Graphing Linear Equations
... Graphing Linear Equations using Coordinate Points: (x, y) is a _____________________ __________. “x” is the x-coordinate and “y” is the y-coordinate. We count to the right (positive) or left (negative) using the ___ - coordinate and up (positive) or down (negative) using the ___-coordinate. We can g ...
... Graphing Linear Equations using Coordinate Points: (x, y) is a _____________________ __________. “x” is the x-coordinate and “y” is the y-coordinate. We count to the right (positive) or left (negative) using the ___ - coordinate and up (positive) or down (negative) using the ___-coordinate. We can g ...
Unit 2 Review Sheet
... Customers can buy rolls of plain wrapping paper and rolls of shiny wrapping paper. The band sold a total of 55 rolls and made $950. If a roll of plain costs $14 and a roll of shiny costs $20, how many rolls of each did they ...
... Customers can buy rolls of plain wrapping paper and rolls of shiny wrapping paper. The band sold a total of 55 rolls and made $950. If a roll of plain costs $14 and a roll of shiny costs $20, how many rolls of each did they ...
The Matrix Equation A x = b (9/17/04)
... has the same solution set as the vector equation x1 a1 + x2 a2 +…+ xn an = b , which in turn has the same solution set as the system of linear equations with augmented matrix [a1 a2 … an b] ...
... has the same solution set as the vector equation x1 a1 + x2 a2 +…+ xn an = b , which in turn has the same solution set as the system of linear equations with augmented matrix [a1 a2 … an b] ...
Math 1310 Review Section 0 Integers (positive, negative, zero):
... identify solutions (don’t forget units) check to see if solution is OK 2.3 Solving Linear Inequalities Number line -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 ...
... identify solutions (don’t forget units) check to see if solution is OK 2.3 Solving Linear Inequalities Number line -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 ...
10th chapter: Pair of Linear Equations in two Variables
... 13. If the lines represented by the pair of linear equations 2x + 5y = 3, 2(k + 2) y + (k + 1) x = 2k are coincident then the value of k is ____ (a) –3 (b) 3 (c) 1 (d) –2 14. The coordinates of the point where x-axis and the line represented by x/2 + 4/3 = 1 intersect, are (a) (0, 3) (b) (3, 0) (c) ...
... 13. If the lines represented by the pair of linear equations 2x + 5y = 3, 2(k + 2) y + (k + 1) x = 2k are coincident then the value of k is ____ (a) –3 (b) 3 (c) 1 (d) –2 14. The coordinates of the point where x-axis and the line represented by x/2 + 4/3 = 1 intersect, are (a) (0, 3) (b) (3, 0) (c) ...
8-3 Addition method AKA Combination or Elimination
... 8-3 Addition method AKA Combination or Elimination 9P9: Solve 2X2 systems by elimination ...
... 8-3 Addition method AKA Combination or Elimination 9P9: Solve 2X2 systems by elimination ...
File
... 7.EE.4a. Solve word problems leading to equations of the form px + q = r and p(x + q) = r, where p, q, and r are specific rational numbers. Solve equations of these forms fluently. Compare an algebraic solution to an arithmetic solution, identifying the sequence of the operations used in each approa ...
... 7.EE.4a. Solve word problems leading to equations of the form px + q = r and p(x + q) = r, where p, q, and r are specific rational numbers. Solve equations of these forms fluently. Compare an algebraic solution to an arithmetic solution, identifying the sequence of the operations used in each approa ...
4.3 Determinants and Cramer`s Rule
... The x coefficients are replaced with the constants c1 and c2 ...
... The x coefficients are replaced with the constants c1 and c2 ...
Do-Now 01/12/2014
... Step 1 into the other equation and solve for the other variable. 3. Substitute the value from Step 2 into one of the original equations and solve. ...
... Step 1 into the other equation and solve for the other variable. 3. Substitute the value from Step 2 into one of the original equations and solve. ...
PDF
... Consider the system of equations f (x, y) = 0, g(x, y) = 0 where f (x, y) = 3x2 + 2xy + 3y 2 − 2 g(x, y) = 3x2 − 2xy + 3y 2 − 2 We will consider f and g as polynomials in x whose coefficients are functions of x. What this means can be seen by writing f and g as (3)x2 + (2y)x + (3y 2 − 2) (3)x2 + (−2 ...
... Consider the system of equations f (x, y) = 0, g(x, y) = 0 where f (x, y) = 3x2 + 2xy + 3y 2 − 2 g(x, y) = 3x2 − 2xy + 3y 2 − 2 We will consider f and g as polynomials in x whose coefficients are functions of x. What this means can be seen by writing f and g as (3)x2 + (2y)x + (3y 2 − 2) (3)x2 + (−2 ...
No Solution - Cloudfront.net
... CA Standards: 4.0: Students simplify expressions before solving linear equations in one variable. 12.0: Students simplify fractions with polynomials in the numerator and denominator by factoring both and reducing them to the lowest terms. ...
... CA Standards: 4.0: Students simplify expressions before solving linear equations in one variable. 12.0: Students simplify fractions with polynomials in the numerator and denominator by factoring both and reducing them to the lowest terms. ...
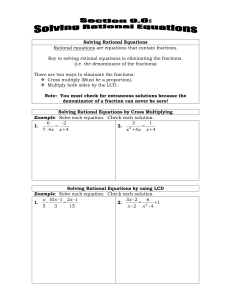
Lesson 1.2A Notes
... Ch 1 Learning Goal: The student will be able to understand functions by solving and graphing all types of equations and inequalities. Today’s Objective: Be able to solve a rational equations with variables ...
... Ch 1 Learning Goal: The student will be able to understand functions by solving and graphing all types of equations and inequalities. Today’s Objective: Be able to solve a rational equations with variables ...
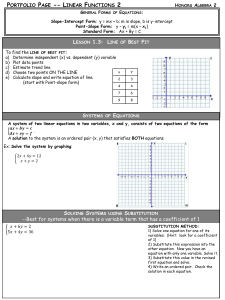
solving the system
... Each line has infinitely many pairs (x, y) that satisfy it. But taken together, only one pair (3, -2) satisfies both. Finding this pair is called solving the system. In 3.1, you learned to solve a system of two equations in two variables by graphing (approximation). In this section you will learn tw ...
... Each line has infinitely many pairs (x, y) that satisfy it. But taken together, only one pair (3, -2) satisfies both. Finding this pair is called solving the system. In 3.1, you learned to solve a system of two equations in two variables by graphing (approximation). In this section you will learn tw ...