Support of high elevation in the southern Basin and Range based
... satisfy a variance reduction cutoff above 80% and retain their highest amplitude, the direct P, within one second of the zero time on the deconvolved trace. Direct P sources are selected from epicentral distances of 30 to 90° and yield a dataset where most events are clustered in northern and southw ...
... satisfy a variance reduction cutoff above 80% and retain their highest amplitude, the direct P, within one second of the zero time on the deconvolved trace. Direct P sources are selected from epicentral distances of 30 to 90° and yield a dataset where most events are clustered in northern and southw ...
Geochemistry, Mineralogy and Petrogenesis of El
... Ghor Al-Katar. They occur either as plateau basalts, or as local flows, (e.g., Wadi fills) or as individual volcanic bodies (cones, plugs, sills, and dikes). In spite of the fact that substantial horizontal sinistral displacement of N-S striking the Dead Sea Transform Fault (DST) is accompanied by s ...
... Ghor Al-Katar. They occur either as plateau basalts, or as local flows, (e.g., Wadi fills) or as individual volcanic bodies (cones, plugs, sills, and dikes). In spite of the fact that substantial horizontal sinistral displacement of N-S striking the Dead Sea Transform Fault (DST) is accompanied by s ...
Thermal history of the Earth and its petrological expression
... compositions are important to constrain because their MgO and FeO contents increase with mantle potential temperature TP (Langmuir et al., 1992; Putirka, 2005; Herzberg et al., 2007; Herzberg and Asimow, 2008). They provide a petrological record of the thermal state of the mantle from which they for ...
... compositions are important to constrain because their MgO and FeO contents increase with mantle potential temperature TP (Langmuir et al., 1992; Putirka, 2005; Herzberg et al., 2007; Herzberg and Asimow, 2008). They provide a petrological record of the thermal state of the mantle from which they for ...
Geophysical Journal International - Archimer
... modelling of the crustal and upper mantle, where only depth and velocity nodes necessary to fit the data in the limits of the picking order. In the sedimentary layers the structures from reflection seismic modelling were included; however care was taken to not unnecessarily introduce lateral velocit ...
... modelling of the crustal and upper mantle, where only depth and velocity nodes necessary to fit the data in the limits of the picking order. In the sedimentary layers the structures from reflection seismic modelling were included; however care was taken to not unnecessarily introduce lateral velocit ...
Amherst County Public Schools Earth Science Curriculum Pacing
... by geologic processes and the activities of humans. Key concepts include a) processes of soil development; b) development of karst topography; c) relationships between groundwater zones, including saturated an unsaturated zones, and the water table; d) identification of sources of fresh water includ ...
... by geologic processes and the activities of humans. Key concepts include a) processes of soil development; b) development of karst topography; c) relationships between groundwater zones, including saturated an unsaturated zones, and the water table; d) identification of sources of fresh water includ ...
The Bouguer gravity map of the Mediterranean Sea
... The values of gravity observed at the Earth's surface are strongly correlated with terrain morphology and hence with residual effects of tectonics, which are better preserved at sea than on land. In oceanic regions, gravity is also strongly correlated with crustal thickness and composition: it is ge ...
... The values of gravity observed at the Earth's surface are strongly correlated with terrain morphology and hence with residual effects of tectonics, which are better preserved at sea than on land. In oceanic regions, gravity is also strongly correlated with crustal thickness and composition: it is ge ...
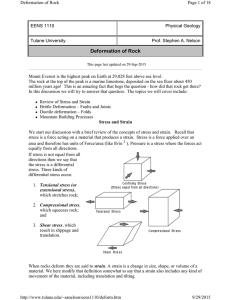
Deformation of Rock
... enough stress. Such fracturing, while it does produce irregular cracks in the rock, sometimes produces planar features that provide evidence of the stresses acting at the time of formation of the cracks. Two major types of more or less planar fractures can occur: joints and faults. Joints As we lear ...
... enough stress. Such fracturing, while it does produce irregular cracks in the rock, sometimes produces planar features that provide evidence of the stresses acting at the time of formation of the cracks. Two major types of more or less planar fractures can occur: joints and faults. Joints As we lear ...
Controlled Electromagnetic Sources for Measuring Electrical
... of the conductivity of the ocean crust and upper mantle, especiallylow conductivity zones, is demonstrated. If the mantle conductivityis low enough, horizontal ranges of 50 km and conductivity estimatesto over 20 km depth can be achieved. ...
... of the conductivity of the ocean crust and upper mantle, especiallylow conductivity zones, is demonstrated. If the mantle conductivityis low enough, horizontal ranges of 50 km and conductivity estimatesto over 20 km depth can be achieved. ...
Continental margins near New-Caledonia
... symmetrical pattern, compared with the Fiji Islands, of both the New Hebrides and Tonga-Kermadec arcs with opposite-facing lithospheric consumption zones and the existence, in their concavity, of an expansion basin where the oceanic lithosphere is formed. Other important features are the basic diffe ...
... symmetrical pattern, compared with the Fiji Islands, of both the New Hebrides and Tonga-Kermadec arcs with opposite-facing lithospheric consumption zones and the existence, in their concavity, of an expansion basin where the oceanic lithosphere is formed. Other important features are the basic diffe ...
HG World Map - North Kitsap School District
... NOT the Arctic. Draw and label. Read it with me. For comparison, Antarctica is twice the size of Australia. 98% of this continent is covered by an ice sheet. Show photo. 5:1 Review the 7 continents. Heads Together. Our world is also made of oceanic crust. Say oceanic crust. There are 5 oceans. Your ...
... NOT the Arctic. Draw and label. Read it with me. For comparison, Antarctica is twice the size of Australia. 98% of this continent is covered by an ice sheet. Show photo. 5:1 Review the 7 continents. Heads Together. Our world is also made of oceanic crust. Say oceanic crust. There are 5 oceans. Your ...
Mechanism and timing of Pb transport from subducted oceanic crust
... samples, and the relative timing of Pb addition from the subducting oceanic crust and subducting sediment. Lavas from these islands have distinctive, radiogenic Pb isotope compositions, which are inherited from the basaltic crust of the subducting Louisville Seamount Chain on the Pacific Plate. The s ...
... samples, and the relative timing of Pb addition from the subducting oceanic crust and subducting sediment. Lavas from these islands have distinctive, radiogenic Pb isotope compositions, which are inherited from the basaltic crust of the subducting Louisville Seamount Chain on the Pacific Plate. The s ...
Magmatism at Rift Zones: The Generation of Volcanic Continental
... We note in passingthat we can say little about how tion aboutwherethe mantleplumesmay be [e.g.,Mordeep in the Earth the convectionpenetrates. Courlney gan, 1981],it is lessreliablefor this purposethan are and While[1986]modeledconvection in the upperman- the geoid or residual depth anomalies. ...
... We note in passingthat we can say little about how tion aboutwherethe mantleplumesmay be [e.g.,Mordeep in the Earth the convectionpenetrates. Courlney gan, 1981],it is lessreliablefor this purposethan are and While[1986]modeledconvection in the upperman- the geoid or residual depth anomalies. ...
Sources of Pb for Indian Ocean ferromanganese crusts: a
... Pb=204 Pb and 207 Pb=206 Pb have been distinct only from ¾5 Ma ago (Fig. 2). Prior to that time no clear provinciality is evident. The cause of the major shift in Atlantic Pb isotopes from 5 Ma ago is not fully understood. It is possible that the closure of the Panama Gateway may have contributed to ...
... Pb=204 Pb and 207 Pb=206 Pb have been distinct only from ¾5 Ma ago (Fig. 2). Prior to that time no clear provinciality is evident. The cause of the major shift in Atlantic Pb isotopes from 5 Ma ago is not fully understood. It is possible that the closure of the Panama Gateway may have contributed to ...
Active Crustal Subduction and Exhumation in Taiwan
... While such features are the first order effects of the collision between Eurasia and the Philippine Sea plate, closer examination requires modifications to this simple picture. For example, Lin and Roecker (1993) showed that a zone of anomalously deep (20 to 100 km depth) earthquakes beneath the cen ...
... While such features are the first order effects of the collision between Eurasia and the Philippine Sea plate, closer examination requires modifications to this simple picture. For example, Lin and Roecker (1993) showed that a zone of anomalously deep (20 to 100 km depth) earthquakes beneath the cen ...
Structure, tectonic and petrology of mid-oceanic ridges and the
... crystallinity ranges between holohyaline and holocrystalline. The presence of highly embayed phenocrysts in disequilibrium with the host magma supports the importance of magma mixing in the evolution of MORB. The commonly observed phenocryst assemblages in OFB are: olivine ± Mg–Cr spinel; plagioclas ...
... crystallinity ranges between holohyaline and holocrystalline. The presence of highly embayed phenocrysts in disequilibrium with the host magma supports the importance of magma mixing in the evolution of MORB. The commonly observed phenocryst assemblages in OFB are: olivine ± Mg–Cr spinel; plagioclas ...
Plate tectonics and the origins of resources
... rocks are basaltic in composition that were formed by the magma produced by partial melting of the upper‘s mantle peridotites. The second type of plates movement is the convergent movement, where an oceanic plate slides beneath another continental or even thicker oceanic plate forming the so called ...
... rocks are basaltic in composition that were formed by the magma produced by partial melting of the upper‘s mantle peridotites. The second type of plates movement is the convergent movement, where an oceanic plate slides beneath another continental or even thicker oceanic plate forming the so called ...
Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland Bulletin 33
... extends for a distance of almost 1800 km across the Arctic Ocean (Fig. 3). The ridge is 45 to 200 km wide, mostly flat-topped to slightly rounded at its crest and rises from water depths of more than 4300 m in the adjacent basins to typically 1000 to 1300 m. The shallowest part of the ridge is found ...
... extends for a distance of almost 1800 km across the Arctic Ocean (Fig. 3). The ridge is 45 to 200 km wide, mostly flat-topped to slightly rounded at its crest and rises from water depths of more than 4300 m in the adjacent basins to typically 1000 to 1300 m. The shallowest part of the ridge is found ...
The fate of fluids released from subducting slab in
... Using the approach of Zelt and Barton (1998), a synthetic velocity model was generated by the addition of a laterally and vertically alternating anomaly pattern of positive and negative squares (32 km × 32 km × 8 km) to the final velocity model obtained by tomographic inversion. The hypocenterstatio ...
... Using the approach of Zelt and Barton (1998), a synthetic velocity model was generated by the addition of a laterally and vertically alternating anomaly pattern of positive and negative squares (32 km × 32 km × 8 km) to the final velocity model obtained by tomographic inversion. The hypocenterstatio ...
Crustal structure and evolution of the Mariana intra
... crustal, and lower-crustal layers in the northern Izu arc are 496 km3/km, 732 km3/km, 963 km3/km, and 2455 km3/km, and their proportions are 11%, 16%, 21%, and 53%, respectively (Table 1). It might be expected that the proportions of the three arcs would be roughly similar; however, the proportion o ...
... crustal, and lower-crustal layers in the northern Izu arc are 496 km3/km, 732 km3/km, 963 km3/km, and 2455 km3/km, and their proportions are 11%, 16%, 21%, and 53%, respectively (Table 1). It might be expected that the proportions of the three arcs would be roughly similar; however, the proportion o ...
Word format
... Faults can occur a long way from the plate boundaries, producing a second class of earthquakes in regions referred to as _________________________. Some of these may be ancient faults that are no longer active, but many are still active today. Where was the largest earthquake in the recorded history ...
... Faults can occur a long way from the plate boundaries, producing a second class of earthquakes in regions referred to as _________________________. Some of these may be ancient faults that are no longer active, but many are still active today. Where was the largest earthquake in the recorded history ...
IM_chapter8 Earthquakes and Interior
... Topic 4. The Origin of Deep Earthquakes. The focus of most earthquakes is less than 50 km depth because at greater depths rock deforms plastically and does not generate earthquakes. Yet the focus of some quakes is deeper. These quakes occur beneath subduction zones where the down-going slab is relat ...
... Topic 4. The Origin of Deep Earthquakes. The focus of most earthquakes is less than 50 km depth because at greater depths rock deforms plastically and does not generate earthquakes. Yet the focus of some quakes is deeper. These quakes occur beneath subduction zones where the down-going slab is relat ...
Geodynamic basis of heat transport in the Earth
... Clearly, only enstatite chondrites, not ordinary chondrites, have a sufficiently high iron alloy content to comprise a massive core planet like the Earth. Moreover, the mass ratios of petrologically determined parts of a primitive enstatite chondrite match quite precisely the seismically determined ...
... Clearly, only enstatite chondrites, not ordinary chondrites, have a sufficiently high iron alloy content to comprise a massive core planet like the Earth. Moreover, the mass ratios of petrologically determined parts of a primitive enstatite chondrite match quite precisely the seismically determined ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.