Rock Identification Lab
... Igneous Rocks The igneous rocks in this collection are numbered 2, 3, 6, 8, 15, 16, 18 & 19. This type of rock is formed by the cooling of magma either above or below the Earth’s surface. If the molten material reaches the surface to form a volcano, the erupted rocks are called extrusive (volcanic). ...
... Igneous Rocks The igneous rocks in this collection are numbered 2, 3, 6, 8, 15, 16, 18 & 19. This type of rock is formed by the cooling of magma either above or below the Earth’s surface. If the molten material reaches the surface to form a volcano, the erupted rocks are called extrusive (volcanic). ...
the geology of the moon
... The Apollo astronauts brought back 381.69kg of rock and soil samples referred to as regolith. Regolith is the geological term for loose, solid material that covers the bedrock of a planet type body; in this case the Moon. The original 2,196 samples collected have now been separated into 35,600 sampl ...
... The Apollo astronauts brought back 381.69kg of rock and soil samples referred to as regolith. Regolith is the geological term for loose, solid material that covers the bedrock of a planet type body; in this case the Moon. The original 2,196 samples collected have now been separated into 35,600 sampl ...
What is a Metamorphic Rock?
... How can these metamorphic rocks be used? • 10. Marble- it has an even grain therefore it can be cut into thin slabs or carved into many shapes. It is also easily polished. Lastly, sculptures use it for statues and ...
... How can these metamorphic rocks be used? • 10. Marble- it has an even grain therefore it can be cut into thin slabs or carved into many shapes. It is also easily polished. Lastly, sculptures use it for statues and ...
Document
... Sr substitutes for Ca in Ca-bearing minerals 2. Rb and Sr are fractionated by igneous processes: Rb tends to prefer melt (more “incompatible” than Sr) ...
... Sr substitutes for Ca in Ca-bearing minerals 2. Rb and Sr are fractionated by igneous processes: Rb tends to prefer melt (more “incompatible” than Sr) ...
Section 18.3 - CPO Science
... 18.3 Common minerals and cleavage planes Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth’s crust. Unlike feldspar, quartz lacks cleavage planes. When quartz breaks, it does not split along planes. ...
... 18.3 Common minerals and cleavage planes Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth’s crust. Unlike feldspar, quartz lacks cleavage planes. When quartz breaks, it does not split along planes. ...
rocks - Earth Science
... and ______________________ form sedimentary rocks. 7. The ______________________ & _____________________ of sediments form sedimentary rocks. 8. __________________________ of rock forms sediments. 9. _______________________ then moves the sediments. 10. Heat and pressure change rocks into __________ ...
... and ______________________ form sedimentary rocks. 7. The ______________________ & _____________________ of sediments form sedimentary rocks. 8. __________________________ of rock forms sediments. 9. _______________________ then moves the sediments. 10. Heat and pressure change rocks into __________ ...
Chapters 4 and 5
... The “Swiss cheese-like” texture of some volcanic rocks is called a _____________________texture. This texture develops in the upper part of the lava flow from expanding _________________________. Some rocks form from particles of volcanic fragments. Sometimes this type of rock forms inside the volca ...
... The “Swiss cheese-like” texture of some volcanic rocks is called a _____________________texture. This texture develops in the upper part of the lava flow from expanding _________________________. Some rocks form from particles of volcanic fragments. Sometimes this type of rock forms inside the volca ...
Minerals, Rocks and Resources Outline
... •Nearly all ___________ are composed of _________ or more _____________ •_________________ classify rocks according to how they were ______________ –_______________ rocks form from _________ when it reaches the surface, ____________ and solidifies –________________________ rocks result from the ____ ...
... •Nearly all ___________ are composed of _________ or more _____________ •_________________ classify rocks according to how they were ______________ –_______________ rocks form from _________ when it reaches the surface, ____________ and solidifies –________________________ rocks result from the ____ ...
09-22-14 Do Now
... 2. Would you pay more for your cellphones if doing so would help victims of the war in Congo? Explain your answer. 3. Has reading this article made you feel any differently about the high-tech products you use? Explain. ...
... 2. Would you pay more for your cellphones if doing so would help victims of the war in Congo? Explain your answer. 3. Has reading this article made you feel any differently about the high-tech products you use? Explain. ...
GY303 Petrology Hand Specimen Identification of Volcanic Rocks
... phenocrysts that formed in the magma before the eruption same as above but also contains a foliation that is produced by compaction of the unit when the pyroclastic deposit is greater than approximately 10 m thick. Pumice clasts are often noticeably flattened into the horizontal plane (i.e. parallel ...
... phenocrysts that formed in the magma before the eruption same as above but also contains a foliation that is produced by compaction of the unit when the pyroclastic deposit is greater than approximately 10 m thick. Pumice clasts are often noticeably flattened into the horizontal plane (i.e. parallel ...
Rocks - Montville.net
... 5.What must the water conditions be like in order for a reef to grow? __It must be warm __________ 6. How do the limestone deposits of coral reefs provide us with evidence about how the Earth’s surface has changed over time? __There must have been an ancient sea or ocean there at some point in the p ...
... 5.What must the water conditions be like in order for a reef to grow? __It must be warm __________ 6. How do the limestone deposits of coral reefs provide us with evidence about how the Earth’s surface has changed over time? __There must have been an ancient sea or ocean there at some point in the p ...
Do now! - MrSimonPorter
... sedimentary rocks. The rocks are under tons of pressure, which causes heat build up, and this causes them to change. ...
... sedimentary rocks. The rocks are under tons of pressure, which causes heat build up, and this causes them to change. ...
Do now! - MrSimonPorter
... sedimentary rocks. The rocks are under tons of pressure, which causes heat build up, and this causes them to change. ...
... sedimentary rocks. The rocks are under tons of pressure, which causes heat build up, and this causes them to change. ...
Mantle Plumes, Hot Spots and Igneous Rocks
... In this part of the laboratory you will be asked to identify a variety of volcanic rocks based on their color and texture and, to a lesser extent, on their composition. The following is a description of the materials you will be asked to identify. Volcanic rocks (whether intrusive or extrusive rocks ...
... In this part of the laboratory you will be asked to identify a variety of volcanic rocks based on their color and texture and, to a lesser extent, on their composition. The following is a description of the materials you will be asked to identify. Volcanic rocks (whether intrusive or extrusive rocks ...
March 17, 2014 - Mrs. Lamkin's Sixth Grade
... 1. What are the three types of rocks? 2.How do geologists classify rocks? 3.Describe igneous rocks. 4.Describe metamorphic rocks. 5.Describe sedimentary rocks. 6.What was your favorite part of ...
... 1. What are the three types of rocks? 2.How do geologists classify rocks? 3.Describe igneous rocks. 4.Describe metamorphic rocks. 5.Describe sedimentary rocks. 6.What was your favorite part of ...
Rocks and Minerals Webquest
... 1. What are the three main types of rocks? Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic 2. How does a sedimentary rock turn into a metamorphic rock? A sedimentary rock turns into a metamorphic rock from heat and pressure. 3. How does an igneous rock turn into a metamorphic rock? A igneous rock turns into a ...
... 1. What are the three main types of rocks? Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic 2. How does a sedimentary rock turn into a metamorphic rock? A sedimentary rock turns into a metamorphic rock from heat and pressure. 3. How does an igneous rock turn into a metamorphic rock? A igneous rock turns into a ...
igneous rock textures
... phenocrysts formed and a second at or near the surface where the matrix grains crystallized. ...
... phenocrysts formed and a second at or near the surface where the matrix grains crystallized. ...
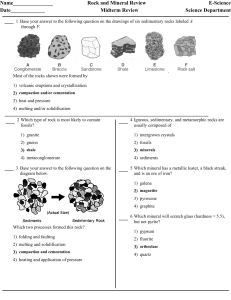
Rocks and Minerals Midterm Rev
... Most of the rocks shown were formed by 1) volcanic eruptions and crystallization 2) compaction and/or cementation 3) heat and pressure 4) melting and/or solidification 2 Which type of rock is most likely to contain fossils? ...
... Most of the rocks shown were formed by 1) volcanic eruptions and crystallization 2) compaction and/or cementation 3) heat and pressure 4) melting and/or solidification 2 Which type of rock is most likely to contain fossils? ...
Ppt_Optl_Garnierite
... • GARNIERITE COMPOSITION 1. Ni-BEARING TALC – WILLEMSEITE ( UP TO 25 WT % Ni) 2. Ni-LIZARDITE – NEPOUITE (UP TO 34 WT% Ni) 3. NI-SEPIOLITE – FALCONDIOTE (UP TO 24 WT% NiZ) LATERIZATION OF ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS • DISSOLUTION & REMOVAL OF Ni & SiO2 TO RESIDUAL CONCENTRATION OF Ni & Fe IN GOETHITE-RICH S ...
... • GARNIERITE COMPOSITION 1. Ni-BEARING TALC – WILLEMSEITE ( UP TO 25 WT % Ni) 2. Ni-LIZARDITE – NEPOUITE (UP TO 34 WT% Ni) 3. NI-SEPIOLITE – FALCONDIOTE (UP TO 24 WT% NiZ) LATERIZATION OF ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS • DISSOLUTION & REMOVAL OF Ni & SiO2 TO RESIDUAL CONCENTRATION OF Ni & Fe IN GOETHITE-RICH S ...
The Rock Cycle
... heat and pressure • igneous or sedimentary rocks can be changed into metamorphic rocks ...
... heat and pressure • igneous or sedimentary rocks can be changed into metamorphic rocks ...
Types of Rocks - Sikkimsprings
... Sedimentary rocks: Rocks formed from the weathering, erosion and deposition & compaction of rock material through agents like wind, water, ice and chemical precipitation. ...
... Sedimentary rocks: Rocks formed from the weathering, erosion and deposition & compaction of rock material through agents like wind, water, ice and chemical precipitation. ...
01 - Cobb Learning
... 4. The heat and pressure at which some metamorphic rocks originally form allow them to sometimes remain ______________________ at pressures and temperatures that would melt other rock. 5. Pressure caused by large movements within the crust sometimes cause the ____________________grains in metamorphi ...
... 4. The heat and pressure at which some metamorphic rocks originally form allow them to sometimes remain ______________________ at pressures and temperatures that would melt other rock. 5. Pressure caused by large movements within the crust sometimes cause the ____________________grains in metamorphi ...
ROCKS and how to identify them
... “born of fire”. In other words, they were once molten and upon cooling, the magma (molten rock) crystallized into solid rock. Igneous rocks may form deep inside the Earth or at the Earth’s surface when a volcano erupts. (*) ...
... “born of fire”. In other words, they were once molten and upon cooling, the magma (molten rock) crystallized into solid rock. Igneous rocks may form deep inside the Earth or at the Earth’s surface when a volcano erupts. (*) ...
ROCKS and how to identify them
... “born of fire”. In other words, they were once molten and upon cooling, the magma (molten rock) crystallized into solid rock. Igneous rocks may form deep inside the Earth or at the Earth’s surface when a volcano erupts. (*) ...
... “born of fire”. In other words, they were once molten and upon cooling, the magma (molten rock) crystallized into solid rock. Igneous rocks may form deep inside the Earth or at the Earth’s surface when a volcano erupts. (*) ...
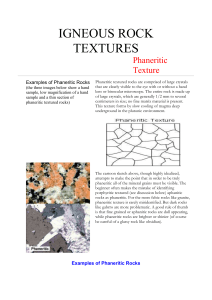
Igneous rock

Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ignis meaning fire) is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rock may form with or without crystallization, either below the surface as intrusive (plutonic) rocks or on the surface as extrusive (volcanic) rocks. This magma can be derived from partial melts of pre-existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Over 700 types of igneous rocks have been described, most of them having formed beneath the surface of Earth's crust.