The Model of Oceanic Crust Expansion
... belt being 66 km, the cycle to form a group of oceanic crusts is approximately 750 thousand years, and the expansion speed of oceanic crust is approximately 8.8 cm per year [1]. The expansion speed of the ocean crust observed in the modern era is approximate to 6 cm to 9 cm per year. At this expansi ...
... belt being 66 km, the cycle to form a group of oceanic crusts is approximately 750 thousand years, and the expansion speed of oceanic crust is approximately 8.8 cm per year [1]. The expansion speed of the ocean crust observed in the modern era is approximate to 6 cm to 9 cm per year. At this expansi ...
Grand Challenges in Geodynamics
... Geodynamics occupies a unique position in the solid Earth Sciences. First and foremost, it is primarily concerned with the dynamical processes that affect the Earth, especially within its interior but also at its surface. Geodynamics is also applied to the interiors and surfaces of other terrestrial ...
... Geodynamics occupies a unique position in the solid Earth Sciences. First and foremost, it is primarily concerned with the dynamical processes that affect the Earth, especially within its interior but also at its surface. Geodynamics is also applied to the interiors and surfaces of other terrestrial ...
The westward drift of the lithosphere
... Assuming an active pull from only that part of a slab between depths of 50 km and 350 km, and considering for example the Marianas slab, the following concerns can be envisaged. The negative buoyancy of an ~300-km-long slab should be able to pull the 10,000-km-long Pacific plate, overcoming the fric ...
... Assuming an active pull from only that part of a slab between depths of 50 km and 350 km, and considering for example the Marianas slab, the following concerns can be envisaged. The negative buoyancy of an ~300-km-long slab should be able to pull the 10,000-km-long Pacific plate, overcoming the fric ...
True Polar Wander: Linking Deep and Shallow
... the same rate (centimeters per year) as continental plate motions (l'vlitrovica et (fl., 2001 a, 2001 b, 200S; Nakada, 2002; Nakiboglu and Lambed, 1980; Sabadini and Peltier, 1(181; Sabadini, 2002; Sabadini et rd, 2002; Vermeersen and Sabadini, 19(9) However, the ~ 10 ky timescale fe)r dampening of ...
... the same rate (centimeters per year) as continental plate motions (l'vlitrovica et (fl., 2001 a, 2001 b, 200S; Nakada, 2002; Nakiboglu and Lambed, 1980; Sabadini and Peltier, 1(181; Sabadini, 2002; Sabadini et rd, 2002; Vermeersen and Sabadini, 19(9) However, the ~ 10 ky timescale fe)r dampening of ...
The Mantle and its Products
... Because it is impossible to obtain samples of the mantle directly, Earth scientists have to resort to a variety of methods to evaluate both its mineralogy and chemical composition. Using chemical data obtained from meteorites (especially the group of meteorites known as “chondrites”) it is possible ...
... Because it is impossible to obtain samples of the mantle directly, Earth scientists have to resort to a variety of methods to evaluate both its mineralogy and chemical composition. Using chemical data obtained from meteorites (especially the group of meteorites known as “chondrites”) it is possible ...
The Westward Drift of the Lithosphere: A rotational drag?
... on the lithosphere that opposes to direction of mantle flow. This force can be exerted either by the lithosphere itself (e.g., slab pull or ridge push), or by an external force such as tidal drag. Slab pull is frequently invoked (e.g., Anderson, 2001; Conrad and Lithgow-Bertelloni, 2003) and is not ...
... on the lithosphere that opposes to direction of mantle flow. This force can be exerted either by the lithosphere itself (e.g., slab pull or ridge push), or by an external force such as tidal drag. Slab pull is frequently invoked (e.g., Anderson, 2001; Conrad and Lithgow-Bertelloni, 2003) and is not ...
Linking collisional and accretionary orogens during Rodinia
... interactions that gave rise to Gondwana and the consequent relocation of subduction zones to the periphery of this supercontinent. The temporal link between external subduction and internal extension suggests that breakup was initiated by a top-down process driven by accretionary tectonics along the ...
... interactions that gave rise to Gondwana and the consequent relocation of subduction zones to the periphery of this supercontinent. The temporal link between external subduction and internal extension suggests that breakup was initiated by a top-down process driven by accretionary tectonics along the ...
A relatively reduced Hadean continental crust and - HAL
... estimated to be, on average, ~2 log units (1: Trail et al., 2011), note that given an error of 50 °C in temperature for example (see below), the calculated fO2 relative to the QFM system would be shifted by ~1.0-1.5 log units; however, the calculated fO2 of the modern continental crust, mostly QFM- ...
... estimated to be, on average, ~2 log units (1: Trail et al., 2011), note that given an error of 50 °C in temperature for example (see below), the calculated fO2 relative to the QFM system would be shifted by ~1.0-1.5 log units; however, the calculated fO2 of the modern continental crust, mostly QFM- ...
A model for the layered upper mantle
... effectively dividing the mantle into two regions, which could then crystallize and evolve separately. These considerations suggest that an early magma ocean responsible for the differentiation of the observable mantle was limited to depths not greatly exceeding 670 kin. A two-layered mantle is the m ...
... effectively dividing the mantle into two regions, which could then crystallize and evolve separately. These considerations suggest that an early magma ocean responsible for the differentiation of the observable mantle was limited to depths not greatly exceeding 670 kin. A two-layered mantle is the m ...
Earth/Space Science Pretest 2014-2015 Multiple Choice Identify the
... a. geosphere only b. hydrosphere and atmosphere only c. atmosphere, hydrosphere, and geosphere d. hydrosphere only ____ 45. What force causes most of the erosion in desert areas? a. wind c. running water b. gravity d. ice ____ 46. Why can a heavy rain shower cause a large amount of erosion in a dese ...
... a. geosphere only b. hydrosphere and atmosphere only c. atmosphere, hydrosphere, and geosphere d. hydrosphere only ____ 45. What force causes most of the erosion in desert areas? a. wind c. running water b. gravity d. ice ____ 46. Why can a heavy rain shower cause a large amount of erosion in a dese ...
Earth Science Ch. 4 Practice Test
... Oceanic crust near the mid-ocean ridge is younger than oceanic crust farther away from the ridge. _________________________ ____ 38. If subduction occurs faster than oceanic crust can be created, an ocean will expand. _________________________ ____ 39. Along a spreading boundary, two plates slip pas ...
... Oceanic crust near the mid-ocean ridge is younger than oceanic crust farther away from the ridge. _________________________ ____ 38. If subduction occurs faster than oceanic crust can be created, an ocean will expand. _________________________ ____ 39. Along a spreading boundary, two plates slip pas ...
PALAEOMAGNETISM, PLATE MOTION AND POLAR WANDER
... magnetic/geographic pole is wandering while the continent remains fixed, or a combination of the two. Because different continents yield different polar wander paths (e.g. the poles determined from Palaeozoic and Mesozoic rocks of Europe are systematically displaced eastward from poles determined fr ...
... magnetic/geographic pole is wandering while the continent remains fixed, or a combination of the two. Because different continents yield different polar wander paths (e.g. the poles determined from Palaeozoic and Mesozoic rocks of Europe are systematically displaced eastward from poles determined fr ...
Dynamic Earth: crustal and mantle heterogeneity
... The dynamic processes within the Earth leave their record in geophysical and geochemical variation about the general stratification with depth. A snapshot of current structure is provided by geophysical evidence, whereas geochemical information provides a perspective over the age of the Earth. The co ...
... The dynamic processes within the Earth leave their record in geophysical and geochemical variation about the general stratification with depth. A snapshot of current structure is provided by geophysical evidence, whereas geochemical information provides a perspective over the age of the Earth. The co ...
The Lithosphere – Asthenosphere System: Nature of the Tectonic
... mantle that are sometimes interpreted as the LAB. These reflectors roughly correlate with the location of discontinuities in radial seismic anisotropy but do not correlate with the location of discontinuities in azimuthal anisotropy. We test these recent interpretations against measurements of cryst ...
... mantle that are sometimes interpreted as the LAB. These reflectors roughly correlate with the location of discontinuities in radial seismic anisotropy but do not correlate with the location of discontinuities in azimuthal anisotropy. We test these recent interpretations against measurements of cryst ...
Three distinct types of hotspots in the Earth`s mantle
... homogeneity, we provisionally exclude Marquesas, which is retained in other analyses (see below and [8]). As far as Macdonald is concerned, it was not included in the short list because of a count of only two. Should an associated track and oceanic plateau be recognized, as suggested by some authors ...
... homogeneity, we provisionally exclude Marquesas, which is retained in other analyses (see below and [8]). As far as Macdonald is concerned, it was not included in the short list because of a count of only two. Should an associated track and oceanic plateau be recognized, as suggested by some authors ...
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors Supercontinent
... form in stagnation regions of the CMB that are commonly below the central regions of major tectonic plates and are controlled by the distribution of subducted slabs, consistent with the statistical analysis of hot spot distribution (Weinstein and Olson, 1989) and seismic tomography imaging (e.g., No ...
... form in stagnation regions of the CMB that are commonly below the central regions of major tectonic plates and are controlled by the distribution of subducted slabs, consistent with the statistical analysis of hot spot distribution (Weinstein and Olson, 1989) and seismic tomography imaging (e.g., No ...
Seismology - Università degli studi di Trieste
... Given the arrival times and amplitudes of several seismic phases on a number of stations, compute distribution of velocity, density and attenuation coefficient with depth, and positions of all discontinuities. This is very difficult and often does not give a unique solution. Instead, a range of solu ...
... Given the arrival times and amplitudes of several seismic phases on a number of stations, compute distribution of velocity, density and attenuation coefficient with depth, and positions of all discontinuities. This is very difficult and often does not give a unique solution. Instead, a range of solu ...
Earth,Tests,Ch12
... B) lower P-wave velocities in the mantle than in the crust C) refraction of P waves crossing the mantle-outer core boundary D) reflection of P waves at the boundary between the inner and outer cores Answer: C Diff: 1 ...
... B) lower P-wave velocities in the mantle than in the crust C) refraction of P waves crossing the mantle-outer core boundary D) reflection of P waves at the boundary between the inner and outer cores Answer: C Diff: 1 ...
CT Science Center
... to the topic of geologic forces. Specifically how do constructive and destructive forces shape the Earth’s surface? We have focused the investigations on how have those constructive and destructive forces shaped the surface of Connecticut? This package also includes engaging investigations that give ...
... to the topic of geologic forces. Specifically how do constructive and destructive forces shape the Earth’s surface? We have focused the investigations on how have those constructive and destructive forces shaped the surface of Connecticut? This package also includes engaging investigations that give ...
Dismantling the Deep Earth: Geochemical
... Large dataset, so filter it to include only samples that best represent the high 3He/4He mantle: A.) Interested in the 87Sr/86Sr (and Nd, Pb) of only the high 3He/4He mantle, so examine only the lavas with the highest 3He/4He from hotspots that have high 3He/4He. B.) High 3He/4He lavas from some env ...
... Large dataset, so filter it to include only samples that best represent the high 3He/4He mantle: A.) Interested in the 87Sr/86Sr (and Nd, Pb) of only the high 3He/4He mantle, so examine only the lavas with the highest 3He/4He from hotspots that have high 3He/4He. B.) High 3He/4He lavas from some env ...
Document
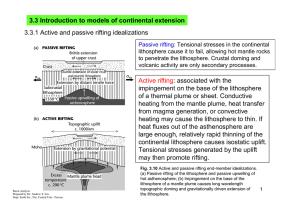
... Magmatic activity: the intrusion of melts at high values of stretching modifies the heat flow history and thermal subsidence at passive margins. Induced mantle convection: the stretching of the lithosphere may induce secondary mantle convection in the region of upwelled asthenosphere. Radiogen ...
... Magmatic activity: the intrusion of melts at high values of stretching modifies the heat flow history and thermal subsidence at passive margins. Induced mantle convection: the stretching of the lithosphere may induce secondary mantle convection in the region of upwelled asthenosphere. Radiogen ...
PC_Earth_Science_Macomb_April08
... part of established scientific consensus. They will use their scientific knowledge to assess the costs, risks, and benefits of technological systems as they make personal choices and participate in public policy decisions. These insights will help them analyze the role science plays in society, tech ...
... part of established scientific consensus. They will use their scientific knowledge to assess the costs, risks, and benefits of technological systems as they make personal choices and participate in public policy decisions. These insights will help them analyze the role science plays in society, tech ...
Plate Tectonics Conceptest
... Melting of rocks produces magma associated with the formation of lithosphere at oceanic ridges and the generation of volcanoes near oceanic ...
... Melting of rocks produces magma associated with the formation of lithosphere at oceanic ridges and the generation of volcanoes near oceanic ...
Earth Science - International Science Center
... 1500 bars[1]) causing profound physical and/or chemical change. The protolith may be sedimentary rock, igneous rock or another older metamorphic rock. Metamorphic rocks make up a large part of the Earth's crust and are classified by texture and by chemical and mineral assemblage (metamorphic facies) ...
... 1500 bars[1]) causing profound physical and/or chemical change. The protolith may be sedimentary rock, igneous rock or another older metamorphic rock. Metamorphic rocks make up a large part of the Earth's crust and are classified by texture and by chemical and mineral assemblage (metamorphic facies) ...
PDF
... to lose 4.2×1013 W of heat: 32 TW is conducted through the surface thermal boundary layer (lithosphere) and about 10 TW may be lost by hydrothermal activity at mid-ocean ridges[27]. Tectonically active planets like Earth lose more heat than they produce and thus progressively cool, but it is also po ...
... to lose 4.2×1013 W of heat: 32 TW is conducted through the surface thermal boundary layer (lithosphere) and about 10 TW may be lost by hydrothermal activity at mid-ocean ridges[27]. Tectonically active planets like Earth lose more heat than they produce and thus progressively cool, but it is also po ...
Spherical Earth

The concept of a spherical Earth dates back to around the 6th century BC, when it was mentioned in ancient Greek philosophy, but remained a matter of philosophical speculation until the 3rd century BC, when Hellenistic astronomy established the spherical shape of the earth as a physical given. The paradigm was gradually adopted throughout the Old World during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. A practical demonstration of Earth's sphericity was achieved by Ferdinand Magellan and Juan Sebastián Elcano's expedition's circumnavigation (1519−1522).The concept of a spherical Earth displaced earlier beliefs in a flat Earth: In early Mesopotamian mythology, the world was portrayed as a flat disk floating in the ocean and surrounded by a spherical sky, and this forms the premise for early world maps like those of Anaximander and Hecataeus of Miletus. Other speculations on the shape of Earth include a seven-layered ziggurat or cosmic mountain, alluded to in the Avesta and ancient Persian writings (see seven climes).The realization that the figure of the Earth is more accurately described as an ellipsoid dates to the 18th century (Maupertuis).In the early 19th century, the flattening of the earth ellipsoid was determined to be of the order of 1/300 (Delambre, Everest). The modern value as determined by the US DoD World Geodetic System since the 1960s is close to 1/298.25.