Unit 5.4 PowerPoint File
... Minerals may also change in size or shape, or they may separate into parallel bands that give the rock a layered appearance. Hot fluids may circulate through the rock and change the mineral composition of the rock by dissolving some materials and by ...
... Minerals may also change in size or shape, or they may separate into parallel bands that give the rock a layered appearance. Hot fluids may circulate through the rock and change the mineral composition of the rock by dissolving some materials and by ...
Final Exam, Fall, 2015
... 14. Felsic magmas typically produce plutonic rocks, rather than volcanic ones, because a. felsic magmas are formed deep in the mantle, and it's too far to the surface. b. felsic magmas only form in the crust, not in volcanoes. c. felsic magmas are much more viscous than mafic magmas. d. felsic magma ...
... 14. Felsic magmas typically produce plutonic rocks, rather than volcanic ones, because a. felsic magmas are formed deep in the mantle, and it's too far to the surface. b. felsic magmas only form in the crust, not in volcanoes. c. felsic magmas are much more viscous than mafic magmas. d. felsic magma ...
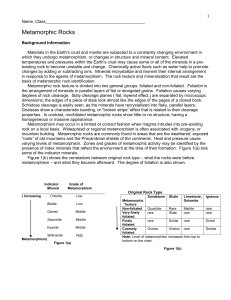
Metamorphic Rock
... One way rock can undergo metamorphism is by being heated by nearby magma. When magma moves through the crust, the magma heats the surrounding rock and changes it. Some minerals in the surrounding rock are changed into other minerals by this increase in temperature. The greatest change takes place wh ...
... One way rock can undergo metamorphism is by being heated by nearby magma. When magma moves through the crust, the magma heats the surrounding rock and changes it. Some minerals in the surrounding rock are changed into other minerals by this increase in temperature. The greatest change takes place wh ...
Book G Ch. 2 L2 NOTES [10/17/2016]
... A.) Differential Weathering p.38 1.) Differential weathering – a process by which softer, less weather resistant rocks wear away & leave harder, more weather resistant rocks behind. a.) telephone poles in the desert are often worn thin B.) The Shape of Rocks p.39 1.) Weathering takes place on the ou ...
... A.) Differential Weathering p.38 1.) Differential weathering – a process by which softer, less weather resistant rocks wear away & leave harder, more weather resistant rocks behind. a.) telephone poles in the desert are often worn thin B.) The Shape of Rocks p.39 1.) Weathering takes place on the ou ...
Sedimentary Rocks Lecture-HO
... Lithification involves two processes 1. Compaction - The volume of a deposit of sediment decreases as the weight of overlying sediment causes a reduction in pore space (open space) as particles pack more closely together. Compaction alone is sufficient for lithification of mud into shale. ...
... Lithification involves two processes 1. Compaction - The volume of a deposit of sediment decreases as the weight of overlying sediment causes a reduction in pore space (open space) as particles pack more closely together. Compaction alone is sufficient for lithification of mud into shale. ...
Rocks
... Sedimentary rocks get packed together by compaction or cementation Compaction occurs by erosion moves sediments to a new location, where they are deposited, over time sediments get piled up and the layers of sediment push down to form a rock ...
... Sedimentary rocks get packed together by compaction or cementation Compaction occurs by erosion moves sediments to a new location, where they are deposited, over time sediments get piled up and the layers of sediment push down to form a rock ...
The Rock Cycle - Enter Physics Locker
... How are fossils formed? When small rock fragments are transported to the sea, they are deposited (sink) and form a sediment. Dead creatures may become trapped within the sediment. Over millions of years, the pressure of layers above cements the sediment together. This is how sedimentary rocks like ...
... How are fossils formed? When small rock fragments are transported to the sea, they are deposited (sink) and form a sediment. Dead creatures may become trapped within the sediment. Over millions of years, the pressure of layers above cements the sediment together. This is how sedimentary rocks like ...
Geochemistry of fine-grained clastic sedimentary rocks of the
... Supergroup of the Tanzania Craton, is comprised of conglomerates, quartzites, shales, siltstones, red sandstones with rare flagstones and gritstones and is regionally subdivided into four lithostratigraphic units namely the Makobo, Kinenge, Sumuji and Masati Formations. We report geochemical data fo ...
... Supergroup of the Tanzania Craton, is comprised of conglomerates, quartzites, shales, siltstones, red sandstones with rare flagstones and gritstones and is regionally subdivided into four lithostratigraphic units namely the Makobo, Kinenge, Sumuji and Masati Formations. We report geochemical data fo ...
Earth`s Story Through a Rock
... into magma and the cycle continues • Review completed rock cycle for understanding. 2. Read book or view video How to Dig a Hole to the Other Side of the World. ...
... into magma and the cycle continues • Review completed rock cycle for understanding. 2. Read book or view video How to Dig a Hole to the Other Side of the World. ...
Relative Dating of Rock Sequences Rocks Tell Their Stories All that
... This is the "story" for Rock Sequence 2: 1- Submergence followed by Deposition and the Formation of layers 1 and 2 (the sandstone and limestone). 2- Emergence and Erosion of layer 2 (limestone). 3- Submergence followed by Deposition and the Formation of layer 3, (the shale) producing an unconformit ...
... This is the "story" for Rock Sequence 2: 1- Submergence followed by Deposition and the Formation of layers 1 and 2 (the sandstone and limestone). 2- Emergence and Erosion of layer 2 (limestone). 3- Submergence followed by Deposition and the Formation of layer 3, (the shale) producing an unconformit ...
Role of Chaman Transform Boundary Fault in the Deformation of
... thickness based on gravity and magnetic data sets. The seismic reflection data also reveal a similar sedimentary fill. Seismic data reveal that the Eocene carbonates of the Kharan Formation extend in the sub surface across the entire Kharan Basin. These carbonates are represented by strong acoustic ...
... thickness based on gravity and magnetic data sets. The seismic reflection data also reveal a similar sedimentary fill. Seismic data reveal that the Eocene carbonates of the Kharan Formation extend in the sub surface across the entire Kharan Basin. These carbonates are represented by strong acoustic ...
rock-cycle
... means by which they are located conditions under which they are formed minerals of which they are composed locations in which they are found ...
... means by which they are located conditions under which they are formed minerals of which they are composed locations in which they are found ...
5.2 Sandstones
... B. Potassium feldspars often suggest sources of alkaline plutonic igneous or metamorphic rocks. C. Sodic (Na-) plagioclases often suggest alkaline volcanic rocks. D. Calcic (Ca-) plagioclase often comes from basic volcanic rocks. E. Quartz: (1) Low-grade metamorphic source rocks: high percentage of ...
... B. Potassium feldspars often suggest sources of alkaline plutonic igneous or metamorphic rocks. C. Sodic (Na-) plagioclases often suggest alkaline volcanic rocks. D. Calcic (Ca-) plagioclase often comes from basic volcanic rocks. E. Quartz: (1) Low-grade metamorphic source rocks: high percentage of ...
DE Science Elementary “5
... • Use the Exploration with the whole class so students can discover how to create the three different types of rocks. The exploration allows students the opportunity to try different combinations and get different results. • Use the Reading Passage for students who are independent readers, and allow ...
... • Use the Exploration with the whole class so students can discover how to create the three different types of rocks. The exploration allows students the opportunity to try different combinations and get different results. • Use the Reading Passage for students who are independent readers, and allow ...
Saskatchewan Rocks! - Royal Saskatchewan Museum
... receding and small mammals had developed into huge brontotheres, meat eaters called creodonts, various species of rhinoceros, a pig-like creature called an entelodont, and small dog-sized leaf-eaters called Mesohippus. Mesohippus is an early relative of modern-day horses. Horses evolved in North Ame ...
... receding and small mammals had developed into huge brontotheres, meat eaters called creodonts, various species of rhinoceros, a pig-like creature called an entelodont, and small dog-sized leaf-eaters called Mesohippus. Mesohippus is an early relative of modern-day horses. Horses evolved in North Ame ...
Weathering The process of breaking down of rocks
... Types of Mechanical Weathering Ice Wedging- Water in the cracks of rocks freeze Abrasion- Particles of sand are carried by the wind and water Plant Action – roots from plants grow in the cracks of rocks Release pressure – when pressure is removed from rocks ...
... Types of Mechanical Weathering Ice Wedging- Water in the cracks of rocks freeze Abrasion- Particles of sand are carried by the wind and water Plant Action – roots from plants grow in the cracks of rocks Release pressure – when pressure is removed from rocks ...
Metamorphic Rocks Notes
... to heat and pressure generated by nearby colliding, subducting tectonic plates and the heat from the mantle. This changes preexisting rocks into metamorphic rocks. Contact metamorphism occurs when rocks are directly exposed to the contact areas of subducting tectonic plates (pressure) and the molten ...
... to heat and pressure generated by nearby colliding, subducting tectonic plates and the heat from the mantle. This changes preexisting rocks into metamorphic rocks. Contact metamorphism occurs when rocks are directly exposed to the contact areas of subducting tectonic plates (pressure) and the molten ...
2.9: Nomenclature of sedimentary rocks
... should be printed in roman in scientific texts. More loosely used terms that are often used according to the preference of a specific author will be printed here in roman. Subdivision of sedimentary rocks Sedimentary rocks originate at the earth’s surface, at the bottom of water bodies, and in caves ...
... should be printed in roman in scientific texts. More loosely used terms that are often used according to the preference of a specific author will be printed here in roman. Subdivision of sedimentary rocks Sedimentary rocks originate at the earth’s surface, at the bottom of water bodies, and in caves ...
Introduction to Metamorphic Rock Forms
... Metamorphic rocks are formed from sedimentary or igneous rocks with physical or chemical alterations caused by heat, pressure, or the infiltration of other materials. Metamorphic rocks can be classified as either foliated or nonfoliated; foliation refers to the rock flaking or splitting into thin sl ...
... Metamorphic rocks are formed from sedimentary or igneous rocks with physical or chemical alterations caused by heat, pressure, or the infiltration of other materials. Metamorphic rocks can be classified as either foliated or nonfoliated; foliation refers to the rock flaking or splitting into thin sl ...
Lab - Metamorphic Ro..
... Materials in the Earth’s crust and mantle are subjected to a constantly changing environment in which they undergo metamorphism, or changes in structure and mineral content. Elevated temperatures and pressures within the Earth’s crust may cause some or all of the minerals in a preexisting rock to be ...
... Materials in the Earth’s crust and mantle are subjected to a constantly changing environment in which they undergo metamorphism, or changes in structure and mineral content. Elevated temperatures and pressures within the Earth’s crust may cause some or all of the minerals in a preexisting rock to be ...
Weathering Outline- Standards Teacher Copy
... 5. Think about the following processes: Dissolving a piece of rock salt in a pan of water and grinding a peach pit in a garbage disposal. Which process is more like mechanical weathering and which is like chemical weathering? Chem= Dissolved in pan ...
... 5. Think about the following processes: Dissolving a piece of rock salt in a pan of water and grinding a peach pit in a garbage disposal. Which process is more like mechanical weathering and which is like chemical weathering? Chem= Dissolved in pan ...
Deep within the earth, hot, molten material called magma is formed
... compression by the weight of later deposits. Chemical changes may also take place such as cementation, when water from the ground seeps through sand, depositing minerals between the grains and forming a natural cement. The cemented particles become Sedimentary rocks which mostly rock such as if the ...
... compression by the weight of later deposits. Chemical changes may also take place such as cementation, when water from the ground seeps through sand, depositing minerals between the grains and forming a natural cement. The cemented particles become Sedimentary rocks which mostly rock such as if the ...
Derby Notes IE 5.1
... 5.1 Classifying Rocks Target: I can use characteristics to identify rocks. Two characteristics are: 1 Grain: size, shape, pattern (page 146) 2 Texture : smooth, glassy, chalky ...
... 5.1 Classifying Rocks Target: I can use characteristics to identify rocks. Two characteristics are: 1 Grain: size, shape, pattern (page 146) 2 Texture : smooth, glassy, chalky ...
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles (detritus) to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution. Particles that form a sedimentary rock by accumulating are called sediment. Before being deposited, sediment was formed by weathering and erosion in a source area, and then transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice, mass movement or glaciers which are called agents of denudation.The sedimentary rock cover of the continents of the Earth's crust is extensive, but the total contribution of sedimentary rocks is estimated to be only 8% of the total volume of the crust. Sedimentary rocks are only a thin veneer over a crust consisting mainly of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Sedimentary rocks are deposited in layers as strata, forming a structure called bedding. The study of sedimentary rocks and rock strata provides information about the subsurface that is useful for civil engineering, for example in the construction of roads, houses, tunnels, canals or other structures. Sedimentary rocks are also important sources of natural resources like coal, fossil fuels, drinking water or ores.The study of the sequence of sedimentary rock strata is the main source for scientific knowledge about the Earth's history, including palaeogeography, paleoclimatology and the history of life. The scientific discipline that studies the properties and origin of sedimentary rocks is called sedimentology. Sedimentology is part of both geology and physical geography and overlaps partly with other disciplines in the Earth sciences, such as pedology, geomorphology, geochemistry and structural geology.


![Book G Ch. 2 L2 NOTES [10/17/2016]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002315492_1-f96ba6f30f191722da434580a8d2d44e-300x300.png)