Module 4 Test Review
... Module 4 Test Review 1. What causes volcanoes? 2. Where do most volcanoes occur globally and why? 3. Describe one type of volcanic formation. 4. Describe some mineral tests and characteristics you can use to identify an unknown mineral. 5. How are minerals different from rocks? 6. What is the relati ...
... Module 4 Test Review 1. What causes volcanoes? 2. Where do most volcanoes occur globally and why? 3. Describe one type of volcanic formation. 4. Describe some mineral tests and characteristics you can use to identify an unknown mineral. 5. How are minerals different from rocks? 6. What is the relati ...
Metamorphic Rocks -- Rocks that Change
... "Metamorphic" comes from a Greek word that means "change of form." Metamorphic rocks can be formed from other metamorphic rocks. They can form from sedimentary and igneous rocks, too. ...
... "Metamorphic" comes from a Greek word that means "change of form." Metamorphic rocks can be formed from other metamorphic rocks. They can form from sedimentary and igneous rocks, too. ...
ASSIGNMENT – JANUARY 3RD – READ AND ANSWER
... From where does the word "Metamorphic" come from? What is another name for igneous rock? What makes igneous rocks? AND How does igneous rock form below ground? Explain the different uses for igneous rocks. How do we use minerals every day? ...
... From where does the word "Metamorphic" come from? What is another name for igneous rock? What makes igneous rocks? AND How does igneous rock form below ground? Explain the different uses for igneous rocks. How do we use minerals every day? ...
Worksheet
... When a candle burns, a runny wax is formed that trickles down its side and solidifies. Igneous rocks are formed in a similar way. The rocks solidify from a mass of molten rock, such as when a lava flow cools and hardens. Because of the heat needed to form igneous rocks, they are sometimes called “ro ...
... When a candle burns, a runny wax is formed that trickles down its side and solidifies. Igneous rocks are formed in a similar way. The rocks solidify from a mass of molten rock, such as when a lava flow cools and hardens. Because of the heat needed to form igneous rocks, they are sometimes called “ro ...
Igneous Rock
... Link to the extrusive igneous rocks page. Read through the page, and view the igneous rock samples. Link to the intrusive igneous rocks page. Read through the page, and view the igneous rock samples. ...
... Link to the extrusive igneous rocks page. Read through the page, and view the igneous rock samples. Link to the intrusive igneous rocks page. Read through the page, and view the igneous rock samples. ...
Rocks
... coarse-grained. In other rocks, the grains are so small that they can only be seen with a microscope. These rocks are said to be fine-grained. Notice the difference in texture between the finegrained slate and the coarse-grained diorite to the right. ...
... coarse-grained. In other rocks, the grains are so small that they can only be seen with a microscope. These rocks are said to be fine-grained. Notice the difference in texture between the finegrained slate and the coarse-grained diorite to the right. ...
ES083 Rocks Assignment When early geologists looked at rocks
... “quenching.” Intrusive, or plutonic igneous rocks are those igneous rocks that finish cooling within the crust (i.e. below Earth’s surface) and have crystal grains that are clearly visible to the naked eye. Extrusive, or volcanic rocks finish cooling at, or on the earth’s surface. The smallest miner ...
... “quenching.” Intrusive, or plutonic igneous rocks are those igneous rocks that finish cooling within the crust (i.e. below Earth’s surface) and have crystal grains that are clearly visible to the naked eye. Extrusive, or volcanic rocks finish cooling at, or on the earth’s surface. The smallest miner ...
Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks
... created oceanic crust from ultramafic mantle rocks. In turn, the mafic oceanic crust created felsic continental crust from partial melting of hydrated basalt. Continental crust is less than 1% of earth’s mass, so there isn’t a lot of felsic material in the earth. Most has risen to the crust. ...
... created oceanic crust from ultramafic mantle rocks. In turn, the mafic oceanic crust created felsic continental crust from partial melting of hydrated basalt. Continental crust is less than 1% of earth’s mass, so there isn’t a lot of felsic material in the earth. Most has risen to the crust. ...
CHAPTER 2CROCKS AND MINERALS C A FIRST LOOK
... 2. Isotopes are atoms of a given element (that is, with the same number of protons) that differ in the number of neutrons in their nuclei. 3. Ions are atoms that have lost or gained electrons. An atom that loses electrons becomes positively charged and is called a cation. An atom that gains electron ...
... 2. Isotopes are atoms of a given element (that is, with the same number of protons) that differ in the number of neutrons in their nuclei. 3. Ions are atoms that have lost or gained electrons. An atom that loses electrons becomes positively charged and is called a cation. An atom that gains electron ...
CHAPTER 2CROCKS AND MINERALS C A FIRST LOOK
... 2. Isotopes are atoms of a given element (that is, with the same number of protons) that differ in the number of neutrons in their nuclei. 3. Ions are atoms that have lost or gained electrons. An atom that loses electrons becomes positively charged and is called a cation. An atom that gains electron ...
... 2. Isotopes are atoms of a given element (that is, with the same number of protons) that differ in the number of neutrons in their nuclei. 3. Ions are atoms that have lost or gained electrons. An atom that loses electrons becomes positively charged and is called a cation. An atom that gains electron ...
Rocks
... This provides a list of Essential Knowledge and Skills that the student must master in order to be successful taking the Virginia SOL Test that will be administered at the end of the course. The student should check off each line item as their knowledge level is achieved. If at ANY TIME the student ...
... This provides a list of Essential Knowledge and Skills that the student must master in order to be successful taking the Virginia SOL Test that will be administered at the end of the course. The student should check off each line item as their knowledge level is achieved. If at ANY TIME the student ...
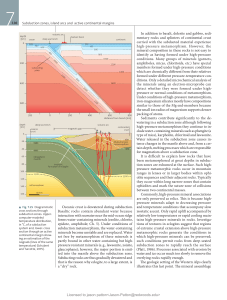
Oceanic crust is dewatered during subduction. Basaltic rocks
... Sediments contribute significantly to the dewatering in a subduction zone although following high-pressure metamorphism they continue to include water-containing minerals such as phengite (a type of mica), karpholite, chloritoid and lawsonite. Water released in the subduction zone causes intense cha ...
... Sediments contribute significantly to the dewatering in a subduction zone although following high-pressure metamorphism they continue to include water-containing minerals such as phengite (a type of mica), karpholite, chloritoid and lawsonite. Water released in the subduction zone causes intense cha ...
Earth Science Midterm Study Guide
... 11. If something is 160 cm long, how many meters is that? 12. If something is 97 cm long, how many mm is that? 13. If something is 42 mm long, how many cm is that? 14. What is the reading on the thermometer to the right? ...
... 11. If something is 160 cm long, how many meters is that? 12. If something is 97 cm long, how many mm is that? 13. If something is 42 mm long, how many cm is that? 14. What is the reading on the thermometer to the right? ...
Ch 5 Sec 3: Sedimentary Rocks Guide for Reading
... solution crystallize. Limestone can form when calcite that is dissolved in lakes, seas, or underground water comes out of solution and forms crystals. They can also form from mineral deposits left when seas or lakes evaporate. Rock salt is made of the mineral halite, which forms by evaporation. ...
... solution crystallize. Limestone can form when calcite that is dissolved in lakes, seas, or underground water comes out of solution and forms crystals. They can also form from mineral deposits left when seas or lakes evaporate. Rock salt is made of the mineral halite, which forms by evaporation. ...
The rock cycle
... rock s to an ocean or water like things . When it gets to the ocean or water like thing it builds up layers witch create the sedimentary rock .The sedimentary rock gets to a certain point to where pressure and heat turn it into a metamorphic rock . The metamorphic rock gets near magma witch turns it ...
... rock s to an ocean or water like things . When it gets to the ocean or water like thing it builds up layers witch create the sedimentary rock .The sedimentary rock gets to a certain point to where pressure and heat turn it into a metamorphic rock . The metamorphic rock gets near magma witch turns it ...
Types of Rocks
... metamorphic rocks. The minerals grains grow and rearrange, however they do not form layers. The grains grow and interlockl like ...
... metamorphic rocks. The minerals grains grow and rearrange, however they do not form layers. The grains grow and interlockl like ...
WHAT IS A ROCK
... metamorphic rocks. The minerals grains grow and rearrange, however they do not form layers. The grains grow and interlockl like ...
... metamorphic rocks. The minerals grains grow and rearrange, however they do not form layers. The grains grow and interlockl like ...
Rocks WebQuest!
... Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form when molten rock cools and becomes solid. Molten rock is called magma when it is below the Earth’s surface and lava when it is above. Igneous rocks are divided into two groups, based on where the rock forms. Igneous rocks that form below the Earth’s surface are calle ...
... Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form when molten rock cools and becomes solid. Molten rock is called magma when it is below the Earth’s surface and lava when it is above. Igneous rocks are divided into two groups, based on where the rock forms. Igneous rocks that form below the Earth’s surface are calle ...
Document
... 28. According to Bowen’s hypothesis, what are the two ways that minerals form? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 29. The rate at which a miner ...
... 28. According to Bowen’s hypothesis, what are the two ways that minerals form? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 29. The rate at which a miner ...
igneous rocks
... What are Sediments? • Sediment are small, solid pieces of rock, mineral grains, or shell fragments • Sediments are formed through the processes of weathering and erosion of rocks exposed at Earth’s surface. • .These rocks are always forming all around you. ...
... What are Sediments? • Sediment are small, solid pieces of rock, mineral grains, or shell fragments • Sediments are formed through the processes of weathering and erosion of rocks exposed at Earth’s surface. • .These rocks are always forming all around you. ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... Metamorphic recrystallization is caused by one or both of 1) elevated temperatures and 2) high pressures 1) Regional Metamorphism is the result of high pressures and elevated temperatures associated with deep burial in an orogenic belt. Platy minerals (micas) and elongate minerals (hornblende) recry ...
... Metamorphic recrystallization is caused by one or both of 1) elevated temperatures and 2) high pressures 1) Regional Metamorphism is the result of high pressures and elevated temperatures associated with deep burial in an orogenic belt. Platy minerals (micas) and elongate minerals (hornblende) recry ...
Metamorphic Rocks Notes
... Metamorphic rocks are formed from ______________ __________ (pre-existing rocks) Parent rocks can be ______________, ________________, or other __________________ rocks. YES, they can be re-metamorphosed and still be metamorphic rocks. ...
... Metamorphic rocks are formed from ______________ __________ (pre-existing rocks) Parent rocks can be ______________, ________________, or other __________________ rocks. YES, they can be re-metamorphosed and still be metamorphic rocks. ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... 3 Ways a Rock Can Melt Temperature – An increase in temperature deep within the Earth’s crust can cause the minerals in a rock to melt. Pressure – The high pressure deep within the Earth forces minerals melt from intense heat and pressure. Composition – Fluids like water and carbon dioxide enter a ...
... 3 Ways a Rock Can Melt Temperature – An increase in temperature deep within the Earth’s crust can cause the minerals in a rock to melt. Pressure – The high pressure deep within the Earth forces minerals melt from intense heat and pressure. Composition – Fluids like water and carbon dioxide enter a ...
Relative Dating Geologic Events
... Earth history is recorded in rocks. Each rock layer and structure that crosses it records an event—such as deposition, faulting, igneous activity, or uplift and erosion. Rocks record climate change, advances and regressions of the sea, tectonic and volcanic events, and prevailing depositional enviro ...
... Earth history is recorded in rocks. Each rock layer and structure that crosses it records an event—such as deposition, faulting, igneous activity, or uplift and erosion. Rocks record climate change, advances and regressions of the sea, tectonic and volcanic events, and prevailing depositional enviro ...
Igneous rock

Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ignis meaning fire) is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rock may form with or without crystallization, either below the surface as intrusive (plutonic) rocks or on the surface as extrusive (volcanic) rocks. This magma can be derived from partial melts of pre-existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Over 700 types of igneous rocks have been described, most of them having formed beneath the surface of Earth's crust.