Chapter 5 Igneous Rocks
... • Bowen’s Reaction Serious – process that demonstrate as magma cools and crystallizes minerals form in predictable patterns • 2 main patterns / branches of crystallization: – Right – continuous, gradual change of mineral compositions in feldspar group – Left – abrupt change of mineral type in iron ...
... • Bowen’s Reaction Serious – process that demonstrate as magma cools and crystallizes minerals form in predictable patterns • 2 main patterns / branches of crystallization: – Right – continuous, gradual change of mineral compositions in feldspar group – Left – abrupt change of mineral type in iron ...
2. Chemical Weathering
... Weathering- the process that breaks down rocks into smaller fragments- resulting in soil. Rates of weathering are affected by: 1. Surface area-when more is exposed, more weathering occurs. ...
... Weathering- the process that breaks down rocks into smaller fragments- resulting in soil. Rates of weathering are affected by: 1. Surface area-when more is exposed, more weathering occurs. ...
Hello Here are the instructions to complete your third blizzard bag
... and appearance of igneous rock depends greatly on how it was formed. Examples of igneous rock include granite, basalt, pumice, and obsidian. ...
... and appearance of igneous rock depends greatly on how it was formed. Examples of igneous rock include granite, basalt, pumice, and obsidian. ...
THE ROCK CYCLE
... As a frothy, igneous rock (pumice), my life began in a volcano where things were pretty hot! After I cooled off and hardened, I thought that the heat wave was over, but after years of… ...
... As a frothy, igneous rock (pumice), my life began in a volcano where things were pretty hot! After I cooled off and hardened, I thought that the heat wave was over, but after years of… ...
1. Read the nonfiction text on the rock cycle 2
... and appearance of igneous rock depends greatly on how it was formed. Examples of igneous rock include granite, basalt, pumice, and obsidian. ...
... and appearance of igneous rock depends greatly on how it was formed. Examples of igneous rock include granite, basalt, pumice, and obsidian. ...
Rock ID handout
... pyroxenes, olivine. Color is dark gray, black or blackish-greenish. • Mafic and Plutonic = peridotite, gabbro • Mafic and volcanic = basalt • Felsic and Plutonic = granite (granodiorite, monzonite, tonalite) • Felsic and volcanic = rhyolite, dacite B. Sedimentary rocks are composed of some combinati ...
... pyroxenes, olivine. Color is dark gray, black or blackish-greenish. • Mafic and Plutonic = peridotite, gabbro • Mafic and volcanic = basalt • Felsic and Plutonic = granite (granodiorite, monzonite, tonalite) • Felsic and volcanic = rhyolite, dacite B. Sedimentary rocks are composed of some combinati ...
Rocks and Culture
... • Igneous rocks are: “plutonic” or “volcanic” based on grain size. In plutonic rocks, all grains are in the visible size range. In volcanics the smallest grains cannot be seen without magnification. The rock on the right had to be magnified for you to be able to see the small grains. ...
... • Igneous rocks are: “plutonic” or “volcanic” based on grain size. In plutonic rocks, all grains are in the visible size range. In volcanics the smallest grains cannot be seen without magnification. The rock on the right had to be magnified for you to be able to see the small grains. ...
ExamView - Untitled.tst - Newark Catholic High School
... 2. Minerals can form when differences in density force magma upward into warmer layers of Earth’s interior. _________________________ ...
... 2. Minerals can form when differences in density force magma upward into warmer layers of Earth’s interior. _________________________ ...
Igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks.
... of molten material within the crust or at the Earth’s surface. Sedimentary Rocks: all rocks formed by deposition and consolidation of mineral grains and those formed from precipitation of minerals from solution in water. The grains and solutions derived from the breakdown of pre-existing rocks at th ...
... of molten material within the crust or at the Earth’s surface. Sedimentary Rocks: all rocks formed by deposition and consolidation of mineral grains and those formed from precipitation of minerals from solution in water. The grains and solutions derived from the breakdown of pre-existing rocks at th ...
Science Study Guide
... Science Study Guide Rocks and Minerals 1. The way a mineral shines is called its luster. 2. A solid material made up of one or more minerals is rock. 3. A mineral’s tendency to split along flat surfaces is cleavage. 4. Rock that forms when existing rock is changed by heat and pressure beneath Earth’ ...
... Science Study Guide Rocks and Minerals 1. The way a mineral shines is called its luster. 2. A solid material made up of one or more minerals is rock. 3. A mineral’s tendency to split along flat surfaces is cleavage. 4. Rock that forms when existing rock is changed by heat and pressure beneath Earth’ ...
Glossary - Lunar and Planetary Institute
... Magmatic dgferentiarion-The production of rocks of differing chemical composition during cooling and crystallization of a silicate melt or magma by processes such as removal of early formed mineral phases. Mascon-Regions on the Moon of excess mass concentrations per unit area identified by positive ...
... Magmatic dgferentiarion-The production of rocks of differing chemical composition during cooling and crystallization of a silicate melt or magma by processes such as removal of early formed mineral phases. Mascon-Regions on the Moon of excess mass concentrations per unit area identified by positive ...
Geology
... indicates that a Flash file has been embedded into the PowerPoint slide. These files are ...
... indicates that a Flash file has been embedded into the PowerPoint slide. These files are ...
Learning Series: Alabama`s Rocks and Minerals – The “Super Sites”
... Rock and Mineral Collecting Sites In addition to being useful, many of the minerals discussed above are of interest to collectors. Alabama is home to a variety of gemstones and other specimen-quality minerals that are sought after just for their appearance and characteristics. The diverse geologic ...
... Rock and Mineral Collecting Sites In addition to being useful, many of the minerals discussed above are of interest to collectors. Alabama is home to a variety of gemstones and other specimen-quality minerals that are sought after just for their appearance and characteristics. The diverse geologic ...
Reading Science!
... slowly worn away by erosion. But no matter the age of the rock, they were all formed in some way. ...
... slowly worn away by erosion. But no matter the age of the rock, they were all formed in some way. ...
Rock Cycle - Ms. Banjavcic`s Science
... removed by erosion. – These take a long time to cool which produces mineral grains that are large enough to see with an unaided eye. • Extrusive igneous rocks – rocks that are formed as lava cools ON the surface of the Earth. – Lava cools quickly once it reaches the surface. The quick cooling rate k ...
... removed by erosion. – These take a long time to cool which produces mineral grains that are large enough to see with an unaided eye. • Extrusive igneous rocks – rocks that are formed as lava cools ON the surface of the Earth. – Lava cools quickly once it reaches the surface. The quick cooling rate k ...
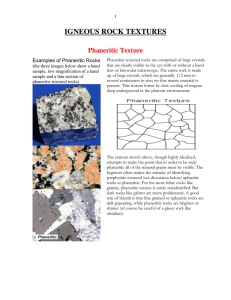
Igneous Rock Textures
... phenocrysts formed and a second at or near the surface where the matrix grains crystallized. ...
... phenocrysts formed and a second at or near the surface where the matrix grains crystallized. ...
Derby Notes IE 5.1
... 2. Sedimentary rocks (section 5.3 page 152) When layers of debris build up, are compressed and squeezed over time ...
... 2. Sedimentary rocks (section 5.3 page 152) When layers of debris build up, are compressed and squeezed over time ...
Types of Rock and Their Formation
... Metamorphic Rock Identification: • Hard rocks • Foliated bands of fused minerals ...
... Metamorphic Rock Identification: • Hard rocks • Foliated bands of fused minerals ...
UNIT 11 Igneous Activity (Chapter 4) Study Guide
... - Convergent Zone Minerals and Magmas - Quartz and orthoclase (which are silicic or felsic minerals rich in silica) are directly associated with areas of continental crust and are available for melting. - Sand and ooze (silicic or felsic minerals of quartz and orthoclase) are often found on top of s ...
... - Convergent Zone Minerals and Magmas - Quartz and orthoclase (which are silicic or felsic minerals rich in silica) are directly associated with areas of continental crust and are available for melting. - Sand and ooze (silicic or felsic minerals of quartz and orthoclase) are often found on top of s ...
Metamorphic Rocks - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... -There are three kinds of planar texture found in foliated rocks: 1) Slaty texture - the rock splits easily into flat, parallel planes, along invisible boundaries between mineral grains or crystals. 2) Schistose texture – the rock splits along visible, parallel planes made of needle-shaped mineral g ...
... -There are three kinds of planar texture found in foliated rocks: 1) Slaty texture - the rock splits easily into flat, parallel planes, along invisible boundaries between mineral grains or crystals. 2) Schistose texture – the rock splits along visible, parallel planes made of needle-shaped mineral g ...
Reviewing Minerals
... 16. Obsidian on the other hand has a _______________ texture whish indicates its cooling was _______________. 17. How does the density of pumice compare to water? _______________ 18. Light colored igneous rocks are rich in _______________ and _______________. 19. Give an example of a light colored ...
... 16. Obsidian on the other hand has a _______________ texture whish indicates its cooling was _______________. 17. How does the density of pumice compare to water? _______________ 18. Light colored igneous rocks are rich in _______________ and _______________. 19. Give an example of a light colored ...
Rock Identification Lab
... Igneous Rocks The igneous rocks in this collection are numbered 2, 3, 6, 8, 15, 16, 18 & 19. This type of rock is formed by the cooling of magma either above or below the Earth’s surface. If the molten material reaches the surface to form a volcano, the erupted rocks are called extrusive (volcanic). ...
... Igneous Rocks The igneous rocks in this collection are numbered 2, 3, 6, 8, 15, 16, 18 & 19. This type of rock is formed by the cooling of magma either above or below the Earth’s surface. If the molten material reaches the surface to form a volcano, the erupted rocks are called extrusive (volcanic). ...
Igneous rock

Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ignis meaning fire) is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rock may form with or without crystallization, either below the surface as intrusive (plutonic) rocks or on the surface as extrusive (volcanic) rocks. This magma can be derived from partial melts of pre-existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Over 700 types of igneous rocks have been described, most of them having formed beneath the surface of Earth's crust.