Discovering Plate Boundaries
... •Earthquakes complex, shallow (to medium) on both sides •Age data not symmetrical, one side of boundary •Complex topography, wide mountains and basins •Rocks? ...
... •Earthquakes complex, shallow (to medium) on both sides •Age data not symmetrical, one side of boundary •Complex topography, wide mountains and basins •Rocks? ...
26 Sep: Volcano Processes
... Obs: Earthquake “sequences” (Sumatra, Turkey) where large stress changes following one event favor another Obs: “Slow fault slip” events, harmonic (seismic) tremor May someday be possible to predict EQs; need improved understanding of physics & MUCH better measurements Today: • Volcanism ...
... Obs: Earthquake “sequences” (Sumatra, Turkey) where large stress changes following one event favor another Obs: “Slow fault slip” events, harmonic (seismic) tremor May someday be possible to predict EQs; need improved understanding of physics & MUCH better measurements Today: • Volcanism ...
Earth`s plates
... The lithosphere is broken up into pieces called tectonic plates They float on the mantle Different sizes and shapes ...
... The lithosphere is broken up into pieces called tectonic plates They float on the mantle Different sizes and shapes ...
The Theory of Plate Tectonics - Brighten AcademyMiddle School
... • Plate tectonics (511) – Earth’s surface is made of rigid slabs of rock, or plates, that move with respect to each other • Lithosphere (512) – the cold and rigid outermost rock layer • Divergent plate boundary (513) – forms where two plates separate • Transform plate boundary (513) – Forms where tw ...
... • Plate tectonics (511) – Earth’s surface is made of rigid slabs of rock, or plates, that move with respect to each other • Lithosphere (512) – the cold and rigid outermost rock layer • Divergent plate boundary (513) – forms where two plates separate • Transform plate boundary (513) – Forms where tw ...
Ocean Basins (Chapter 19) - Ms. Whitt's Science Classes
... the location of objects or to communicate Submersibles- Human piloted or self piloted, vessels sent underwater that can do a various of jobs like taking photographs, collecting mineral samples. ...
... the location of objects or to communicate Submersibles- Human piloted or self piloted, vessels sent underwater that can do a various of jobs like taking photographs, collecting mineral samples. ...
File
... • Main objection to Wegener’s proposal was its inability to provide a mechanism (what causes them to move?) ...
... • Main objection to Wegener’s proposal was its inability to provide a mechanism (what causes them to move?) ...
Layers of the Earth
... The asthenosphere is composed of matter in the molten or semimolten state. Asthenosphere temperature is normally between 1,400 degree Celsius to 3,000 degree Celsius. The very high temperatures in this layer cause everything, including rocks, to melt. It is composed mainly of silicates of iron and m ...
... The asthenosphere is composed of matter in the molten or semimolten state. Asthenosphere temperature is normally between 1,400 degree Celsius to 3,000 degree Celsius. The very high temperatures in this layer cause everything, including rocks, to melt. It is composed mainly of silicates of iron and m ...
LAB 4-3: Seafloor Spreading
... already learned, the earth’s crust is broken up into a large number of tectonic plates that are moving in relation to one another. The focus of this lab is to examine the sea floor of the Atlantic Ocean where two tectonic plates are moving apart creating a divergent plate boundary. Divergent plate b ...
... already learned, the earth’s crust is broken up into a large number of tectonic plates that are moving in relation to one another. The focus of this lab is to examine the sea floor of the Atlantic Ocean where two tectonic plates are moving apart creating a divergent plate boundary. Divergent plate b ...
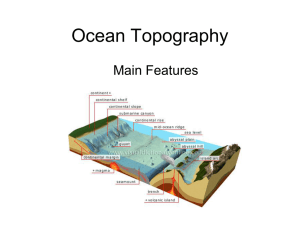
Ocean Topography
... Continental shelf • The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain, and was part of the continent during the glacial periods, but is undersea during interglacial periods. ...
... Continental shelf • The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain, and was part of the continent during the glacial periods, but is undersea during interglacial periods. ...
Name ____Justin Powers______ Date ______ Period ____ Plate
... Mountain – A high, large mass of earth and rock that rises above the Earth’s surface with steep or sloping sides 2. At divergent boundaries, tectonic plates are moving away from each other. One result of huge masses of crust moving apart is seafloor spreading. This occurs when two plates made of oce ...
... Mountain – A high, large mass of earth and rock that rises above the Earth’s surface with steep or sloping sides 2. At divergent boundaries, tectonic plates are moving away from each other. One result of huge masses of crust moving apart is seafloor spreading. This occurs when two plates made of oce ...
Plate Tectonics PowerPoint
... – Each cycle of spreading and the intrusion of magma results in the formation of another small section of ocean floor, which slowly moves away from the ridge. ...
... – Each cycle of spreading and the intrusion of magma results in the formation of another small section of ocean floor, which slowly moves away from the ridge. ...
Civics – Unit 1 Jeopardy
... forces such as erosion and deposition, this outermost layer of the Earth is between 6 and 100 km thick. ...
... forces such as erosion and deposition, this outermost layer of the Earth is between 6 and 100 km thick. ...
Plate Tectonics Guided Notes NAME__________________________________________________________D_____________P_____
... plate. At this point, water from the ocean will rush in, forming a new ____________ or _____________ ____________ in the rift zone. ...
... plate. At this point, water from the ocean will rush in, forming a new ____________ or _____________ ____________ in the rift zone. ...
Plate Boundaries
... Plate Boundaries: class worksheet; use as a study guide for exam #1 Reading a tectonic map Use the map below to answer the questions. ...
... Plate Boundaries: class worksheet; use as a study guide for exam #1 Reading a tectonic map Use the map below to answer the questions. ...
Inside the Earth
... thinnest layer) • 2 types of crust – Oceanic (very dense) – Continental (less dense) ...
... thinnest layer) • 2 types of crust – Oceanic (very dense) – Continental (less dense) ...
Integrated Science Chapter 19 Name
... Z. a crack in the Earth created when rocks on either side of a break move ...
... Z. a crack in the Earth created when rocks on either side of a break move ...
Volcano Age - Mercer Island School District
... Ocean Ridges—____________ plate boundaries), deep sea trenches (___________ boundaries), or major faults that primarily separate sections of mid-ocean ridges (________________ plate boundaries). ...
... Ocean Ridges—____________ plate boundaries), deep sea trenches (___________ boundaries), or major faults that primarily separate sections of mid-ocean ridges (________________ plate boundaries). ...
Plate Tectonics
... Pieces of the lithosphere that move around on top of the asthenosphere are called tectonic plates Tectonic plates “float” on the asthenosphere in a similar way. The plates cover the surface of the asthenosphere, and they touch one another and move around. The lithosphere displaces the asthenosphere. ...
... Pieces of the lithosphere that move around on top of the asthenosphere are called tectonic plates Tectonic plates “float” on the asthenosphere in a similar way. The plates cover the surface of the asthenosphere, and they touch one another and move around. The lithosphere displaces the asthenosphere. ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.