Continental Drift—An Idea Before Its Time
... • Plates slide past one another and no new lithosphere is created or destroyed - two segments of a mid-ocean ridge • Transform faults are oriented perpendicular to mid-ocean ridge —Permits plates to move from offset ridge segments • Shallow but strong earthquakes ...
... • Plates slide past one another and no new lithosphere is created or destroyed - two segments of a mid-ocean ridge • Transform faults are oriented perpendicular to mid-ocean ridge —Permits plates to move from offset ridge segments • Shallow but strong earthquakes ...
John "Zack" Smith`s Paper
... under the plates is the cause of why the plates shift. When two plates collide they can create earthquakes, mountains, or trenches. These plates are the cause of the earth’s bad complexion. Earthquakes are bad. After much research it was found that these “bad earthquakes” are caused near oceanic tre ...
... under the plates is the cause of why the plates shift. When two plates collide they can create earthquakes, mountains, or trenches. These plates are the cause of the earth’s bad complexion. Earthquakes are bad. After much research it was found that these “bad earthquakes” are caused near oceanic tre ...
Wegener—Continental Drift
... D. Deep ocean studies showing no zones of movement on the ocean floor. ...
... D. Deep ocean studies showing no zones of movement on the ocean floor. ...
File
... What was another piece of evidence Wegener used to support continental drift? Why didn’t other scientists support the theory of continental drift? What is the difference between plate tectonics and continental drift? ...
... What was another piece of evidence Wegener used to support continental drift? Why didn’t other scientists support the theory of continental drift? What is the difference between plate tectonics and continental drift? ...
Brain Pop-Plate Tectonics ANSWER KEY
... Divergent boundaries are where plates are moving apart from one another and new crust forms. 8. What are convergent boundaries? Explain and draw a picture. ...
... Divergent boundaries are where plates are moving apart from one another and new crust forms. 8. What are convergent boundaries? Explain and draw a picture. ...
PLATE TECTONICS
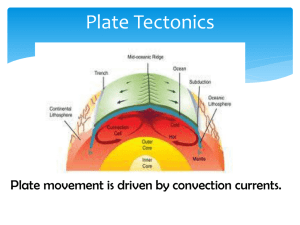
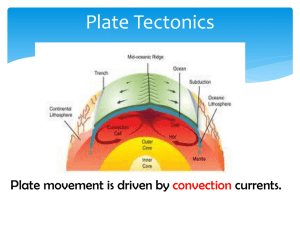
... cold magma sinks creating a current Heat comes from radioactivity Plates “ride” on this current ...
... cold magma sinks creating a current Heat comes from radioactivity Plates “ride” on this current ...
Earth Science Concepts
... faults slip and slide Hypocenter: The location below the surface where the rupture happens along the fault Epicenter: The point right above the hypocenter on the earths surface Earthquakes are known to cause mass destruction depending on their waves o P wave (primary wave): The fastest ...
... faults slip and slide Hypocenter: The location below the surface where the rupture happens along the fault Epicenter: The point right above the hypocenter on the earths surface Earthquakes are known to cause mass destruction depending on their waves o P wave (primary wave): The fastest ...
plates - Northside Middle School
... subducts underneath the continental lithosphere • Oceanic lithosphere heats and dehydrates as it subsides • The melt rises forming volcanism • E.g. The Andes ...
... subducts underneath the continental lithosphere • Oceanic lithosphere heats and dehydrates as it subsides • The melt rises forming volcanism • E.g. The Andes ...
Learning Targets Answer Key
... magnetic reversals in the rock on the sea floor also show that new rock continually forms at mid-ocean ridges. 11. What force causes tectonic plates to move and where does it occur? Convection currents of heated rock in Earth’s mantle is the force that causes tectonic plates to move. 12. Illustrate ...
... magnetic reversals in the rock on the sea floor also show that new rock continually forms at mid-ocean ridges. 11. What force causes tectonic plates to move and where does it occur? Convection currents of heated rock in Earth’s mantle is the force that causes tectonic plates to move. 12. Illustrate ...
Plate Tectonic Test Use the pictures above to answer questions 1
... ____ 23. Convection currents in the Earth’s mantle cause crustal plates to move. The drawing above shows a lab set up designed to model this process. If the two corks floating on the water represent the continents, which of the following outcomes is most likely to result from this investigation? ...
... ____ 23. Convection currents in the Earth’s mantle cause crustal plates to move. The drawing above shows a lab set up designed to model this process. If the two corks floating on the water represent the continents, which of the following outcomes is most likely to result from this investigation? ...
Plate Tectonics Notes
... Currents are caused by heat in Earth’s interior Hotter material is less dense, rises toward the surface Cooler material pushed out of the way, sinks back toward the core Lithosphere is pushed up and melted above rising convection currents Lithosphere is pulled downward above sinking curren ...
... Currents are caused by heat in Earth’s interior Hotter material is less dense, rises toward the surface Cooler material pushed out of the way, sinks back toward the core Lithosphere is pushed up and melted above rising convection currents Lithosphere is pulled downward above sinking curren ...
Plate Tectonics
... Currents are caused by heat in Earth’s interior Hotter material is less dense, rises toward the surface Cooler material pushed out of the way, sinks back toward the core Lithosphere is pushed up and melted above rising convection currents Lithosphere is pulled downward above sinking curren ...
... Currents are caused by heat in Earth’s interior Hotter material is less dense, rises toward the surface Cooler material pushed out of the way, sinks back toward the core Lithosphere is pushed up and melted above rising convection currents Lithosphere is pulled downward above sinking curren ...
Growing and Shrinking Oceans
... You are already familiar with the idea of divergent boundaries. Divergent boundaries are the result of two tectonic plates that are pulling apart. When this happens under the ocean, magma comes up to the surface, cools, hardens, and forms new rock along the ocean floor. Older rock gets pushed furthe ...
... You are already familiar with the idea of divergent boundaries. Divergent boundaries are the result of two tectonic plates that are pulling apart. When this happens under the ocean, magma comes up to the surface, cools, hardens, and forms new rock along the ocean floor. Older rock gets pushed furthe ...
New Title
... b. An oceanic plate sinks beneath a continental plate when the two plates collide. c. Where two plates meet, the one that is more dense sinks under the other. d. Mountain ranges form where two plates carrying continental crust ...
... b. An oceanic plate sinks beneath a continental plate when the two plates collide. c. Where two plates meet, the one that is more dense sinks under the other. d. Mountain ranges form where two plates carrying continental crust ...
Earth
... thicker toward continents – Older fossils and rocks near continents, becoming younger near rifts ...
... thicker toward continents – Older fossils and rocks near continents, becoming younger near rifts ...
Name___________________________ Date: Plate Tectonics
... When an oceanic crust collides with a continental crust, the ocean crust sinks (subducts) because it is thinner and more dense. 8. What happens along a subduction zone? Subduction zones occur at a convergent boundary between an oceanic plate and continental plate. The more dense oceanic crust sinks. ...
... When an oceanic crust collides with a continental crust, the ocean crust sinks (subducts) because it is thinner and more dense. 8. What happens along a subduction zone? Subduction zones occur at a convergent boundary between an oceanic plate and continental plate. The more dense oceanic crust sinks. ...
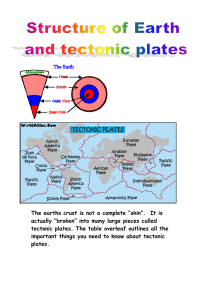
The earths crust is not a complete “skin”. It is actually “broken” into
... convection currents in the mantle. (remember the mantle can flow like a liquid) – see beginning of this booklet for info on convection currents. ...
... convection currents in the mantle. (remember the mantle can flow like a liquid) – see beginning of this booklet for info on convection currents. ...
AIM: Introduce you to scientific study of the world`s oceans and seas
... –Creates new lithosphere •Plates move past each other in oceanic FZs & across continental transcurrent faults –Lithosphere neither created nor destroyed •Plates move toward each other at DOTs and in active mountain belts –Lithosphere consumed by subduction ...
... –Creates new lithosphere •Plates move past each other in oceanic FZs & across continental transcurrent faults –Lithosphere neither created nor destroyed •Plates move toward each other at DOTs and in active mountain belts –Lithosphere consumed by subduction ...
Plate Tectonics
... mantle is warmer. It expands, becomes less dense and rises. When it reaches the upper mantle it cools, contracts, becoming more dense and sinks. This constant rise and fall of magma causes the convection currents that drive plate tectonics. The crust plates ride along on top of these convection curr ...
... mantle is warmer. It expands, becomes less dense and rises. When it reaches the upper mantle it cools, contracts, becoming more dense and sinks. This constant rise and fall of magma causes the convection currents that drive plate tectonics. The crust plates ride along on top of these convection curr ...
Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences
... extensional and compressional boundary zones between the plates are the scenes of the real action, with major earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, large displacements and mountain building. Plate motion is maintained by convection created by the Earth’s heat engine. McKenzie’s early numerical modelling ...
... extensional and compressional boundary zones between the plates are the scenes of the real action, with major earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, large displacements and mountain building. Plate motion is maintained by convection created by the Earth’s heat engine. McKenzie’s early numerical modelling ...
Lecture 2 - Early Earth and Plate Tectonics
... of a few large, thick plates that move slowly and change in size Intense geologic activity is concentrated at plate boundaries, where plates move away, toward, or past each other Combination of continental drift and seafloor spreading hypotheses in late 1960s ...
... of a few large, thick plates that move slowly and change in size Intense geologic activity is concentrated at plate boundaries, where plates move away, toward, or past each other Combination of continental drift and seafloor spreading hypotheses in late 1960s ...
Plate Tectonics * Guided Notes
... 5. _________________ _______________ type of convergent boundary created where one plate bends and sinks beneath the other. • Old Sea Floor being destroyed 6. The newly formed magma is forced upward along these plate boundaries, forming ___________________. Where Plates Collide 1. A subduction zone ...
... 5. _________________ _______________ type of convergent boundary created where one plate bends and sinks beneath the other. • Old Sea Floor being destroyed 6. The newly formed magma is forced upward along these plate boundaries, forming ___________________. Where Plates Collide 1. A subduction zone ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.