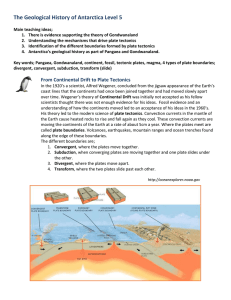
plates
... boundary formed by the collision of two lithospheric plates Divergent ► ____________boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other Transform ► ____________boundary between tectonic plates that are sliding past each other horizontally ...
... boundary formed by the collision of two lithospheric plates Divergent ► ____________boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other Transform ► ____________boundary between tectonic plates that are sliding past each other horizontally ...
NCEA Level 3 Science (90731) 2012 Assessment Schedule
... subducting plate boundary with the Pacific Plate subducting under the Australian Plate. The lower South Island is also subducting but the Australian Plate subducts under the Pacific Plate. The middle of the South Island is a transform fault with the two plates sliding past each other. The diagram sh ...
... subducting plate boundary with the Pacific Plate subducting under the Australian Plate. The lower South Island is also subducting but the Australian Plate subducts under the Pacific Plate. The middle of the South Island is a transform fault with the two plates sliding past each other. The diagram sh ...
Plate Tectonics
... Pieces of the lithosphere that move around on top of the asthenosphere are called tectonic plates Tectonic plates “float” on the asthenosphere in a similar way. The plates cover the surface of the asthenosphere, and they touch one another and move around. The lithosphere displaces the asthenosphere. ...
... Pieces of the lithosphere that move around on top of the asthenosphere are called tectonic plates Tectonic plates “float” on the asthenosphere in a similar way. The plates cover the surface of the asthenosphere, and they touch one another and move around. The lithosphere displaces the asthenosphere. ...
Midterm Exam
... Because they float on the oceans Because they float on Earth’s liquid mantle Because of “trench-pull” and “ridge-push forces” ...
... Because they float on the oceans Because they float on Earth’s liquid mantle Because of “trench-pull” and “ridge-push forces” ...
PHYSICAL GEOLOGY
... know on sight several minerals and rocks that commonly occur on the earth’s surface distinguish the major classes of rocks and explain their origin understand the various processes of physical and chemical weathering and be able to recognize them in the field explain the different agents of erosion ...
... know on sight several minerals and rocks that commonly occur on the earth’s surface distinguish the major classes of rocks and explain their origin understand the various processes of physical and chemical weathering and be able to recognize them in the field explain the different agents of erosion ...
The India - Eurasia collision, Himalaya and the Tibetan
... Himalaya and the Tibetan plateau. Some important characteristics: • Very long duration of continental collision and shortening • Thickest crust and highest topography on earth ...
... Himalaya and the Tibetan plateau. Some important characteristics: • Very long duration of continental collision and shortening • Thickest crust and highest topography on earth ...
Quiz 3
... Matching: select the best response from Column B for each phrase in Column A. Selections from Column B may be used more than once or not at all. ...
... Matching: select the best response from Column B for each phrase in Column A. Selections from Column B may be used more than once or not at all. ...
Word - LEARNZ
... What do you think the edges of the different plate boundaries will look like? Where is the Rift Valley ? Why do you think it is called that ? Discuss the fossil evidence for Gondwanaland. Is it convincing? What do you think this fossil evidence can tell us about the climate at the time of Gondwanala ...
... What do you think the edges of the different plate boundaries will look like? Where is the Rift Valley ? Why do you think it is called that ? Discuss the fossil evidence for Gondwanaland. Is it convincing? What do you think this fossil evidence can tell us about the climate at the time of Gondwanala ...
Earth`s Systems and Resources Unit Test
... 28. Where would an explosive volcano MOST LIKELY occur? A. In the middle of a large plate of earth. B. Where plates of earth are coming apart. C. Where large plates of earth are transforming. D. Where large plates of earth are colliding. 29. Use the map to the right to answer this question. Califor ...
... 28. Where would an explosive volcano MOST LIKELY occur? A. In the middle of a large plate of earth. B. Where plates of earth are coming apart. C. Where large plates of earth are transforming. D. Where large plates of earth are colliding. 29. Use the map to the right to answer this question. Califor ...
The India
... Some important characteristics: • Very long duration of continental collision and shortening • Thickest crust and highest topography on earth ...
... Some important characteristics: • Very long duration of continental collision and shortening • Thickest crust and highest topography on earth ...
Mountains - SharpSchool
... • The rigid, upper part of Earth’s mantle and the crust is called the lithosphere. ...
... • The rigid, upper part of Earth’s mantle and the crust is called the lithosphere. ...
tectonic plates
... 3. Continental Plate vs Continental Plate When two huge masses of continental plates meet head-on, neither one can sink because both plates are too buoyant. At these boundaries solid rock is crumpled and faulted. Huge slivers of rock, many kilometres wide are thrust on top of one another, forming a ...
... 3. Continental Plate vs Continental Plate When two huge masses of continental plates meet head-on, neither one can sink because both plates are too buoyant. At these boundaries solid rock is crumpled and faulted. Huge slivers of rock, many kilometres wide are thrust on top of one another, forming a ...
unit 1 review_1
... Circle the number above to tell where the Tectonic plates are on Earth. We’ve talked about models that could represent the layers of the Earth. What foods did we say would make a good model of the layers of the Earth? Write your answers below: ________________________ ________________________ ...
... Circle the number above to tell where the Tectonic plates are on Earth. We’ve talked about models that could represent the layers of the Earth. What foods did we say would make a good model of the layers of the Earth? Write your answers below: ________________________ ________________________ ...
Unit 5: Ocean Floor Structure and Plate Tectonics
... 1. divergent – “pulled apart” - the crust is extended, thinned, and fractured by the rising of hot mantle material (new crust is being formed as magma comes out of rifts or volcanoes). Parallel ridges emerge as new ocean floor spreads out on either side of an ocean ridge. 2. convergent – “collide to ...
... 1. divergent – “pulled apart” - the crust is extended, thinned, and fractured by the rising of hot mantle material (new crust is being formed as magma comes out of rifts or volcanoes). Parallel ridges emerge as new ocean floor spreads out on either side of an ocean ridge. 2. convergent – “collide to ...
7 The coastline and the Tasman Sea
... It is thought that today’s east coast formed during continental rifting processes, with thick continental crust being split and a new ocean progressively formed each side of a volcanically active mid-ocean ridge - a process that is underway today in the Red Sea and the Great Rift Valley of Africa. T ...
... It is thought that today’s east coast formed during continental rifting processes, with thick continental crust being split and a new ocean progressively formed each side of a volcanically active mid-ocean ridge - a process that is underway today in the Red Sea and the Great Rift Valley of Africa. T ...
7.4 Forces that move plates.
... Tension – is stress that occurs when forces act to stretch an object. Occurs Ex. ...
... Tension – is stress that occurs when forces act to stretch an object. Occurs Ex. ...
How do Earth`s plates move?
... Diagrams may vary. Arrows should show plates moving in opposite directions and new lithosphere forming between them. ...
... Diagrams may vary. Arrows should show plates moving in opposite directions and new lithosphere forming between them. ...
Earthquakes at Sea
... are in the ocean, so many earthquakes occur in the oceanic crust that forms the seafloor. This is especially true around the Pacific Ocean. The Pacific has many deep ocean trenches along the edges of its ocean basin. Ocean trenches form where one tectonic plate is sliding, or subducting, beneath ano ...
... are in the ocean, so many earthquakes occur in the oceanic crust that forms the seafloor. This is especially true around the Pacific Ocean. The Pacific has many deep ocean trenches along the edges of its ocean basin. Ocean trenches form where one tectonic plate is sliding, or subducting, beneath ano ...
Lab 2 work sheet
... Based on your work in 3 is the Earth shrinking, expanding or staying about the same? Cite your reasoning and evidence. ...
... Based on your work in 3 is the Earth shrinking, expanding or staying about the same? Cite your reasoning and evidence. ...
Restless Earth - The Geographer online
... • The crust is the layer you live on. •It is a thin layer of rock around the Earth •There are two types of crust: 1. Continental crust (where there is land) which is 30km thick 2. Oceanic crust (under the sea) which is 5km thick ...
... • The crust is the layer you live on. •It is a thin layer of rock around the Earth •There are two types of crust: 1. Continental crust (where there is land) which is 30km thick 2. Oceanic crust (under the sea) which is 5km thick ...
crust
... The crust is composed of two rocks. The continental crust is mostly granite. The oceanic crust is basalt. Basalt is much denser than the granite. Because of this the less dense continents ride on the denser oceanic plates. ...
... The crust is composed of two rocks. The continental crust is mostly granite. The oceanic crust is basalt. Basalt is much denser than the granite. Because of this the less dense continents ride on the denser oceanic plates. ...
File
... another and converge. The heavier (or denser) oceanic plate sinks below the continental one. This area of downward movement is known as the subduction zone. The sinking plate melts due to the heat in the mantle. The magma rises and reaches the surface through vents, fissures or cracks in the contine ...
... another and converge. The heavier (or denser) oceanic plate sinks below the continental one. This area of downward movement is known as the subduction zone. The sinking plate melts due to the heat in the mantle. The magma rises and reaches the surface through vents, fissures or cracks in the contine ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.