Notes - Plate Tectonics
... Continental rocks date the Earth at about 4.6 billion years old. Since the ocean floor is lower in the lithosphere, scientists expected to find older rocks at those depths. ...
... Continental rocks date the Earth at about 4.6 billion years old. Since the ocean floor is lower in the lithosphere, scientists expected to find older rocks at those depths. ...
Core Unit 1: Patterns and Processes in the Physical Environment
... Plates move as passengers on the semi molten asthenosphere. As plates move they slide, diverge and collide. This movement gives rise to earthquakes, volcanic activity, sea floor spreading and the creation of ocean ridges. ...
... Plates move as passengers on the semi molten asthenosphere. As plates move they slide, diverge and collide. This movement gives rise to earthquakes, volcanic activity, sea floor spreading and the creation of ocean ridges. ...
Plate Tectonics Crossword
... generally occurring along convergent and divergent boundaries, where magma, ash, and gases escape from below the surface? ...
... generally occurring along convergent and divergent boundaries, where magma, ash, and gases escape from below the surface? ...
Science study guide for Ch
... 10. When plates move past each other they are called sliding boundaries. 11. The hottest layer of the Earth is the inner core. 12. At diverging boundaries, two plates move away from each other. 13. The thickest layer of the Earth is called the mantle. 14. At converging boundaries, two plate move tow ...
... 10. When plates move past each other they are called sliding boundaries. 11. The hottest layer of the Earth is the inner core. 12. At diverging boundaries, two plates move away from each other. 13. The thickest layer of the Earth is called the mantle. 14. At converging boundaries, two plate move tow ...
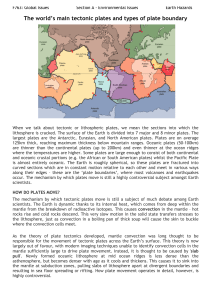
The world`s main tectonic plates and types of
... responsible for the movement of tectonic plates across the Earth’s surface. This theory is now largely out of favour, with modern imaging techniques unable to identify convection cells in the mantle sufficiently large to drive plate movement. Instead, it is thought to be caused by 'slab pull'. Newly ...
... responsible for the movement of tectonic plates across the Earth’s surface. This theory is now largely out of favour, with modern imaging techniques unable to identify convection cells in the mantle sufficiently large to drive plate movement. Instead, it is thought to be caused by 'slab pull'. Newly ...
Are the continents moving? What are plate tectonics?
... magma is pushed up from the mantle to the surface. The upward movement of magma causes tension, or a stretch or push, on the plates. This push moves the ocean floor apart and separates the plate. This is called sea floor spreading. As the hot rock reaches the surface it cools and builds up equally o ...
... magma is pushed up from the mantle to the surface. The upward movement of magma causes tension, or a stretch or push, on the plates. This push moves the ocean floor apart and separates the plate. This is called sea floor spreading. As the hot rock reaches the surface it cools and builds up equally o ...
Word format
... Many mountain belts around the world show tell-tale signs of having been formed at convergent plate boundaries sometime in the geologic past (e.g., Appalachians). ...
... Many mountain belts around the world show tell-tale signs of having been formed at convergent plate boundaries sometime in the geologic past (e.g., Appalachians). ...
4. Plate Tectonics II (p. 46-67)
... Many mountain belts around the world show tell-tale signs of having been formed at convergent plate boundaries sometime in the geologic past (e.g., Appalachians). ...
... Many mountain belts around the world show tell-tale signs of having been formed at convergent plate boundaries sometime in the geologic past (e.g., Appalachians). ...
Continental drift: An idea before its time Pangaea approximately 200
... evidence confirming seafloor spreading has come from drilling directly into ocean-floor sediment – Age of deepest sediments – Thickness of ocean-floor sediments verifies seafloor spreading ...
... evidence confirming seafloor spreading has come from drilling directly into ocean-floor sediment – Age of deepest sediments – Thickness of ocean-floor sediments verifies seafloor spreading ...
Theory of PLATE TECTONICS
... Plates and Plate Boundaries • The crustal (lithospheric) plates typically contain oceanic and continental crust. • As the plates move, they can separate, collide, or slide past one another. • This results in three kinds of plate boundaries animations 1. Divergent -apart 2. Convergent-together 3. Tr ...
... Plates and Plate Boundaries • The crustal (lithospheric) plates typically contain oceanic and continental crust. • As the plates move, they can separate, collide, or slide past one another. • This results in three kinds of plate boundaries animations 1. Divergent -apart 2. Convergent-together 3. Tr ...
Lecture 2: Dynamic Earth: Plate Tectonics
... at the level of map precision available to Alfred Wegener, who proposed that the continents once existed as a vast supercontinent, Pangea, that later fragmented. Test the fit of the continents for yourself by clicking and dragging a continent to a new location; then, using the arrow keys on your key ...
... at the level of map precision available to Alfred Wegener, who proposed that the continents once existed as a vast supercontinent, Pangea, that later fragmented. Test the fit of the continents for yourself by clicking and dragging a continent to a new location; then, using the arrow keys on your key ...
Internal Structure of the Earth
... • ____________ believed that the continents __________ on the waters of the ocean to get to their current locations. ...
... • ____________ believed that the continents __________ on the waters of the ocean to get to their current locations. ...
Tectonic plates File - Learning on the Loop
... surface of the Earth’s crust that solidifies to form new layers of rock. Is composed mainly of Fe. ...
... surface of the Earth’s crust that solidifies to form new layers of rock. Is composed mainly of Fe. ...
Geology of Planet Earth
... 1. What is the most likely geologic hazard in your part of the country? Is there more than one, if so what are they? 2. What are the three types of plate boundaries and where does each most commonly occur on the Earth? Circle and example location of each on the map. ...
... 1. What is the most likely geologic hazard in your part of the country? Is there more than one, if so what are they? 2. What are the three types of plate boundaries and where does each most commonly occur on the Earth? Circle and example location of each on the map. ...
Earth*s Structure
... •Lithosphere- crust and rigid upper mantle; tectonic plates •Asthenosphere- soft rock of the mantle; how tectonic plates move •Mesosphere- between outer core and asthenosphere •Outer core- completely liquid; iron and nickel •Inner core- solid and dense ...
... •Lithosphere- crust and rigid upper mantle; tectonic plates •Asthenosphere- soft rock of the mantle; how tectonic plates move •Mesosphere- between outer core and asthenosphere •Outer core- completely liquid; iron and nickel •Inner core- solid and dense ...
Blank Jeopardy
... Convergent boundaries: can result in a subduction zone (when one plate is oceanic and sinks below a continental plate) or create large mountain ranges (when two continental plates collide) ...
... Convergent boundaries: can result in a subduction zone (when one plate is oceanic and sinks below a continental plate) or create large mountain ranges (when two continental plates collide) ...
Geosphere PowerPoint
... When two plates collide, some crust is destroyed in the impact and the plates become smaller. Oceanic Plate and Continental Plate - When a thin, dense oceanic plate collides with a relatively light, thick continental plate, the oceanic plate is forced under : SUBDUCTION! Two Oceanic Plates – One is ...
... When two plates collide, some crust is destroyed in the impact and the plates become smaller. Oceanic Plate and Continental Plate - When a thin, dense oceanic plate collides with a relatively light, thick continental plate, the oceanic plate is forced under : SUBDUCTION! Two Oceanic Plates – One is ...
Plate Tectonics - Cloudfront.net
... states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. The theory explains the formation, movement, and subduction of Earth’s Plates. » Map with boundaries » Plate tectonic video ...
... states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. The theory explains the formation, movement, and subduction of Earth’s Plates. » Map with boundaries » Plate tectonic video ...
File
... • Describe natural processes in which heat transfer in the Earth occurs by conduction, convection, and radiation. – Convection of heat in the Earth’s mantle is thought to drive the motion of plates. • Explain how plate tectonics accounts for the features and processes (sea floor spreading, mid-ocean ...
... • Describe natural processes in which heat transfer in the Earth occurs by conduction, convection, and radiation. – Convection of heat in the Earth’s mantle is thought to drive the motion of plates. • Explain how plate tectonics accounts for the features and processes (sea floor spreading, mid-ocean ...
GEOL1033-SQS07R
... 11. Referring to the question above, what is the name of the boundary between these two subdivisions? ________________________ 12. How many subdivisions of Earth's core are there? 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5? 13. Which subdivision of the Earth's core is molten? ...
... 11. Referring to the question above, what is the name of the boundary between these two subdivisions? ________________________ 12. How many subdivisions of Earth's core are there? 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5? 13. Which subdivision of the Earth's core is molten? ...
Plate Tectonics - cloudfront.net
... states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. The theory explains the formation, movement, and subduction of Earth’s Plates. » Map with boundaries » Plate tectonic video ...
... states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. The theory explains the formation, movement, and subduction of Earth’s Plates. » Map with boundaries » Plate tectonic video ...
Earth`s Lithosphere Study Guide
... No possible force could move something as large as a continent. ...
... No possible force could move something as large as a continent. ...
Plate tectonics
... inner layer above the core. The plates act like a hard and rigid shell compared to Earth's interior. ...
... inner layer above the core. The plates act like a hard and rigid shell compared to Earth's interior. ...
Quiz Study Guide Interior of Earth
... properties. (Example: the inner core is solid and the outer core is liquid.) ...
... properties. (Example: the inner core is solid and the outer core is liquid.) ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.