not grow much before the rock cools. This gives extrusive rocks a finegrained ...
Identify the best answer. Answers are on the last page.
... a. Is the source of Sun’s energy b. Occurs when the nucleus of an atom fissions and releases energy c. Radiates throughout the universe d. Is the reason that Jupiter has no solid surface e. All the above 3. Mercury, Venus, and Mars are different than Earth because: a. They are closer to the Sun. b. ...
... a. Is the source of Sun’s energy b. Occurs when the nucleus of an atom fissions and releases energy c. Radiates throughout the universe d. Is the reason that Jupiter has no solid surface e. All the above 3. Mercury, Venus, and Mars are different than Earth because: a. They are closer to the Sun. b. ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... • Metamorphism progresses from low to high grades • Rocks remain solid during metamorphism ...
... • Metamorphism progresses from low to high grades • Rocks remain solid during metamorphism ...
Earth Materials: Sedimentary Rocks
... Abrasion by flowing water Water typically carries sand and gravel. These particles bump into each other and larger rocks wearing them down over time. ...
... Abrasion by flowing water Water typically carries sand and gravel. These particles bump into each other and larger rocks wearing them down over time. ...
Metamorphism
... • The transition of one rock into another by temperatures and/or pressures unlike those in which it formed • Metamorphic rocks are produced from • Igneous rocks • Sedimentary rocks • Other metamorphic rocks ...
... • The transition of one rock into another by temperatures and/or pressures unlike those in which it formed • Metamorphic rocks are produced from • Igneous rocks • Sedimentary rocks • Other metamorphic rocks ...
CE6301-Engineering Geology - KSK college of Engineering and
... 2. Differentiate between water table & perched water table. 3. Define the term aquifer & Mention its types. 4. What is meant by an subduction zone: What is its significance. 5. What is difference between an aquifer & an aquiclude? 6. Write short note on mercalli scale. 7. Explain the term plate tect ...
... 2. Differentiate between water table & perched water table. 3. Define the term aquifer & Mention its types. 4. What is meant by an subduction zone: What is its significance. 5. What is difference between an aquifer & an aquiclude? 6. Write short note on mercalli scale. 7. Explain the term plate tect ...
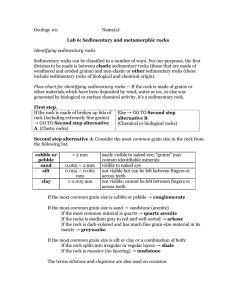
Lab 6
... 10. a. Use the facies from question 12c to determine the range of possible maximum pressures and the range of possible maximum temperatures at which R34 formed. Use units of °C for temperature and kbar for pressure. ...
... 10. a. Use the facies from question 12c to determine the range of possible maximum pressures and the range of possible maximum temperatures at which R34 formed. Use units of °C for temperature and kbar for pressure. ...
Geology 10 review- Test #2 Read Chapters 6, 7, 8 and 10 from
... Describe how 14C is used to date certain kinds of rocks. What type of rock or sediment would be used for 14C dating? Describe how the dating system works. Where or how are radiogenic isotopes trapped in the rock, and what is the decay series? ...
... Describe how 14C is used to date certain kinds of rocks. What type of rock or sediment would be used for 14C dating? Describe how the dating system works. Where or how are radiogenic isotopes trapped in the rock, and what is the decay series? ...
What is a Mineral - Community Unit School District 308
... • Each mineral has a definite crystalline shape or repeating inner pattern of atoms • All minerals can be classified according to their crystal structure ...
... • Each mineral has a definite crystalline shape or repeating inner pattern of atoms • All minerals can be classified according to their crystal structure ...
Table of Contents - for Jack L. Pierce
... definitions of various igneous textural terms used in this lab: phanaritic – minerals are visible to the naked eye and form a “mosaic” of interlocking crystal aggregates. Typically, mineral grains are greater than 1 mm. aphanitic – mineral grains are too small to see without a hand lens and generall ...
... definitions of various igneous textural terms used in this lab: phanaritic – minerals are visible to the naked eye and form a “mosaic” of interlocking crystal aggregates. Typically, mineral grains are greater than 1 mm. aphanitic – mineral grains are too small to see without a hand lens and generall ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... ___bands__ is called ___nonfoliated___. The minerals are not __aligned__ (not lined up). 18. These rocks are commonly made of _1__ or only a ...
... ___bands__ is called ___nonfoliated___. The minerals are not __aligned__ (not lined up). 18. These rocks are commonly made of _1__ or only a ...
Name: Date
... only heat and chemically active fluids 3. The agents of metamorphism include heat, pressure, and ...
... only heat and chemically active fluids 3. The agents of metamorphism include heat, pressure, and ...
4th Grade Nonfiction Rocks and Minerals Project
... Is an extremely common mineral in the earth’s crust. It is composed of silicon and oxygen. ...
... Is an extremely common mineral in the earth’s crust. It is composed of silicon and oxygen. ...
pdf of 6 units below
... stored in the ground below us, where different types of rocks can act as reservoirs. Sand or sandstone is the best material for a reservoir and forms extensive aquifers underground, but not all sands are created equal, as students will find out in lab. Filtering water through different porous substa ...
... stored in the ground below us, where different types of rocks can act as reservoirs. Sand or sandstone is the best material for a reservoir and forms extensive aquifers underground, but not all sands are created equal, as students will find out in lab. Filtering water through different porous substa ...
Earth Materials Summary
... earth—rocks and minerals. The focus is on taking materials apart to find what they are made of and putting materials together to better understand their properties. The module introduces fundamental concepts in earth science and takes advantage of the students’ intrinsic interest in the subject matt ...
... earth—rocks and minerals. The focus is on taking materials apart to find what they are made of and putting materials together to better understand their properties. The module introduces fundamental concepts in earth science and takes advantage of the students’ intrinsic interest in the subject matt ...
V i - Minnesota DNR
... Explosion of Life Life on earth quietly "exploded" about 600 million years ago. It evolved from single-celled bacteria to complex marine animals, in a fairly short time. It was hot in North America. The continent, nearly flat, lay near the equator. Many times the tropical sea flooded the land and t ...
... Explosion of Life Life on earth quietly "exploded" about 600 million years ago. It evolved from single-celled bacteria to complex marine animals, in a fairly short time. It was hot in North America. The continent, nearly flat, lay near the equator. Many times the tropical sea flooded the land and t ...
the guide - Learning Resources UK
... sand, mud, and pieces of rock or shell. Sediments are geologic travelers. Wind, water, and ice move the sediment over the surface of the Earth. When sediment finally clumps together and then slowly hardens, sedimentary rock is formed. Here’s one example of how sedimentary rock is formed: A river car ...
... sand, mud, and pieces of rock or shell. Sediments are geologic travelers. Wind, water, and ice move the sediment over the surface of the Earth. When sediment finally clumps together and then slowly hardens, sedimentary rock is formed. Here’s one example of how sedimentary rock is formed: A river car ...
What type of rock?
... Some of the rock got so hot that it even melted back into magma and traveled back to the mantle. By this time, Iggy had also melted. When Iggy saw that all of him had melted and was now back together, he was very excited. He just hoped the volcano wouldn’t get sick again. THE END. ...
... Some of the rock got so hot that it even melted back into magma and traveled back to the mantle. By this time, Iggy had also melted. When Iggy saw that all of him had melted and was now back together, he was very excited. He just hoped the volcano wouldn’t get sick again. THE END. ...
GEOS254Lec2
... Sanidine and orthoclase (monoclinic) have 2 different sites for Si and Al. Sanidine has no preference with 25% Al & 75% Si in both. In orthoclase the red site takes 30% Al and the blue only 20% Microcline (triclinic) has four sites. Red dots have 56% Al, blue ...
... Sanidine and orthoclase (monoclinic) have 2 different sites for Si and Al. Sanidine has no preference with 25% Al & 75% Si in both. In orthoclase the red site takes 30% Al and the blue only 20% Microcline (triclinic) has four sites. Red dots have 56% Al, blue ...
Petrology of Ibillo-Mangongo area of Igarra, Edo State
... The contact between the migmatites and metasediments are fault-bounded in most cases. The metasedimentary succession in the Igarra formation consist of; Quartz-biotite-schist, mica-schist, marbles and calc-silicates and metaconglomerates [16]. These shows that the area is within metamorphic terrain. ...
... The contact between the migmatites and metasediments are fault-bounded in most cases. The metasedimentary succession in the Igarra formation consist of; Quartz-biotite-schist, mica-schist, marbles and calc-silicates and metaconglomerates [16]. These shows that the area is within metamorphic terrain. ...
... Write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement in the spaces provided. _________ 1. Each of the following could be a sediment, except a. gravel. b. sand. c. water. d. seashells. _________ 2. Most sedimentary rocks are formed in a. volcanoes. b. the mantle. c. mountains. ...
GY 111 Lecture Note Series Extrusive Igneous Rocks
... Fortunately for use, we have more or less already covered this subject in earlier lectures and the introductory lab lecture for the igneous rocks. The major rock types that is produced when mafic lava is erupted at the surface of the Earth is Basalt. This rock is usually aphanetic or porphyritic in ...
... Fortunately for use, we have more or less already covered this subject in earlier lectures and the introductory lab lecture for the igneous rocks. The major rock types that is produced when mafic lava is erupted at the surface of the Earth is Basalt. This rock is usually aphanetic or porphyritic in ...
No Slide Title
... thick. The base of the CRUST is marked by a sharp increase in density - known as the MOHO DISCONTINUITY - this marks the transition from lower density rocks of the crust to higher density rocks of the mantle. The upper part of the mantle is rigid and solid together with the overlying crust this form ...
... thick. The base of the CRUST is marked by a sharp increase in density - known as the MOHO DISCONTINUITY - this marks the transition from lower density rocks of the crust to higher density rocks of the mantle. The upper part of the mantle is rigid and solid together with the overlying crust this form ...
Portfolio Assessment Sheet - Unit 1 Nature of Science
... of the differences between mass, weight, density & volume and the metric units used to measure them. Compare and contrast the Earth's crust, mantle, and core including temperature, density, and composition. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the earth through different types of ...
... of the differences between mass, weight, density & volume and the metric units used to measure them. Compare and contrast the Earth's crust, mantle, and core including temperature, density, and composition. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the earth through different types of ...
AMAZING sedimentary rock
... How Sedimentary Rock is Formed Strong natural forces like wind, heat, cold, or glaciers wear away into tiny pieces. Rivers and rain wash them away then a million years later those pieces turn into Sedimentary rock. ...
... How Sedimentary Rock is Formed Strong natural forces like wind, heat, cold, or glaciers wear away into tiny pieces. Rivers and rain wash them away then a million years later those pieces turn into Sedimentary rock. ...
Igneous rock

Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ignis meaning fire) is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rock may form with or without crystallization, either below the surface as intrusive (plutonic) rocks or on the surface as extrusive (volcanic) rocks. This magma can be derived from partial melts of pre-existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Over 700 types of igneous rocks have been described, most of them having formed beneath the surface of Earth's crust.