Rock Cookie Lab
... c. How do various types of rocks fit into the rock cycle? d. Why are rocks different from each other? 2. Write a life story of each of the 3 main types of rocks: metamorphic, sedimentary, igneous. Each story needs to be a paragraph, not 3-4 sentences. a. Make sure to identify the forces involved in ...
... c. How do various types of rocks fit into the rock cycle? d. Why are rocks different from each other? 2. Write a life story of each of the 3 main types of rocks: metamorphic, sedimentary, igneous. Each story needs to be a paragraph, not 3-4 sentences. a. Make sure to identify the forces involved in ...
Sample Lesson Plan - Desert Outdoor Center
... “Ig” comes from the Latin word for fire. • Name and explain the two types of igneous rocks. • Intrusive rocks (also known as plutonic rocks) solidify (harden) within the Earth’s crust and only appear at the surface after the rocks above them have eroded away. Because these rocks cool very slowly the ...
... “Ig” comes from the Latin word for fire. • Name and explain the two types of igneous rocks. • Intrusive rocks (also known as plutonic rocks) solidify (harden) within the Earth’s crust and only appear at the surface after the rocks above them have eroded away. Because these rocks cool very slowly the ...
Directed Reading A (Lesson 4-4) Section: Metamorphic Rock
... b. forms only in sedimentary rock c. forms only at certain temperatures d. forms only in metamorphic rocks _____ 11. Which of the following minerals is an example of an index mineral? a. calcite b. quartz c. staurolite d. hematite _____ 12. Which of the following is an example of a mineral that indi ...
... b. forms only in sedimentary rock c. forms only at certain temperatures d. forms only in metamorphic rocks _____ 11. Which of the following minerals is an example of an index mineral? a. calcite b. quartz c. staurolite d. hematite _____ 12. Which of the following is an example of a mineral that indi ...
igneous rocks
... What are Sediments? • Sediment are small, solid pieces of rock, mineral grains, or shell fragments • Sediments are formed through the processes of weathering and erosion of rocks exposed at Earth’s surface. • .These rocks are always forming all around you. ...
... What are Sediments? • Sediment are small, solid pieces of rock, mineral grains, or shell fragments • Sediments are formed through the processes of weathering and erosion of rocks exposed at Earth’s surface. • .These rocks are always forming all around you. ...
Rock Classification Notes Teacher
... Objectives: Describe and identify different rock textures; use rock textures and other rock characteristics to classify rocks. Scientists classify rocks Geologitsts observe the rock’s color, texture, and determine its mineral composition to classify a rock. This helps a scientist learn the rock’s or ...
... Objectives: Describe and identify different rock textures; use rock textures and other rock characteristics to classify rocks. Scientists classify rocks Geologitsts observe the rock’s color, texture, and determine its mineral composition to classify a rock. This helps a scientist learn the rock’s or ...
Introduction to Geology, Lab 2
... and similar to shale but without laminations Shale – fissile rock composed of layers of claylike, fine-grained sediments Sandstone – a sedimentary rock formed by the consolidation and compaction of sand and held together by a natural cement, such as silica Conglomerate – sedimentary rock, a signific ...
... and similar to shale but without laminations Shale – fissile rock composed of layers of claylike, fine-grained sediments Sandstone – a sedimentary rock formed by the consolidation and compaction of sand and held together by a natural cement, such as silica Conglomerate – sedimentary rock, a signific ...
Minerals Are - Net Start Class
... (magma) cools and hardens inside Earth or on the surface • Some form when a solution evaporates on Earth’s surface – Ex. Halite NaCl ...
... (magma) cools and hardens inside Earth or on the surface • Some form when a solution evaporates on Earth’s surface – Ex. Halite NaCl ...
GEOS 254 Order of crystallisation
... K-feldspar is the last to crystallise from granite but commonly they are very large. For a porphyritic rock the phenocrysts will have formed before any minerals just in the groundmass. ...
... K-feldspar is the last to crystallise from granite but commonly they are very large. For a porphyritic rock the phenocrysts will have formed before any minerals just in the groundmass. ...
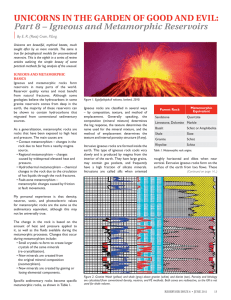
Igneous and Metamorphic Reservoirs
... the rock near the intrusion. Extrusives only heat the rock below them, and may not cause much alteration due to rapid cooling. Extrusives can be buried by later sedimentation, and are difficult to distinguish from intrusives, except by their chemical composition and grain size. The mineral compositi ...
... the rock near the intrusion. Extrusives only heat the rock below them, and may not cause much alteration due to rapid cooling. Extrusives can be buried by later sedimentation, and are difficult to distinguish from intrusives, except by their chemical composition and grain size. The mineral compositi ...
Weathering, erosion, fossils and the rock cycle.
... away top soil on sloped land. Gravity (the force that pulls stuff down) is the force that makes eroded material slide down hill Erosion from the Colorado River formed the Grand Cannyon. ...
... away top soil on sloped land. Gravity (the force that pulls stuff down) is the force that makes eroded material slide down hill Erosion from the Colorado River formed the Grand Cannyon. ...
Solutions - Heritage Collegiate
... 2. About seventy-five percent of all rock outcrops on the continents are sedimentary. 3. Igneous rocks are the rock type most likely to contain fossils. 4. Igneous rock, when subjected to heat and pressure far below Earth's surface, will change to sedimentary rock. ...
... 2. About seventy-five percent of all rock outcrops on the continents are sedimentary. 3. Igneous rocks are the rock type most likely to contain fossils. 4. Igneous rock, when subjected to heat and pressure far below Earth's surface, will change to sedimentary rock. ...
Volcano Review sheet - new for 2016-17
... A. This is an extrusive igneous rock that cooled quickly B. This is an extrusive igneous rock that cooled slowly C. This is an intrusive igneous rock that cooled quickly D. This in an intrusive igneous rock that cooled slowly E. This is a metamorphic rock that cooled quickly AB. This is a metamorphi ...
... A. This is an extrusive igneous rock that cooled quickly B. This is an extrusive igneous rock that cooled slowly C. This is an intrusive igneous rock that cooled quickly D. This in an intrusive igneous rock that cooled slowly E. This is a metamorphic rock that cooled quickly AB. This is a metamorphi ...
Metamorphic Rocks Tutorial Notes
... 1. A metamorphic rock is a rock that has been changed by _____________ and/or_________________ 2. Where does regional metamorphism usually occur? _______________________________________ 3. Where does contact metamorphism usually occur? ________________________________________ 4. What is a parent roc ...
... 1. A metamorphic rock is a rock that has been changed by _____________ and/or_________________ 2. Where does regional metamorphism usually occur? _______________________________________ 3. Where does contact metamorphism usually occur? ________________________________________ 4. What is a parent roc ...
Lab 2. Igneous Rocks and the Gems Produced from
... exotic elements excluded from the main mass of igneous magma, this very-fluid, exotic-element rich “gem soup” forms gem pockets on the outer margin of the larger igneous rock bodies. These very fluid magmas create pegmatites. Figure 1 Igneous rock formation by intrusion into layered sedimentary rock ...
... exotic elements excluded from the main mass of igneous magma, this very-fluid, exotic-element rich “gem soup” forms gem pockets on the outer margin of the larger igneous rock bodies. These very fluid magmas create pegmatites. Figure 1 Igneous rock formation by intrusion into layered sedimentary rock ...
Chapter Three
... made of mineral crystals. Igneous rocks are classified according to their origin, texture, and mineral composition. ...
... made of mineral crystals. Igneous rocks are classified according to their origin, texture, and mineral composition. ...
directed reading metamorphic rock
... b. forms only in sedimentary rock c. forms only at certain temperatures d. forms only in metamorphic rocks _____ 11. Which of the following minerals is an example of an index mineral? a. calcite b. quartz c. staurolite d. hematite _____ 12. Which of the following is an example of a mineral that indi ...
... b. forms only in sedimentary rock c. forms only at certain temperatures d. forms only in metamorphic rocks _____ 11. Which of the following minerals is an example of an index mineral? a. calcite b. quartz c. staurolite d. hematite _____ 12. Which of the following is an example of a mineral that indi ...
Document
... b. forms only in sedimentary rock c. forms only at certain temperatures d. forms only in metamorphic rocks _____ 11. Which of the following minerals is an example of an index mineral? a. calcite b. quartz c. staurolite d. hematite _____ 12. Which of the following is an example of a mineral that indi ...
... b. forms only in sedimentary rock c. forms only at certain temperatures d. forms only in metamorphic rocks _____ 11. Which of the following minerals is an example of an index mineral? a. calcite b. quartz c. staurolite d. hematite _____ 12. Which of the following is an example of a mineral that indi ...
science-3-pet-rock-field-guide-best
... sand held together by silica or calcite. Sandstone is formed in lakes from the sand carried in by rivers. Sandstone is usually grey, brown or beige unless another mineral is present. It often forms in layers. Sometimes, ripple marks from the water or wind can be seen on the surface. The lustre of sa ...
... sand held together by silica or calcite. Sandstone is formed in lakes from the sand carried in by rivers. Sandstone is usually grey, brown or beige unless another mineral is present. It often forms in layers. Sometimes, ripple marks from the water or wind can be seen on the surface. The lustre of sa ...
Identifying Rocks and Minerals
... Identifying Rocks and Minerals Background: The material that makes up the solid parts of Earth is known as rock. Based on the processes that form and change the rocks of Earth’s crust, geologists classify rocks into three major types by the way the rocks form. Igneous rock forms when magma (molten r ...
... Identifying Rocks and Minerals Background: The material that makes up the solid parts of Earth is known as rock. Based on the processes that form and change the rocks of Earth’s crust, geologists classify rocks into three major types by the way the rocks form. Igneous rock forms when magma (molten r ...
1 - TECC Science
... (b) Rocks can be broken by weathering when: 1. Water gets into cracks in rocks. 2. The water in the cracks turns to ice and expands. 3. The rocks split into smaller pieces. What else must happen during this part of this weathering process? Tick two boxes. The temperature stays the same. The tempera ...
... (b) Rocks can be broken by weathering when: 1. Water gets into cracks in rocks. 2. The water in the cracks turns to ice and expands. 3. The rocks split into smaller pieces. What else must happen during this part of this weathering process? Tick two boxes. The temperature stays the same. The tempera ...
Homework-6.1-6.2
... 10. The weight of overlying sediments forces the sediment grains closer together, causing physical change is called ________________________________________. 11. The process by which mineral growth binds grains together in solid rock is _________________________________________. 12. The best known f ...
... 10. The weight of overlying sediments forces the sediment grains closer together, causing physical change is called ________________________________________. 11. The process by which mineral growth binds grains together in solid rock is _________________________________________. 12. The best known f ...
Mineralogy, Geochemistry, and Chronology of the Caballo and
... K2O. The secondary feldspars are significantly less fractured than primary igneous feldspar, display no perthititic textures, and contain micron size hematite inclusions. The most reddened episyenites are composed largely of interlocked K-feldspar crystals which display no igneous texture. Investiga ...
... K2O. The secondary feldspars are significantly less fractured than primary igneous feldspar, display no perthititic textures, and contain micron size hematite inclusions. The most reddened episyenites are composed largely of interlocked K-feldspar crystals which display no igneous texture. Investiga ...
Some Geology Basics
... Igneous rocks develop as molten magma cools and crystallizes, either deep underground (plutonic or intrusive igneous) or at the Earth’s surface (volcanic or extrusive). Plutonic rocks can be identified by their coarsely crystalline appearance, since crystals can grow large enough to see during the l ...
... Igneous rocks develop as molten magma cools and crystallizes, either deep underground (plutonic or intrusive igneous) or at the Earth’s surface (volcanic or extrusive). Plutonic rocks can be identified by their coarsely crystalline appearance, since crystals can grow large enough to see during the l ...
Types of Rock
... Erosion – Small pieces of broken rocks are carried away from their source by water or wind. Deposition – Small pieces of broken rocks are deposited as loosely packed sediments. Compaction – Sediments are squeezed together under great pressure. Cementation – Sediments are glued together as dissolved ...
... Erosion – Small pieces of broken rocks are carried away from their source by water or wind. Deposition – Small pieces of broken rocks are deposited as loosely packed sediments. Compaction – Sediments are squeezed together under great pressure. Cementation – Sediments are glued together as dissolved ...
Igneous rock

Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ignis meaning fire) is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rock may form with or without crystallization, either below the surface as intrusive (plutonic) rocks or on the surface as extrusive (volcanic) rocks. This magma can be derived from partial melts of pre-existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Over 700 types of igneous rocks have been described, most of them having formed beneath the surface of Earth's crust.