Restrictive Cardiomyopathy in Cats
... with heart murmurs have conditions other than RCM, such as the more common hypertrophic cardiomyopathy). If congestive heart failure is already present at the time of diagnosis, other physical exam findings may be present, such as rapid and labored breathing. Breath sounds heard with a stethoscope m ...
... with heart murmurs have conditions other than RCM, such as the more common hypertrophic cardiomyopathy). If congestive heart failure is already present at the time of diagnosis, other physical exam findings may be present, such as rapid and labored breathing. Breath sounds heard with a stethoscope m ...
2circulatoryHeart
... chambers: an upper atrium and a lower ventricle (four chambers in total) • it is used to push blood through the body and provides a connection between our pulmonary and systemic circulatory systems • it is supplied by blood via the coronary arteries (come off main aorta) ...
... chambers: an upper atrium and a lower ventricle (four chambers in total) • it is used to push blood through the body and provides a connection between our pulmonary and systemic circulatory systems • it is supplied by blood via the coronary arteries (come off main aorta) ...
Sudden Cardiac Death
... What is Sudden Cardiac Death? Sudden cardiac death is an abrupt occurrence where the heart ceases to function and results in death within minutes. It is not a heart attack. It is usually due to a malfunction of the heart's electrical system that coordinates the heart muscle contraction to pump ...
... What is Sudden Cardiac Death? Sudden cardiac death is an abrupt occurrence where the heart ceases to function and results in death within minutes. It is not a heart attack. It is usually due to a malfunction of the heart's electrical system that coordinates the heart muscle contraction to pump ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
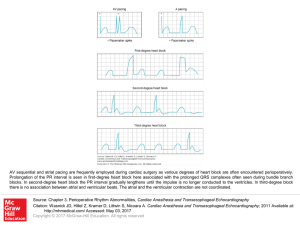
... AV sequential and atrial pacing are frequently employed during cardiac surgery as various degrees of heart block are often encountered perioperatively. Prolongation of the PR interval is seen in first-degree heart block here associated with the prolonged QRS complexes often seen during bundle branch ...
... AV sequential and atrial pacing are frequently employed during cardiac surgery as various degrees of heart block are often encountered perioperatively. Prolongation of the PR interval is seen in first-degree heart block here associated with the prolonged QRS complexes often seen during bundle branch ...
Intervention for congenital and structural heart disease: Beyond the
... the early 2000s and some excluded young infants. Technology has changed considerably: newer low profile balloons and techniques such as rapid right ventricular pacing has augmented the success of balloon valvuloplasty in this age group. It should be realised that both early balloon valvuloplasty as ...
... the early 2000s and some excluded young infants. Technology has changed considerably: newer low profile balloons and techniques such as rapid right ventricular pacing has augmented the success of balloon valvuloplasty in this age group. It should be realised that both early balloon valvuloplasty as ...
Heart Physiology Cardiac Conduction System Electrical System
... allow atria to finish contracting ...
... allow atria to finish contracting ...
As Powerpoint Slide
... Figure 1. Fibrosis of the aging heart. Cardiac aging is associated with significant alterations in cardiac structure and function. Elderly patients often present with left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction while the systolic function is usually preserved. Age-dependent remodeling of ...
... Figure 1. Fibrosis of the aging heart. Cardiac aging is associated with significant alterations in cardiac structure and function. Elderly patients often present with left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction while the systolic function is usually preserved. Age-dependent remodeling of ...
Cardiac Arrhythmia Center - New York Hospital Queens
... As The Heart Hospital of Queens, we are committed to ensuring that the diagnostic and treatment options physicians prefer are available for their patients right here. In the Cardiac Arrhythmia Center’s Electrophysiology Laboratory, you will find the techniques and the technology to treat all types ...
... As The Heart Hospital of Queens, we are committed to ensuring that the diagnostic and treatment options physicians prefer are available for their patients right here. In the Cardiac Arrhythmia Center’s Electrophysiology Laboratory, you will find the techniques and the technology to treat all types ...
cardiology - CatsTCMNotes.com
... stanols/sterols (2 g/day) and viscous (soluble) fiber (1025 g/day) Losing weight Increasing exercise ...
... stanols/sterols (2 g/day) and viscous (soluble) fiber (1025 g/day) Losing weight Increasing exercise ...
File
... valve does not close properly. Explain why this could be a problem. The systemic circulation is affected when the mitral valv is not functioning correctly. 5. Using what you have learned about the structure and function of the heart, explain why left ventricular hypertrophy can be fatal if left untr ...
... valve does not close properly. Explain why this could be a problem. The systemic circulation is affected when the mitral valv is not functioning correctly. 5. Using what you have learned about the structure and function of the heart, explain why left ventricular hypertrophy can be fatal if left untr ...
Electrocardiography - Westchester Medical Center
... Electrocardiography is a commonly used, noninvasive procedure for recording electrical changes in the heart. The record, which is called an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), shows the series of waves that relate to the electrical impulses which occur during each beat of the heart. An ECG is performed ...
... Electrocardiography is a commonly used, noninvasive procedure for recording electrical changes in the heart. The record, which is called an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), shows the series of waves that relate to the electrical impulses which occur during each beat of the heart. An ECG is performed ...
New-‐onset Heart Failure – diagnosis and iniºal management
... • Use of ‘Ultralinq’ to access echo result ...
... • Use of ‘Ultralinq’ to access echo result ...
Asymptomatic Left Ventricular Dysfunction and Diabetes
... Stages of CHF — ACC/AHA Guidelines 2005 Ammar et al. Circulation 2007;1151 563 ...
... Stages of CHF — ACC/AHA Guidelines 2005 Ammar et al. Circulation 2007;1151 563 ...
Cardiac Pathophysiology
... their flexibility. so it's harder for the ventricles to fill with blood between heartbeats. • Thickening often occurs due to abnormal tissue invading the heart muscle (Amyloid) and in elderly. ...
... their flexibility. so it's harder for the ventricles to fill with blood between heartbeats. • Thickening often occurs due to abnormal tissue invading the heart muscle (Amyloid) and in elderly. ...
Word Parts 10
... (felt) at any pulse point (usually radial artery in wrist area). The pulse may also be auscultated (heard with stethoscope) over the chest wall at the apex (bottom point) of the heart. Determining the pulse at the apex is referred to as an apical pulse. ...
... (felt) at any pulse point (usually radial artery in wrist area). The pulse may also be auscultated (heard with stethoscope) over the chest wall at the apex (bottom point) of the heart. Determining the pulse at the apex is referred to as an apical pulse. ...
l-Transposition of the Great Arteries
... have ventricular septal defects, obstruction to flow into the pulmonary artery, or leakage of the valve tricuspid valve. What causes it? The cause is unknown, but genetic factors may contribute to it. How does it affect the heart? In this condition, the blood is normally routed but the right ventric ...
... have ventricular septal defects, obstruction to flow into the pulmonary artery, or leakage of the valve tricuspid valve. What causes it? The cause is unknown, but genetic factors may contribute to it. How does it affect the heart? In this condition, the blood is normally routed but the right ventric ...
cardiovascular_system_quiz
... 7.The visceral layer is also known as the _____________. 8.Relaxation of the heart is also known as ____________. 9.T or F Cardiac output is the amount of blood ejected from each ventricle during a single contraction. 10.Blood is prevented from flowing back into the heart when the ventricles relax b ...
... 7.The visceral layer is also known as the _____________. 8.Relaxation of the heart is also known as ____________. 9.T or F Cardiac output is the amount of blood ejected from each ventricle during a single contraction. 10.Blood is prevented from flowing back into the heart when the ventricles relax b ...
Patient Page
... patient. The patient will tilt upright to stimulate a change in position. This test allows doctors to evaluate your body’s cardiovascular responds to changes in position 11. EECP: A non-invasive therapy that is performed outpatient to help improve heart health. This procedure takes about one hour. T ...
... patient. The patient will tilt upright to stimulate a change in position. This test allows doctors to evaluate your body’s cardiovascular responds to changes in position 11. EECP: A non-invasive therapy that is performed outpatient to help improve heart health. This procedure takes about one hour. T ...
Human Body in health and Disease CV sys
... 6. Trace a drop of blood from the superior vena cava to the lungs and from the lungs to the aorta. 7. Calculate the number of times your heart will beat in your lifetime. ...
... 6. Trace a drop of blood from the superior vena cava to the lungs and from the lungs to the aorta. 7. Calculate the number of times your heart will beat in your lifetime. ...
Icd 10 code for congestive heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
... preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (HFpEF). INTRODUCTION. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a clinical syndrome in which patients have symptoms and signs of HF with normal or near normal. Congestive heart failure occurs when the cardiac output is not adequate enough ...
... preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (HFpEF). INTRODUCTION. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a clinical syndrome in which patients have symptoms and signs of HF with normal or near normal. Congestive heart failure occurs when the cardiac output is not adequate enough ...
Management of Chronic Heart Failure in Adults: Synopsis of the
... Monitoring Patients With HF Moderate quality evidence Therapy guided by serum natriuretic peptide levels results in a reduction of hospitalizations due to HF Therapy guided by serum natriuretic peptide levels reduces mortality in persons younger than 75 Cost effective analysis demonstrated ...
... Monitoring Patients With HF Moderate quality evidence Therapy guided by serum natriuretic peptide levels results in a reduction of hospitalizations due to HF Therapy guided by serum natriuretic peptide levels reduces mortality in persons younger than 75 Cost effective analysis demonstrated ...
Lucia is an 8 year old girl who is a patient of Dr. Paulson who
... Lucia is an 8 year old girl who is a patient of Dr. Paulson who suffered a cardiac arrest in her front yard last spring. Mom did CPR and the police used a defibrillator to get her heart going again. She had an MRI that looked pretty bad and her parents were told she’d never walk or talk again. Howev ...
... Lucia is an 8 year old girl who is a patient of Dr. Paulson who suffered a cardiac arrest in her front yard last spring. Mom did CPR and the police used a defibrillator to get her heart going again. She had an MRI that looked pretty bad and her parents were told she’d never walk or talk again. Howev ...
The Heart - Northern Highlands
... The Heart Overview of Heart Anatomy: Use the following website to complete the following questions about the anatomy of the heart: http://www.worldinvisible.com/apologet/humbody/heart.htm ...
... The Heart Overview of Heart Anatomy: Use the following website to complete the following questions about the anatomy of the heart: http://www.worldinvisible.com/apologet/humbody/heart.htm ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.