- White Rose Research Online
... High piezoelectricity of (K,Na)NbO3 (KNN) lead-free materials benefits from a polymorphic phase transition (PPT) around room temperature, but its temperature sensitivity has been a bottleneck impeding their applications. We find that good thermal stability can be achieved in CaZrO3-modified KNN lead ...
... High piezoelectricity of (K,Na)NbO3 (KNN) lead-free materials benefits from a polymorphic phase transition (PPT) around room temperature, but its temperature sensitivity has been a bottleneck impeding their applications. We find that good thermal stability can be achieved in CaZrO3-modified KNN lead ...
Accepted version - Queen Mary University of London
... the tetragonal unit cell. However, lattice distortions remained almost constant upon substitution: ct/at 0.71 for the tetragonal phase and ch/ah 2.46 and αr59.87º for the rhombohedral phase. The XRD peaks of BNT-based ceramics near 2θ=40° (Fig. 2) show significant variations after poling. Both ...
... the tetragonal unit cell. However, lattice distortions remained almost constant upon substitution: ct/at 0.71 for the tetragonal phase and ch/ah 2.46 and αr59.87º for the rhombohedral phase. The XRD peaks of BNT-based ceramics near 2θ=40° (Fig. 2) show significant variations after poling. Both ...
2.1 Fundamentals of Magnetism The magnetic
... that the magnetic force within the domain is strong. When a ferromagnetic material is in the unmagnetized state, the domains are nearly randomly organized and the net magnetic field for the part as a whole is zero. When a magnetizing force is applied, the domains become aligned to produce a strong m ...
... that the magnetic force within the domain is strong. When a ferromagnetic material is in the unmagnetized state, the domains are nearly randomly organized and the net magnetic field for the part as a whole is zero. When a magnetizing force is applied, the domains become aligned to produce a strong m ...
The Improved Electromagnetic Equations and
... Hall effect. One sees from the Appendix A that, free volume charges are symbiotic with the electric field Er due to self-Hall-effect in an infinitely long straight circular nonmagnetic wire carrying a steady current J. They are connected by Eqs. (12) and (14), from which we obtain Er = c 2 ρBθ /(ε r ...
... Hall effect. One sees from the Appendix A that, free volume charges are symbiotic with the electric field Er due to self-Hall-effect in an infinitely long straight circular nonmagnetic wire carrying a steady current J. They are connected by Eqs. (12) and (14), from which we obtain Er = c 2 ρBθ /(ε r ...
spin_conference_xie
... When graphene is in the SSC the non-local resistance is very large, because that the spin current can dissipationlessly flow through the super-spin-fluid region. Here we emphasize that the changes of the normal resistance and non-local resistance are sharp, similar as the resistance change when a sa ...
... When graphene is in the SSC the non-local resistance is very large, because that the spin current can dissipationlessly flow through the super-spin-fluid region. Here we emphasize that the changes of the normal resistance and non-local resistance are sharp, similar as the resistance change when a sa ...
How the Most Promising Hoverboards Actually Work I`m not sure
... The Lexus Hoverboard: Yes, it’s true. Lexus made a hoverboard. It really works too. I’m still not sure why they did it. ...
... The Lexus Hoverboard: Yes, it’s true. Lexus made a hoverboard. It really works too. I’m still not sure why they did it. ...
Title The Magnetic Properties of Ni(OH)₂ and β-Co(OH)₂
... 1. At temperatures below 30°K, Ni(OH)2 was antiferromagnetic and the spin axis was directed in parallel to the c-axis. The susceptibility well above the Neel temperature obeyed the Curie-Weiss law with a positive paramagnetic Curie point (35°K). Effective Bohr magneton number was deduced to be 3.2 / ...
... 1. At temperatures below 30°K, Ni(OH)2 was antiferromagnetic and the spin axis was directed in parallel to the c-axis. The susceptibility well above the Neel temperature obeyed the Curie-Weiss law with a positive paramagnetic Curie point (35°K). Effective Bohr magneton number was deduced to be 3.2 / ...
- JPS Journals
... electron materials.3) It was found that in the strongly correlated metallic regime, both quasiparticle features and Hubbard bands are present in the spectra.2) This conclusion was independently drawn from experimental observations by Fujimori.23) The evolution of the spectral function at zero temper ...
... electron materials.3) It was found that in the strongly correlated metallic regime, both quasiparticle features and Hubbard bands are present in the spectra.2) This conclusion was independently drawn from experimental observations by Fujimori.23) The evolution of the spectral function at zero temper ...
AC Losses and Their Thermal Effect in High
... Abstract—In transient operations or fault conditions, hightemperature superconducting (HTS) machines suffer ac losses, which have an influence on the thermal stability of superconducting windings. In this paper, a method to calculate ac losses and their thermal effect in HTS machines is presented. T ...
... Abstract—In transient operations or fault conditions, hightemperature superconducting (HTS) machines suffer ac losses, which have an influence on the thermal stability of superconducting windings. In this paper, a method to calculate ac losses and their thermal effect in HTS machines is presented. T ...
Defects and Disorders in Hafnium Oxide and at Hafnium O id /Sili I t f
... dielectrics because of the higher energy level of O vacancies in the ionic oxide. VO formation may also result in the generation of excess electrons in the conduction band. VO in HfO2 film may be formed through the following two ...
... dielectrics because of the higher energy level of O vacancies in the ionic oxide. VO formation may also result in the generation of excess electrons in the conduction band. VO in HfO2 film may be formed through the following two ...
How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? • Fundamental
... ¾ HCP is one more common structure of metallic crystals ¾ Six atoms form regular hexagon, surrounding one atom in center. Another plane is situated halfway up unit cell (c-axis), with 3 additional atoms situated at interstices of hexagonal (close-packed) planes ¾ Cd, Mg, Zn, Ti have this crystal str ...
... ¾ HCP is one more common structure of metallic crystals ¾ Six atoms form regular hexagon, surrounding one atom in center. Another plane is situated halfway up unit cell (c-axis), with 3 additional atoms situated at interstices of hexagonal (close-packed) planes ¾ Cd, Mg, Zn, Ti have this crystal str ...
Evidence for a large enrichment of interstitial oxygen atoms in the
... It is well known that impurities located in crystalline materials induce changes in many of their properties. For example, mechanical properties of several bcc metals suffer drastic modifications in the presence of hydrogen atoms in interstitial sites since they become brittle.1 The temperature of t ...
... It is well known that impurities located in crystalline materials induce changes in many of their properties. For example, mechanical properties of several bcc metals suffer drastic modifications in the presence of hydrogen atoms in interstitial sites since they become brittle.1 The temperature of t ...
How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? • Fundamental
... atoms as being hard spheres with well-defined radii. In this hard-sphere model, the shortest distance between two like atoms is one diameter of the hard sphere. ...
... atoms as being hard spheres with well-defined radii. In this hard-sphere model, the shortest distance between two like atoms is one diameter of the hard sphere. ...
A Computational and Experimental Study
... To further assess the roles of chemical topology on the elastic anisotropy of 1, we constructed a pseudo-orthorhombic unit cell, designated as 1’ (red outline in Figure 1 B), whereby its x-axis corresponds to the a-axis in the original triclinic cell, while its y’- and z’-axes are oriented almost pe ...
... To further assess the roles of chemical topology on the elastic anisotropy of 1, we constructed a pseudo-orthorhombic unit cell, designated as 1’ (red outline in Figure 1 B), whereby its x-axis corresponds to the a-axis in the original triclinic cell, while its y’- and z’-axes are oriented almost pe ...
Flux penetration into flat superconductors of arbitrary shape
... magnetic field is investigated in detail. The magnetic field distribution at the sample surface is observed by the magneto-optical Faraday effect and calculated from first principles. The investigations are performed on DyBa 2 Cu 3 O 72 d and YBa 2 Cu 3 O 72 d samples which were shaped into a cross ...
... magnetic field is investigated in detail. The magnetic field distribution at the sample surface is observed by the magneto-optical Faraday effect and calculated from first principles. The investigations are performed on DyBa 2 Cu 3 O 72 d and YBa 2 Cu 3 O 72 d samples which were shaped into a cross ...
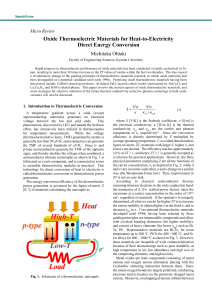
Oxide Thermoelectric Materials for Heat-to
... A number of metal oxides, including well-known layered cuprate high-Tc superconductors, are known to have layered crystal structures. The thermal conductivity of layer-structured materials is expected to be significantly low due to phonon scattering at the interfaces between the layers. Moreover, dr ...
... A number of metal oxides, including well-known layered cuprate high-Tc superconductors, are known to have layered crystal structures. The thermal conductivity of layer-structured materials is expected to be significantly low due to phonon scattering at the interfaces between the layers. Moreover, dr ...
The Science and Engineering of Materials, 4th ed Donald R
... Figure 18.20 The effect of temperature on the carrier concentration of an n-type semiconductor. At low temperatures, the donor or acceptor atoms are not ionized. As temperature increases, the ionization process is complete and the carrier concentration increases to a level that is dictated by the le ...
... Figure 18.20 The effect of temperature on the carrier concentration of an n-type semiconductor. At low temperatures, the donor or acceptor atoms are not ionized. As temperature increases, the ionization process is complete and the carrier concentration increases to a level that is dictated by the le ...
TRANSPORT PHENOMENA IN THE SILVER SULFIDE SINGLE
... investigated. The basic characteristic parameters have been determined: mobility, concentration of the charge carriers, the activation energy of donor levels, effective masses of the charge carriers, temperature factor of the width of the forbidden gap, degree of freedom for electrons, etc. The anal ...
... investigated. The basic characteristic parameters have been determined: mobility, concentration of the charge carriers, the activation energy of donor levels, effective masses of the charge carriers, temperature factor of the width of the forbidden gap, degree of freedom for electrons, etc. The anal ...
Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids
... geometry (e.g., FCC, BCC, HCP). • Crystallographic points, directions and planes are specified in terms of indexing schemes. Crystallographic directions and planes are related to atomic linear densities and planar densities. Chapter 3 - 43 ...
... geometry (e.g., FCC, BCC, HCP). • Crystallographic points, directions and planes are specified in terms of indexing schemes. Crystallographic directions and planes are related to atomic linear densities and planar densities. Chapter 3 - 43 ...
NIFS-886 (pdf file)
... Using present technology, the superconductors would be installed in a thermally insulated multi-layer metal tube with cooling achieved by passing a liquid coolant through a central channel. Such cables have already been developed and are being used reliably for the superconducting bus-line system of ...
... Using present technology, the superconductors would be installed in a thermally insulated multi-layer metal tube with cooling achieved by passing a liquid coolant through a central channel. Such cables have already been developed and are being used reliably for the superconducting bus-line system of ...
High-temperature superconductivity

High-temperature superconductors (abbreviated high-Tc or HTS) are materials that behave as superconductors at unusually high temperatures. The first high-Tc superconductor was discovered in 1986 by IBM researchers Georg Bednorz and K. Alex Müller, who were awarded the 1987 Nobel Prize in Physics ""for their important break-through in the discovery of superconductivity in ceramic materials"".Whereas ""ordinary"" or metallic superconductors usually have transition temperatures (temperatures below which they superconduct) below 30 K (−243.2 °C), and must be cooled using liquid helium in order to achieve superconductivity, HTS have been observed with transition temperatures as high as 138 K (−135 °C), and can be cooled to superconductivity using liquid nitrogen. Until 2008, only certain compounds of copper and oxygen (so-called ""cuprates"") were believed to have HTS properties, and the term high-temperature superconductor was used interchangeably with cuprate superconductor for compounds such as bismuth strontium calcium copper oxide (BSCCO) and yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO). However, several iron-based compounds (the iron pnictides) are now known to be superconducting at high temperatures.For an explanation about Tc (the critical temperature for superconductivity), see Superconductivity § Superconducting phase transition and the second bullet item of BCS theory § Successes of the BCS theory.