My Answers A mineral is a naturally formed solid It`s inorganic and it
... A mineral is a naturally formed solid It’s inorganic and it isn’t a gas or a liquid It has a crystalline structure which means it’s repeated Minerals are made of one or two types of elements The earth’s crust has about ninety-two of them And my answers are buried under the ground All the answers I h ...
... A mineral is a naturally formed solid It’s inorganic and it isn’t a gas or a liquid It has a crystalline structure which means it’s repeated Minerals are made of one or two types of elements The earth’s crust has about ninety-two of them And my answers are buried under the ground All the answers I h ...
Earth Resources: Minerals
... Other minerals such as halite will have several different faces upon which they will cleave, while some other minerals such as quartz have no cleavage (and yes, geologist are know to make bad, sexist jokes during the discussion of this property). 6. Crystalline shape – This is the geometric pattern ...
... Other minerals such as halite will have several different faces upon which they will cleave, while some other minerals such as quartz have no cleavage (and yes, geologist are know to make bad, sexist jokes during the discussion of this property). 6. Crystalline shape – This is the geometric pattern ...
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS - Home
... Shale is one of the most common sedimentary rocks. It is composed of silt or clay that has been compacted or squeezed together to form a solid rock. Shale is usually found in thin layers. The silt or clay that composes shale is made of very small pieces of weathered rock. The pieces are 1/16 to 1/25 ...
... Shale is one of the most common sedimentary rocks. It is composed of silt or clay that has been compacted or squeezed together to form a solid rock. Shale is usually found in thin layers. The silt or clay that composes shale is made of very small pieces of weathered rock. The pieces are 1/16 to 1/25 ...
Radiometric Dating
... • Forms by particle reactions with Cl-35 and Ca40 in surface materials • Half life 300,000 years ...
... • Forms by particle reactions with Cl-35 and Ca40 in surface materials • Half life 300,000 years ...
What are Sedimentary rocks?
... Compaction the process in which the volume and porosity of a sediment is decreased by the weight of overlying sediments as a result of burial beneath other sediments ...
... Compaction the process in which the volume and porosity of a sediment is decreased by the weight of overlying sediments as a result of burial beneath other sediments ...
- 8Semester
... which are predominantly made up of liquid material igneous rock. Igneous rocks are divided into following three sub-groups Volcanic rocks These are the igneous rocks formed on the surface of the Earth by cooling and crystallisation of lava erupted from volcanoes. Since the lava cools down at v ...
... which are predominantly made up of liquid material igneous rock. Igneous rocks are divided into following three sub-groups Volcanic rocks These are the igneous rocks formed on the surface of the Earth by cooling and crystallisation of lava erupted from volcanoes. Since the lava cools down at v ...
Document
... In the kitchen The fixtures and fittings may include wall tiles, work surfaces and floor tiles. These can be made from both china clay and ball clay, which in turn are made from weathered granite. Some work surfaces and floor tiles are made from polished slate, marble or granite and floors may be ma ...
... In the kitchen The fixtures and fittings may include wall tiles, work surfaces and floor tiles. These can be made from both china clay and ball clay, which in turn are made from weathered granite. Some work surfaces and floor tiles are made from polished slate, marble or granite and floors may be ma ...
1 Minerals - yr11geology
... volcanic rocks) or have cooled and crystallised deep underground (as plutonic or intrusive rocks) 2.3 Be aware that the other main variable in igneous rock type is chemical composition; name an igneous rock type given suitable information (Range: basalt, andesite and rhyolite and their plutonic equi ...
... volcanic rocks) or have cooled and crystallised deep underground (as plutonic or intrusive rocks) 2.3 Be aware that the other main variable in igneous rock type is chemical composition; name an igneous rock type given suitable information (Range: basalt, andesite and rhyolite and their plutonic equi ...
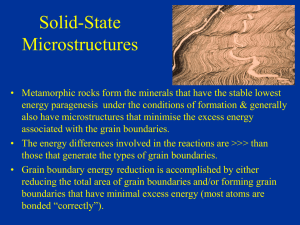
GEOS 254 Sol St Mst
... • The excess energy because of imperfect bonding of atoms in the grain-boundaries is reduced by: • Reducing the total area of grain-boundaries by: – Forming polygonal grains that have low surface area (the solid space filling 3D equivalent of spheres) and – By increasing the grain size that also red ...
... • The excess energy because of imperfect bonding of atoms in the grain-boundaries is reduced by: • Reducing the total area of grain-boundaries by: – Forming polygonal grains that have low surface area (the solid space filling 3D equivalent of spheres) and – By increasing the grain size that also red ...
Chapter 15: Metamorphism, Metamorphic Rocks, and Hydrothermal
... coast, the presence of regional metamorphic rocks in this area is evidence that there was once a convergent plate boundary along the east coast. This is yet another example of how our understanding of the geologic present guides our understanding of the geologic past. Repeat after me…Uniformitariani ...
... coast, the presence of regional metamorphic rocks in this area is evidence that there was once a convergent plate boundary along the east coast. This is yet another example of how our understanding of the geologic present guides our understanding of the geologic past. Repeat after me…Uniformitariani ...
INTRUSION-RELATED DEPOSITS
... (Tungsten), U (uranium), F Fluorine), rare metals, etc.) occur as ore bodies with one or more metals. The composition mainly reflects the chemical composition and less so the tectonic setting of the associated igneous rocks. 1. Granophile Metal Deposits (e.g., Sn, W, F, Mo, U, rare metals including ...
... (Tungsten), U (uranium), F Fluorine), rare metals, etc.) occur as ore bodies with one or more metals. The composition mainly reflects the chemical composition and less so the tectonic setting of the associated igneous rocks. 1. Granophile Metal Deposits (e.g., Sn, W, F, Mo, U, rare metals including ...
Glossary of Terms Related to Prospecting and Exploration
... continental crust is about 35 km in thickness, but can be 50 to 70 km thick under some high mountain ranges. ...
... continental crust is about 35 km in thickness, but can be 50 to 70 km thick under some high mountain ranges. ...
TEACHER RESOURCE GUIDE
... 1 Divide the students into teams of 3 or 4. Give each team a bag of beads and a Classification Chart. Also distribute student worksheets to each student (or team). 2 Each team should begin by choosing only one item from the bag. The team will follow the flow chart beginning at “start here.” Instruct ...
... 1 Divide the students into teams of 3 or 4. Give each team a bag of beads and a Classification Chart. Also distribute student worksheets to each student (or team). 2 Each team should begin by choosing only one item from the bag. The team will follow the flow chart beginning at “start here.” Instruct ...
Chapter 3 Rocks
... The rate of cooling strongly affects the textures of igneous rocks. If magma cools very slowly, few centers of crystal growth develop. Slow cooling also allows charged atoms, or ions, to move large distances within the magma. Slow cooling results in the formation of large crystals. Igneous rocks wit ...
... The rate of cooling strongly affects the textures of igneous rocks. If magma cools very slowly, few centers of crystal growth develop. Slow cooling also allows charged atoms, or ions, to move large distances within the magma. Slow cooling results in the formation of large crystals. Igneous rocks wit ...
Chapter 3 Rocks Section 1 The Rock Cycle Key Concepts What is a
... The rate of cooling strongly affects the textures of igneous rocks. If magma cools very slowly, few centers of crystal growth develop. Slow cooling also allows charged atoms, or ions, to move large distances within the magma. Slow cooling results in the formation of large crystals. Igneous rocks wit ...
... The rate of cooling strongly affects the textures of igneous rocks. If magma cools very slowly, few centers of crystal growth develop. Slow cooling also allows charged atoms, or ions, to move large distances within the magma. Slow cooling results in the formation of large crystals. Igneous rocks wit ...
Sedimentary Rock Lab
... All sedimentary rocks come from sediments. Some sedimentary rocks are called clastic because they are made of rock fragments. These fragments can be as small as microscopic clay particles or as large as boulders. The type of rock that forms is the result of the sorting of sediments that occurs when ...
... All sedimentary rocks come from sediments. Some sedimentary rocks are called clastic because they are made of rock fragments. These fragments can be as small as microscopic clay particles or as large as boulders. The type of rock that forms is the result of the sorting of sediments that occurs when ...
sedimentary rocks
... Describe the major processes involved in the formation of sedimentary rock Distinguish between clastic sedimentary rocks and chemical sedimentary rocks Identify the features that are unique to some sedimentary rocks. ...
... Describe the major processes involved in the formation of sedimentary rock Distinguish between clastic sedimentary rocks and chemical sedimentary rocks Identify the features that are unique to some sedimentary rocks. ...
Ch 2 2 Minerals
... Mineral – naturally occurring, inorganic solid with an orderly crystalline structure and a definite chemical composition Minerals must have the following characteristics: ...
... Mineral – naturally occurring, inorganic solid with an orderly crystalline structure and a definite chemical composition Minerals must have the following characteristics: ...
4.3 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
... There are actually more than 700 different types of igneous rocks. Diorite is extremely hard and is commonly used for art. It was used extensively by ancient civilizations for vases and other decorative art work (Figure 4.11). ...
... There are actually more than 700 different types of igneous rocks. Diorite is extremely hard and is commonly used for art. It was used extensively by ancient civilizations for vases and other decorative art work (Figure 4.11). ...
See Figure 2 by Brasier et al. Nature, Vol. 416 (2002): 76-81.
... The principal method for studying the earliest traces of life in the metamorphosed, oldest (> 3.5 Ga) terrestrial rocks involves determination of isotopic composition of carbon, mainly prevailing as graphite. It is generally believed that this measure can distinguish biogenic graphite from abiogenic ...
... The principal method for studying the earliest traces of life in the metamorphosed, oldest (> 3.5 Ga) terrestrial rocks involves determination of isotopic composition of carbon, mainly prevailing as graphite. It is generally believed that this measure can distinguish biogenic graphite from abiogenic ...
Warm Up 11/1 - Cloudfront.net
... Mineral – naturally occurring, inorganic solid with an orderly crystalline structure and a definite chemical composition Minerals must have the following characteristics: ...
... Mineral – naturally occurring, inorganic solid with an orderly crystalline structure and a definite chemical composition Minerals must have the following characteristics: ...
Sedimentary Rock - Lee County Schools
... are released and deposited in a new area. Sediments are deposited according to size, with larger ...
... are released and deposited in a new area. Sediments are deposited according to size, with larger ...
GEOLOGY - Geological Time
... - Rocks contain naturally occurring, non-living minerals. Most minerals are rare and can be elements (pure substances), or compounds (combinations of pure ...
... - Rocks contain naturally occurring, non-living minerals. Most minerals are rare and can be elements (pure substances), or compounds (combinations of pure ...
Igneous rock

Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ignis meaning fire) is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rock may form with or without crystallization, either below the surface as intrusive (plutonic) rocks or on the surface as extrusive (volcanic) rocks. This magma can be derived from partial melts of pre-existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Over 700 types of igneous rocks have been described, most of them having formed beneath the surface of Earth's crust.