Spin-liquids
... ■ Models are not crazy but contrived. It remains a huge challenge to find these phases in the lab – and develop theoretical techniques to look for them in realistic models. ...
... ■ Models are not crazy but contrived. It remains a huge challenge to find these phases in the lab – and develop theoretical techniques to look for them in realistic models. ...
a = b = c
... •Can be prepared by rapidly cooling molten material. •Rapid – minimizes time for atoms to pack into a more thermodynamically favorable crystalline state. •Two sub-states of amorphous solids: Rubbery and Glassy states. Glass transition temperature Tg = temperature above which the solid transforms fro ...
... •Can be prepared by rapidly cooling molten material. •Rapid – minimizes time for atoms to pack into a more thermodynamically favorable crystalline state. •Two sub-states of amorphous solids: Rubbery and Glassy states. Glass transition temperature Tg = temperature above which the solid transforms fro ...
Preparation methods for bulk materials
... 3N2 ⇒ 2R2Fe17N3 can be carried out at 1 bar nitrogen gas and temperatures of about 400500 °C. The absorption of nitrogen atoms takes place once the temperature is high enough to overcome the activation energy for the absorption process. This gas-solid reaction consists of adsorption of the gas molec ...
... 3N2 ⇒ 2R2Fe17N3 can be carried out at 1 bar nitrogen gas and temperatures of about 400500 °C. The absorption of nitrogen atoms takes place once the temperature is high enough to overcome the activation energy for the absorption process. This gas-solid reaction consists of adsorption of the gas molec ...
Slide 1
... volume of an atom, and Vcrystal is the volume occupied by the crystal. It can be proven mathematically that for one-component structures, the most dense arrangement of atoms has an APF of about 0.74. In reality, this number can be higher due to specific intermolecular factors. For multiple-component ...
... volume of an atom, and Vcrystal is the volume occupied by the crystal. It can be proven mathematically that for one-component structures, the most dense arrangement of atoms has an APF of about 0.74. In reality, this number can be higher due to specific intermolecular factors. For multiple-component ...
Open Access proceedings Journal of Physics: Conference series
... peak overlaps the MgB2 (101) peak at 2θ ≈ 42.5. We observed that all samples sintered at CNT composition 5wt% seem to have well developed MgB2 with small amounts of MgO. It can be observed that the XRD patterns of the CNT doped /Cu wire are almost independent of the sintering temperature. The peaks ...
... peak overlaps the MgB2 (101) peak at 2θ ≈ 42.5. We observed that all samples sintered at CNT composition 5wt% seem to have well developed MgB2 with small amounts of MgO. It can be observed that the XRD patterns of the CNT doped /Cu wire are almost independent of the sintering temperature. The peaks ...
dual-valent
... the individual effect of the just mentioned ruling parameters may reveal more insight into the ordering phenomena. ...
... the individual effect of the just mentioned ruling parameters may reveal more insight into the ordering phenomena. ...
SOLID STATE
... Cubic Close Packing ccp:- The spheres are arranged in a way such that the fourth layer comes vertically above the first layer. The sequence may be represented as ABCABCABC....... This type of arrangement is called cubic close packing or ccp arrangement. The A,B,C represent the different layers of sp ...
... Cubic Close Packing ccp:- The spheres are arranged in a way such that the fourth layer comes vertically above the first layer. The sequence may be represented as ABCABCABC....... This type of arrangement is called cubic close packing or ccp arrangement. The A,B,C represent the different layers of sp ...
Carrier density independent scattering rate in
... electron liquids in SrTiO3 in the regime where it scales with Tn (T is the temperature and n ≤ 2) in the cases when it is varied by electrostatic control and chemical doping, respectively. It is shown that the scattering rate is independent of the carrier density. This is contrary to the expectation ...
... electron liquids in SrTiO3 in the regime where it scales with Tn (T is the temperature and n ≤ 2) in the cases when it is varied by electrostatic control and chemical doping, respectively. It is shown that the scattering rate is independent of the carrier density. This is contrary to the expectation ...
Weak ferromagnetism and magnetoelectric coupling in
... the structural distortions. The ferroelectric R3c structure of BiFeO3 is reached from the ideal cubic perovskite structure by freezing in two unstable normal modes: 共i兲 the polar displacements of all the anion and cation sublattices relative to each other, which lead to the spontaneous electric pola ...
... the structural distortions. The ferroelectric R3c structure of BiFeO3 is reached from the ideal cubic perovskite structure by freezing in two unstable normal modes: 共i兲 the polar displacements of all the anion and cation sublattices relative to each other, which lead to the spontaneous electric pola ...
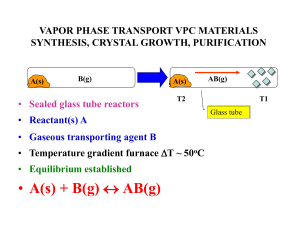
vapor phase transport vpc materials synthesis, crystal growth
... In the effect, there is an exclusion of magnetic flux brought about by “electrical screening currents" that flow at the surface of the superconductor and which generate a magnetic field that exactly cancels (repels) the externally applied field inside the superconductor (Lenz’s law). ...
... In the effect, there is an exclusion of magnetic flux brought about by “electrical screening currents" that flow at the surface of the superconductor and which generate a magnetic field that exactly cancels (repels) the externally applied field inside the superconductor (Lenz’s law). ...
11. Correlated electrons in complex transition metal oxides
... entirely new phenomena appear, possibly with related novel functionalities. These so-called emergent phenomena cannot be anticipated from the local interactions among the electrons and between the electrons and the lattice [1]. This is a typical example of complexity: the laws that describe the beha ...
... entirely new phenomena appear, possibly with related novel functionalities. These so-called emergent phenomena cannot be anticipated from the local interactions among the electrons and between the electrons and the lattice [1]. This is a typical example of complexity: the laws that describe the beha ...
September 6th, 2007
... The domain walls are not infinitely thin, they depend on the material. Materials with large anisotropic constant will tend to have narrow walls since in the wall the spins are largely oriented away from the easy axis (not to convincing) but the anisotropy energy is approximately proportional to the ...
... The domain walls are not infinitely thin, they depend on the material. Materials with large anisotropic constant will tend to have narrow walls since in the wall the spins are largely oriented away from the easy axis (not to convincing) but the anisotropy energy is approximately proportional to the ...
PH6251-Engineering Physics-II - Valliammai Engineering College
... called semiconductors. It is special class of material very small in size and sensitive to heat, light and electricity. ¾ The resistivity lies between 10-4 to 0.5 ohm meters. ¾ At 0K, they behave as insulators. ¾ They empty conduction band and almost filled valence band. ¾ The conductivity of a semi ...
... called semiconductors. It is special class of material very small in size and sensitive to heat, light and electricity. ¾ The resistivity lies between 10-4 to 0.5 ohm meters. ¾ At 0K, they behave as insulators. ¾ They empty conduction band and almost filled valence band. ¾ The conductivity of a semi ...
HSC- Module 9.4 From Ideas to Implementation
... the lattice. 4. identify that resistances in metals is increased by the presence of impurities and scattering of electrons by lattice vibrations. 5. describe the occurrence in superconductors below their critical temperature of a population of electron pairs unaffected by electrical resistance. 6. d ...
... the lattice. 4. identify that resistances in metals is increased by the presence of impurities and scattering of electrons by lattice vibrations. 5. describe the occurrence in superconductors below their critical temperature of a population of electron pairs unaffected by electrical resistance. 6. d ...
Atomic arrangment
... Ionic crystals (> 50% ionic*) *The fraction of bonding that is covalent can be estimated form the equation: Fraction covalent = Exp(-0.25∙ΔE2) ΔE –difference in electronegativity ...
... Ionic crystals (> 50% ionic*) *The fraction of bonding that is covalent can be estimated form the equation: Fraction covalent = Exp(-0.25∙ΔE2) ΔE –difference in electronegativity ...
High-temperature superconductivity

High-temperature superconductors (abbreviated high-Tc or HTS) are materials that behave as superconductors at unusually high temperatures. The first high-Tc superconductor was discovered in 1986 by IBM researchers Georg Bednorz and K. Alex Müller, who were awarded the 1987 Nobel Prize in Physics ""for their important break-through in the discovery of superconductivity in ceramic materials"".Whereas ""ordinary"" or metallic superconductors usually have transition temperatures (temperatures below which they superconduct) below 30 K (−243.2 °C), and must be cooled using liquid helium in order to achieve superconductivity, HTS have been observed with transition temperatures as high as 138 K (−135 °C), and can be cooled to superconductivity using liquid nitrogen. Until 2008, only certain compounds of copper and oxygen (so-called ""cuprates"") were believed to have HTS properties, and the term high-temperature superconductor was used interchangeably with cuprate superconductor for compounds such as bismuth strontium calcium copper oxide (BSCCO) and yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO). However, several iron-based compounds (the iron pnictides) are now known to be superconducting at high temperatures.For an explanation about Tc (the critical temperature for superconductivity), see Superconductivity § Superconducting phase transition and the second bullet item of BCS theory § Successes of the BCS theory.