Unit 3 Rocks Ch. 5 Lecture
... 2. the present physical features of Earth were formed by these same processes, at work over long periods of time. ...
... 2. the present physical features of Earth were formed by these same processes, at work over long periods of time. ...
Practice Questions: Sedimentary Rocks
... Practice Questions: Sedimentary Rocks 1. Which mineral precipitates from oceans and forms rock salt? A) quartz C) halite ...
... Practice Questions: Sedimentary Rocks 1. Which mineral precipitates from oceans and forms rock salt? A) quartz C) halite ...
Book G Ch. 2 L2 NOTES [10/17/2016]
... A.) Differential Weathering p.38 1.) Differential weathering – a process by which softer, less weather resistant rocks wear away & leave harder, more weather resistant rocks behind. a.) telephone poles in the desert are often worn thin B.) The Shape of Rocks p.39 1.) Weathering takes place on the ou ...
... A.) Differential Weathering p.38 1.) Differential weathering – a process by which softer, less weather resistant rocks wear away & leave harder, more weather resistant rocks behind. a.) telephone poles in the desert are often worn thin B.) The Shape of Rocks p.39 1.) Weathering takes place on the ou ...
How are rocks formed?
... 4. Have fossils within them 5. Goes through the process of cooling, melting, and crystallization 6. Goes through the process of heat and pressure 7. Goes through the process of compaction and cementation 8. Consist of Intrusive and extrusive rocks 9. Can change into other rocks, can be foliated and ...
... 4. Have fossils within them 5. Goes through the process of cooling, melting, and crystallization 6. Goes through the process of heat and pressure 7. Goes through the process of compaction and cementation 8. Consist of Intrusive and extrusive rocks 9. Can change into other rocks, can be foliated and ...
What is a Rock? - Davis School District
... that have changed due to intense temperature and pressure “Meta” means “change” and morphosis means “form” in Greek Igneous, sedimentary and other metamorphic rocks can change to become metamorphic rocks ...
... that have changed due to intense temperature and pressure “Meta” means “change” and morphosis means “form” in Greek Igneous, sedimentary and other metamorphic rocks can change to become metamorphic rocks ...
Year 8 Activity Pack sample - UNIT 8HB
... named because the magma has ‘intruded’ into rocks that were already present. Most intrusive igneous rocks have large crystals, but not always! The diagram shows three different ways in which magma can be intruded. Large volumes of igneous rock are called plutons. Sills are thin sheets of igneous roc ...
... named because the magma has ‘intruded’ into rocks that were already present. Most intrusive igneous rocks have large crystals, but not always! The diagram shows three different ways in which magma can be intruded. Large volumes of igneous rock are called plutons. Sills are thin sheets of igneous roc ...
Student Task: Rocks, Rock Hounds, and Rocky Explorations Explore
... 6. Go to the site: http://www.childrensmuseum.org/geomysteries/index2.html Geo Mysteries, and help Rex the Dino Detective solve mysteries about rocks, fossils and minerals. Also find answers to the Frequently Asked Questions. (You don’t need to write anything down for this question. Just have fun!) ...
... 6. Go to the site: http://www.childrensmuseum.org/geomysteries/index2.html Geo Mysteries, and help Rex the Dino Detective solve mysteries about rocks, fossils and minerals. Also find answers to the Frequently Asked Questions. (You don’t need to write anything down for this question. Just have fun!) ...
Earth Sciences 083F Cam`s Notes on the Rocks Assignment I
... dolomite, it’s called dolostone. Coal doesn’t usually have any really distinctive features except that it is usually black, non-crystalline, and looks like a shiny version of charcoal (because it is made of dark-colored organic matter). Igneous Rocks The main aspects of igneous rocks to concentrate ...
... dolomite, it’s called dolostone. Coal doesn’t usually have any really distinctive features except that it is usually black, non-crystalline, and looks like a shiny version of charcoal (because it is made of dark-colored organic matter). Igneous Rocks The main aspects of igneous rocks to concentrate ...
three or more
... Significance Minerals with the same composition but different crystal forms. The product of stress-induced orientation of mineral grains in regional metamorphic rocks. Process primarily responsible for the destruction of original rock textures during metamorphism. Local zone of alteration of country ...
... Significance Minerals with the same composition but different crystal forms. The product of stress-induced orientation of mineral grains in regional metamorphic rocks. Process primarily responsible for the destruction of original rock textures during metamorphism. Local zone of alteration of country ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... Sedimentary Rocks are used for a large variety of resources. Sandstone is a common building material and used to make glass. Limestone and its forms helps make concrete, building materials, chalk and antacids. (That’s why some medicines taste chalky…..they are chalk.) Shale and coal are sources of o ...
... Sedimentary Rocks are used for a large variety of resources. Sandstone is a common building material and used to make glass. Limestone and its forms helps make concrete, building materials, chalk and antacids. (That’s why some medicines taste chalky…..they are chalk.) Shale and coal are sources of o ...
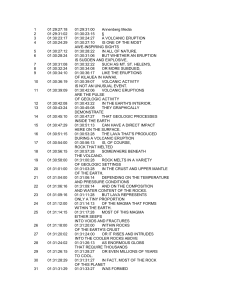
1 01:29:27:18 01:29:31:00 Annenberg Media 2 01:29:31:02 01:30
... IN RESPONSE TO THE IDEA OF WHAT WAS THE ORIGIN-01:41:10:25 WHAT IS THE ORIGIN OF GRANITE? ...
... IN RESPONSE TO THE IDEA OF WHAT WAS THE ORIGIN-01:41:10:25 WHAT IS THE ORIGIN OF GRANITE? ...
Study-Questions2
... 1. How is a mineral different from an element? How is a rock different from a mineral? Put minerals, rocks, and elements in order from simplest to most complex. 2. What are the eight most common or "rock-forming" minerals? Why are they called this? Why are they all silicates? 3. How are igneous rock ...
... 1. How is a mineral different from an element? How is a rock different from a mineral? Put minerals, rocks, and elements in order from simplest to most complex. 2. What are the eight most common or "rock-forming" minerals? Why are they called this? Why are they all silicates? 3. How are igneous rock ...
Rock Identification and stories lab
... Limestone is made of CaCO3, which reacts with dilute HCl acid. Thus, a key test for limestone is to place a drop of acid on it, and, if it fizzes, it's probably limestone. Sometimes you can use vinegar for this test if HCl is not available, since vinegar is also acidic. Limestone is usually a bioche ...
... Limestone is made of CaCO3, which reacts with dilute HCl acid. Thus, a key test for limestone is to place a drop of acid on it, and, if it fizzes, it's probably limestone. Sometimes you can use vinegar for this test if HCl is not available, since vinegar is also acidic. Limestone is usually a bioche ...
The Wonders of Rocks and Minerals
... Answer the following questions to identify minerals that you possess or that are provided by your instructor: (Note: Use the Mineral Identification Key provided for help.) Does the sample have metallic luster? ...
... Answer the following questions to identify minerals that you possess or that are provided by your instructor: (Note: Use the Mineral Identification Key provided for help.) Does the sample have metallic luster? ...
Minerals and Origin of the Moon - Lunar and Planetary Laboratory
... • Probably due to “gardening” of the surface • Highland is made from molten lunar material that crystallized slowly from deep inside • Magma ocean froze over • Radioactive isotopes decayed, warming up interior • Basalt erupted to low areas ...
... • Probably due to “gardening” of the surface • Highland is made from molten lunar material that crystallized slowly from deep inside • Magma ocean froze over • Radioactive isotopes decayed, warming up interior • Basalt erupted to low areas ...
File - 4th Grade Standards
... cemented together, often in layers; igneous: with or without observable crystals that are they look. not in layers or with or without air holes or glasslike; metamorphic: crystals/minerals, often in layers) Classify common rocks found in Utah as sedimentary (sandstone, conglomerate, shale), I can te ...
... cemented together, often in layers; igneous: with or without observable crystals that are they look. not in layers or with or without air holes or glasslike; metamorphic: crystals/minerals, often in layers) Classify common rocks found in Utah as sedimentary (sandstone, conglomerate, shale), I can te ...
1A_RocksEngProperties
... • Al, Si, K in sheets or layers that cannot be seen with the naked eye nor a hand lens. The extremely fine equivalents of micas. • Many form by alteration of Feldspars at the Earth’s surface. This happens quickly and can be seen as light gray to white soft areas on the surface of feldspar crystals o ...
... • Al, Si, K in sheets or layers that cannot be seen with the naked eye nor a hand lens. The extremely fine equivalents of micas. • Many form by alteration of Feldspars at the Earth’s surface. This happens quickly and can be seen as light gray to white soft areas on the surface of feldspar crystals o ...
2B_RocksEngProperties
... • Al, Si, K in sheets or layers that cannot be seen with the naked eye nor a hand lens. The extremely fine equivalents of micas. • Many form by alteration of Feldspars at the Earth’s surface. This happens quickly and can be seen as light gray to white soft areas on the surface of feldspar crystals o ...
... • Al, Si, K in sheets or layers that cannot be seen with the naked eye nor a hand lens. The extremely fine equivalents of micas. • Many form by alteration of Feldspars at the Earth’s surface. This happens quickly and can be seen as light gray to white soft areas on the surface of feldspar crystals o ...
What are minerals?
... What are minerals? • Minerals are naturally occurring inorganic solids formed from an element or compound. ...
... What are minerals? • Minerals are naturally occurring inorganic solids formed from an element or compound. ...
Rock Classification and Cycle
... IGNEOUS ROCKS . Because magma is liquid and usually less dense than surrounding solid rock, it moves upward to cooler regions of the Earth Uplift and exposure of rocks at the Earth's surface destabilizes these mineral structures. The minerals break down into smaller grains which are transported and ...
... IGNEOUS ROCKS . Because magma is liquid and usually less dense than surrounding solid rock, it moves upward to cooler regions of the Earth Uplift and exposure of rocks at the Earth's surface destabilizes these mineral structures. The minerals break down into smaller grains which are transported and ...
START OF STUDY GUIDE
... Rock-an object made up of one or more minerals. We studied 3 types of rocks: 1. Igneous- a rock that was once melted but has cooled and hardened. 2. Sedimentary-rocks that form from material that has settled into layers. The layers are squeezed until they harden into rock. 3. Metamorphic-rocks that ...
... Rock-an object made up of one or more minerals. We studied 3 types of rocks: 1. Igneous- a rock that was once melted but has cooled and hardened. 2. Sedimentary-rocks that form from material that has settled into layers. The layers are squeezed until they harden into rock. 3. Metamorphic-rocks that ...
Rocks
... • Contain substantial dark silicate minerals and calcium-rich plagioclase feldspar • Also referred to as mafic • Common rock is basalt ...
... • Contain substantial dark silicate minerals and calcium-rich plagioclase feldspar • Also referred to as mafic • Common rock is basalt ...
Rock Cookie Lab
... c. How do various types of rocks fit into the rock cycle? d. Why are rocks different from each other? 2. Write a life story of each of the 3 main types of rocks: metamorphic, sedimentary, igneous. Each story needs to be a paragraph, not 3-4 sentences. a. Make sure to identify the forces involved in ...
... c. How do various types of rocks fit into the rock cycle? d. Why are rocks different from each other? 2. Write a life story of each of the 3 main types of rocks: metamorphic, sedimentary, igneous. Each story needs to be a paragraph, not 3-4 sentences. a. Make sure to identify the forces involved in ...
Igneous rock

Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ignis meaning fire) is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rock may form with or without crystallization, either below the surface as intrusive (plutonic) rocks or on the surface as extrusive (volcanic) rocks. This magma can be derived from partial melts of pre-existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Over 700 types of igneous rocks have been described, most of them having formed beneath the surface of Earth's crust.

![Book G Ch. 2 L2 NOTES [10/17/2016]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002315492_1-f96ba6f30f191722da434580a8d2d44e-300x300.png)