Sedimentology Lab Test 2 - Faculty Website Listing
... ___ 35. Sabkha environments and tropical lagoons such as those seen at Coorong, Australia are models for the production of A.limestones B.banded iron formations C.dolomites D.hydrocarbons E.sulfur ___ 36. ? coal is jet-black, with a conchoidal fracture. A.bituminous B.anthracite C.peat D.lignite ___ ...
... ___ 35. Sabkha environments and tropical lagoons such as those seen at Coorong, Australia are models for the production of A.limestones B.banded iron formations C.dolomites D.hydrocarbons E.sulfur ___ 36. ? coal is jet-black, with a conchoidal fracture. A.bituminous B.anthracite C.peat D.lignite ___ ...
metamorphic rock - Mr. Meyer`s Science Page
... • Metamorphic rocks are divided into two categories- foliates and non-foliates. • Foliates are composed of large amounts of micas and chlorites. These minerals have very distinct cleavage. • Foliated metamorphic rocks will split along cleavage lines that are parallel to the minerals that make up the ...
... • Metamorphic rocks are divided into two categories- foliates and non-foliates. • Foliates are composed of large amounts of micas and chlorites. These minerals have very distinct cleavage. • Foliated metamorphic rocks will split along cleavage lines that are parallel to the minerals that make up the ...
Relative Dating : Which Came First?
... break in the geologic record created when rock layers are eroded or when sediment is not deposited for a long period of time. ...
... break in the geologic record created when rock layers are eroded or when sediment is not deposited for a long period of time. ...
Petrology of Ibillo-Mangongo area of Igarra, Edo State
... appears quite similar to sandstone, and the best way to tell the difference is to break both the rocks, while sandstone shatters into many grains, quartzite breaks across the grains. Quartzite forms in two different ways. In the first way, under the high pressures and temperatures of deep burial, sa ...
... appears quite similar to sandstone, and the best way to tell the difference is to break both the rocks, while sandstone shatters into many grains, quartzite breaks across the grains. Quartzite forms in two different ways. In the first way, under the high pressures and temperatures of deep burial, sa ...
view this article in PDF format.
... can still be used as correlative tools. Siliciclastic rocks are desirable because they are more likely to possess sufficient magnetic mineral contents, but successful studies exist from chemical and biochemical sedimentary environments. Fine grain sizes are necessary because only single-domain magne ...
... can still be used as correlative tools. Siliciclastic rocks are desirable because they are more likely to possess sufficient magnetic mineral contents, but successful studies exist from chemical and biochemical sedimentary environments. Fine grain sizes are necessary because only single-domain magne ...
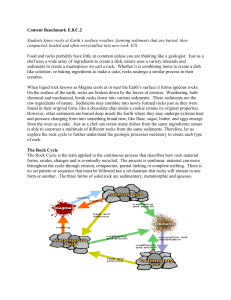
rock cycle.
... • Some bonds are weak. • Cleavage is the tendency of a mineral to cleave, or break, along a flat even surface. • Micas- simplest type of cleavage. • Weak bonds, form thin sheets • Silicates- cleave between the silicon-oxygen structure. • Quartz- no clevage, fractures instead. • Halite- 3 directions ...
... • Some bonds are weak. • Cleavage is the tendency of a mineral to cleave, or break, along a flat even surface. • Micas- simplest type of cleavage. • Weak bonds, form thin sheets • Silicates- cleave between the silicon-oxygen structure. • Quartz- no clevage, fractures instead. • Halite- 3 directions ...
Rock Art - Montclair State University
... 9) As you walk along the trails, point out examples of each of the different types of rocks that were discussed. When appropriate, ask the students to locate the different types of rock. What type of rock makes up the bedrock of the Highlands? Can they find puddingstone on the trail? What mineral ma ...
... 9) As you walk along the trails, point out examples of each of the different types of rocks that were discussed. When appropriate, ask the students to locate the different types of rock. What type of rock makes up the bedrock of the Highlands? Can they find puddingstone on the trail? What mineral ma ...
Student Handout for Density Assignment
... Basalt: Most abundant rock in the shallow oceanic crust Granite: Most abundant rock in the continental crust Magnetite: Mineral composed mainly of iron (Iron is one of the main components of the Earth’s core) Gabbro: Most abundant rock in the deep oceanic crust Olivine: Mineral found in rocks from t ...
... Basalt: Most abundant rock in the shallow oceanic crust Granite: Most abundant rock in the continental crust Magnetite: Mineral composed mainly of iron (Iron is one of the main components of the Earth’s core) Gabbro: Most abundant rock in the deep oceanic crust Olivine: Mineral found in rocks from t ...
weathering and soil baseball
... sheets after temperature change has caused rock to expand and contract) ...
... sheets after temperature change has caused rock to expand and contract) ...
SCI 3410 NAME: Earth Science LAB 2 – ROCK IDENTIFICATION 1
... types, and give two examples (rock name and number) that are present in your kit. ...
... types, and give two examples (rock name and number) that are present in your kit. ...
Click here for printer-friendly version of benchmark
... chemical composition, and on their location of formation. Each row on the chart represents the equivalent of 10% composition, however you should note that each of the rock types listed not only has specific minerals that compose them but actually have a range in the percentage of their mineral compo ...
... chemical composition, and on their location of formation. Each row on the chart represents the equivalent of 10% composition, however you should note that each of the rock types listed not only has specific minerals that compose them but actually have a range in the percentage of their mineral compo ...
Name Date
... 14. Which minerals are found in the igneous rocks gabbro and basalt 1. olivine and basalt 2. olivine and pyroxene 3. pyroxene and orthoclase 4. orthoclase and quartz I5. An igneous rock contains large mineral crystals. The best conclusion to make about this rock is that this rock 1. contains plagioc ...
... 14. Which minerals are found in the igneous rocks gabbro and basalt 1. olivine and basalt 2. olivine and pyroxene 3. pyroxene and orthoclase 4. orthoclase and quartz I5. An igneous rock contains large mineral crystals. The best conclusion to make about this rock is that this rock 1. contains plagioc ...
2_Q3W9__Week_of_March_2-6,_2015_files/Evolution and Fossils
... • Evolution can be seen in the fossil record. – Fossilized species found in older rocks are different from those found in newer rocks ...
... • Evolution can be seen in the fossil record. – Fossilized species found in older rocks are different from those found in newer rocks ...
Part I: Matching
... Changing of one type of rock to another by heat, pressure, and chemical reactions Change in the structure and mineral composition of rock surrounding an igneous intrusion Type of metamorphism that affects rocks over large areas during periods of tectonic activity Sedimentary rock formed from mineral ...
... Changing of one type of rock to another by heat, pressure, and chemical reactions Change in the structure and mineral composition of rock surrounding an igneous intrusion Type of metamorphism that affects rocks over large areas during periods of tectonic activity Sedimentary rock formed from mineral ...
Who Am I? S6E5 Science Rocks
... 46. Glass is formed from the mineral _______________________ but is also in granite. 47. I am small, solid pieces of materials that come from rocks or living things. Who am I? __________________________________ 48. Shells, bones, leaves, stems and other remains of living things are called __________ ...
... 46. Glass is formed from the mineral _______________________ but is also in granite. 47. I am small, solid pieces of materials that come from rocks or living things. Who am I? __________________________________ 48. Shells, bones, leaves, stems and other remains of living things are called __________ ...
Chapter 2: Rocks of the Midwestern US
... A rock is a naturally occurring solid substance composed of one or more minerals. Broadly speaking, there are three types of rock: sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic. The rock cycle describes the many processes that produce rocks, while also illustrating the differences between rock types. One ty ...
... A rock is a naturally occurring solid substance composed of one or more minerals. Broadly speaking, there are three types of rock: sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic. The rock cycle describes the many processes that produce rocks, while also illustrating the differences between rock types. One ty ...
No Slide Title
... a) Quartz sandstone - predominantly quartz grains ("clean sandstone"). Long transportation (quartz survives long transportation because it is relatively hard). Distant from mountainous regions, tectonically stable. Often form at coastlines, in deserts, on higher energy coastal plains and river floo ...
... a) Quartz sandstone - predominantly quartz grains ("clean sandstone"). Long transportation (quartz survives long transportation because it is relatively hard). Distant from mountainous regions, tectonically stable. Often form at coastlines, in deserts, on higher energy coastal plains and river floo ...
Gifford Pinchot State Park—Diabase (Molten Liquid Rock)
... Gifford Pinchot State Park contains examples of the three major rock classes: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary. The most common rock present in the park is the igneous rock diabase, formed below the earth’s surface and originally hot and liquid (molten). The least common rocks in the park are s ...
... Gifford Pinchot State Park contains examples of the three major rock classes: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary. The most common rock present in the park is the igneous rock diabase, formed below the earth’s surface and originally hot and liquid (molten). The least common rocks in the park are s ...
Equilibration in Metamorphic Rocks
... often retain outlines of sedimentary features (e.g. bedding) or igneous features (e.g. pillows). ...
... often retain outlines of sedimentary features (e.g. bedding) or igneous features (e.g. pillows). ...
2-Rocks - WordPress.com
... between the particles. These minerals glue the layers together. Finally, the layers are pressed and cemented together to form rock. ...
... between the particles. These minerals glue the layers together. Finally, the layers are pressed and cemented together to form rock. ...
No Slide Title
... • Sedimentary rocks are almost all stratified • Many igneous rocks – such as a succession of lava flows or ash beds – are stratified and obey the principles of stratigraphy ...
... • Sedimentary rocks are almost all stratified • Many igneous rocks – such as a succession of lava flows or ash beds – are stratified and obey the principles of stratigraphy ...
fossil record
... • separating younger from older rocks, • both of which are parallel to one another ...
... • separating younger from older rocks, • both of which are parallel to one another ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... Progression of Metamorphism Start with a shale and then hit it with heat and pressure! ...
... Progression of Metamorphism Start with a shale and then hit it with heat and pressure! ...
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Rock Cycle
... translucent, or transparent. This property is usually noted for a thin chip of the mineral because if the mineral is strongly colored, it may mask this property. Other Properties of Minerals Specific gravity - measure of each mineral's own unique density and how it compares to the density of water. ...
... translucent, or transparent. This property is usually noted for a thin chip of the mineral because if the mineral is strongly colored, it may mask this property. Other Properties of Minerals Specific gravity - measure of each mineral's own unique density and how it compares to the density of water. ...
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles (detritus) to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution. Particles that form a sedimentary rock by accumulating are called sediment. Before being deposited, sediment was formed by weathering and erosion in a source area, and then transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice, mass movement or glaciers which are called agents of denudation.The sedimentary rock cover of the continents of the Earth's crust is extensive, but the total contribution of sedimentary rocks is estimated to be only 8% of the total volume of the crust. Sedimentary rocks are only a thin veneer over a crust consisting mainly of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Sedimentary rocks are deposited in layers as strata, forming a structure called bedding. The study of sedimentary rocks and rock strata provides information about the subsurface that is useful for civil engineering, for example in the construction of roads, houses, tunnels, canals or other structures. Sedimentary rocks are also important sources of natural resources like coal, fossil fuels, drinking water or ores.The study of the sequence of sedimentary rock strata is the main source for scientific knowledge about the Earth's history, including palaeogeography, paleoclimatology and the history of life. The scientific discipline that studies the properties and origin of sedimentary rocks is called sedimentology. Sedimentology is part of both geology and physical geography and overlaps partly with other disciplines in the Earth sciences, such as pedology, geomorphology, geochemistry and structural geology.