Inside the Earth
... structural layers of Earth, including the inner core, outer core, mantle, crust, asthenosphere, and lithosphere. [6.10A] ...
... structural layers of Earth, including the inner core, outer core, mantle, crust, asthenosphere, and lithosphere. [6.10A] ...
The Earth`s Crust
... meet. When they meet they do not dip under one another. Instead they fold up into mountains such as the Himalayas and the Pyrenees. ...
... meet. When they meet they do not dip under one another. Instead they fold up into mountains such as the Himalayas and the Pyrenees. ...
Layers of the Earth
... • The very center of the earth • The inner core is solid. It is under so much pressure from the layers above that the metal cannot spread out and become liquid. THICKNESS: 1287 kilometers thick – From here to Dallas, TX TEMPERATURE: The inner core is very hot, about 9000 degrees fahrenheit COMPOSITI ...
... • The very center of the earth • The inner core is solid. It is under so much pressure from the layers above that the metal cannot spread out and become liquid. THICKNESS: 1287 kilometers thick – From here to Dallas, TX TEMPERATURE: The inner core is very hot, about 9000 degrees fahrenheit COMPOSITI ...
(>8.0 magnitude, past 100 yrs) Active Volcanoes
... 1. The crust and the upper mantle together make up a zone of rigid, brittle rock called the: ...
... 1. The crust and the upper mantle together make up a zone of rigid, brittle rock called the: ...
3earth layers
... Crust is thinnest layer, It varies from 5km thick (in the ocean floor) to around 70km thick (on land where we live called the continental crust). Mantle. The mantle is much thicker than the crust at almost 3000km deep. It's made up of slightly different silicate rocks with more magnesium and iron. T ...
... Crust is thinnest layer, It varies from 5km thick (in the ocean floor) to around 70km thick (on land where we live called the continental crust). Mantle. The mantle is much thicker than the crust at almost 3000km deep. It's made up of slightly different silicate rocks with more magnesium and iron. T ...
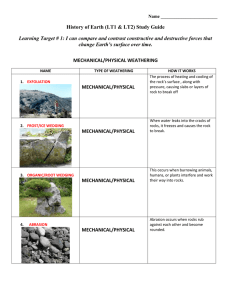
History of Earth Study Guide
... q. Flooding caused by a rainstorm QUICK r. Formation of a tornado QUICK **Compare the time it takes for each, compared, to the other moreso than knowing SLOW or QUICK. 2. Define WEATHERING. Wearing or breaking down; physical and chemical 3. Define EROSION. Moving or carrying away sediment; Sand Dune ...
... q. Flooding caused by a rainstorm QUICK r. Formation of a tornado QUICK **Compare the time it takes for each, compared, to the other moreso than knowing SLOW or QUICK. 2. Define WEATHERING. Wearing or breaking down; physical and chemical 3. Define EROSION. Moving or carrying away sediment; Sand Dune ...
Dynamic Earth WebQuest
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time B ...
... 8. Plate Tectonics Theory has been widely accepted since the ___________’s. It states that Earth’s outer layer or _________________ is broken up into ________________. These plates hold ______________________ and _____________________. They are constantly _________________. 9. Continents over time B ...
Kump_Ch07_TH - Camosun College
... • For the largest earthquakes, the earth “rings like a bell” and vibrates for days. • Elastic waves reflect from and refract through internal layers with different rigidity & density • Speed of sound in rock varies as a function of temperature, pressure and composition • This is useful to provide in ...
... • For the largest earthquakes, the earth “rings like a bell” and vibrates for days. • Elastic waves reflect from and refract through internal layers with different rigidity & density • Speed of sound in rock varies as a function of temperature, pressure and composition • This is useful to provide in ...
Convection currents
... The Mantle is the largest layer of the Earth. The middle mantle is composed of very hot dense rock that flows like asphalt. The movement of the middle mantle (asthenosphere) is the reason that the crustal plates of the Earth move. ...
... The Mantle is the largest layer of the Earth. The middle mantle is composed of very hot dense rock that flows like asphalt. The movement of the middle mantle (asthenosphere) is the reason that the crustal plates of the Earth move. ...
Oceanography 101 Linda Khandro, MAT Homework 2: Opening the
... The rocks just off the west coast of Spain formed during the Early Cretaceous. At that time, when Spain broke away from the Grand Banks, seafloor basalt would have begun to flow into the space between them. ...
... The rocks just off the west coast of Spain formed during the Early Cretaceous. At that time, when Spain broke away from the Grand Banks, seafloor basalt would have begun to flow into the space between them. ...
No Slide Title
... Some seismic waves–energy associated with earthquakes–can pass through Earth. Analysis of how these waves are changed, and the time required for their passage, has told researchers much about conditions inside Earth. Earth is composed of concentric spherical layers, with the least dense layer on the ...
... Some seismic waves–energy associated with earthquakes–can pass through Earth. Analysis of how these waves are changed, and the time required for their passage, has told researchers much about conditions inside Earth. Earth is composed of concentric spherical layers, with the least dense layer on the ...
Chapter 03
... Some seismic waves–energy associated with earthquakes–can pass through Earth. Analysis of how these waves are changed, and the time required for their passage, has told researchers much about conditions inside Earth. Earth is composed of concentric spherical layers, with the least dense layer on the ...
... Some seismic waves–energy associated with earthquakes–can pass through Earth. Analysis of how these waves are changed, and the time required for their passage, has told researchers much about conditions inside Earth. Earth is composed of concentric spherical layers, with the least dense layer on the ...
Plate Tectonics Inside Earth Chapter 1 Study
... a. The mantle is the layer of hot solid material between the Earth’s crust and core. b. The uppermost part of the mantle and the crust together form a very rigid layer called the lithosphere. c. Temperature and pressure increase as the depth increases. d. The heat and pressure make the part of the m ...
... a. The mantle is the layer of hot solid material between the Earth’s crust and core. b. The uppermost part of the mantle and the crust together form a very rigid layer called the lithosphere. c. Temperature and pressure increase as the depth increases. d. The heat and pressure make the part of the m ...
Mountains, Volcanoes and Boundaries Quiz
... Eurasian Plate and Indo-Australian Plate Scientists have studied convergent boundaries and the results of the collisions. Besides the fact that mountains occur at these boundaries, which other part of the rock cycle is most likely associated with these areas of ...
... Eurasian Plate and Indo-Australian Plate Scientists have studied convergent boundaries and the results of the collisions. Besides the fact that mountains occur at these boundaries, which other part of the rock cycle is most likely associated with these areas of ...
Structural Geology 1
... Faults grind rocks to create fault gouge. Walls of a fault bear evidence of this ...
... Faults grind rocks to create fault gouge. Walls of a fault bear evidence of this ...
Earths Interior- Milky Way
... CRUST or LITHOSPHERE – thin, brittle, hard, cold, solid outer shell INNER CORE – hot, solid (very high pressure, contains heavy metals) OUTER CORE – so hot, even pressure can’t force it into a solid. This layer is a liquid Cut the Milky Way bar in half: Label the three layers of the bar according to ...
... CRUST or LITHOSPHERE – thin, brittle, hard, cold, solid outer shell INNER CORE – hot, solid (very high pressure, contains heavy metals) OUTER CORE – so hot, even pressure can’t force it into a solid. This layer is a liquid Cut the Milky Way bar in half: Label the three layers of the bar according to ...
FORCES ON EARTH - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is one of the world’s largest divergent plates, running North to South in just about the center of the Atlantic Ocean. All along this ridge, volcanic activity takes place and the sea floor is spreading East and West at a rate of ...
... The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is one of the world’s largest divergent plates, running North to South in just about the center of the Atlantic Ocean. All along this ridge, volcanic activity takes place and the sea floor is spreading East and West at a rate of ...
Study Guide Answers
... Oceanic crust is denser so when it converges with the continental plate causes subduction. The oceanic plate melts and convection currents recycle it back to point A 5. What is the main cause for earthquakes and volcanoes? Plate tectonics, plate movement, one plate moving past another either by conv ...
... Oceanic crust is denser so when it converges with the continental plate causes subduction. The oceanic plate melts and convection currents recycle it back to point A 5. What is the main cause for earthquakes and volcanoes? Plate tectonics, plate movement, one plate moving past another either by conv ...
Development of the Theory of Plate Tectonics
... The theory of plate tectonics states that the Earth's lithosphere is made up individual plates that are broken down into over a dozen large and small pieces of solid rock. ...
... The theory of plate tectonics states that the Earth's lithosphere is made up individual plates that are broken down into over a dozen large and small pieces of solid rock. ...
Jamies Group - Junee North Public School
... circles stones are 26 feet high and the outer circles stones are 10 feet high. There are two types of stones used in the construction of Stonehenge. The large outer circle is made of Sarsen which is sedimentary Sandstone and the inner circle is made of Bluestone which is a blend of Basalt and Gabbro ...
... circles stones are 26 feet high and the outer circles stones are 10 feet high. There are two types of stones used in the construction of Stonehenge. The large outer circle is made of Sarsen which is sedimentary Sandstone and the inner circle is made of Bluestone which is a blend of Basalt and Gabbro ...
Plate tectonics - s3.amazonaws.com
... Convection Currents and the Mantle Convection – heat transfer by the movement of heated fluid (liquid or gas). This is what makes tectonic plates move. -Convection oven or heating soup -Wind in the atmosphere -Heat from the Earth’s core and the mantle itself causes convection currents in the mantle ...
... Convection Currents and the Mantle Convection – heat transfer by the movement of heated fluid (liquid or gas). This is what makes tectonic plates move. -Convection oven or heating soup -Wind in the atmosphere -Heat from the Earth’s core and the mantle itself causes convection currents in the mantle ...
Grade 6: Earth Science
... ridges, and the distribution of fossils, rock types, and ancient climatic zones provide evidence for plate tectonics. b. the solid Earth is layered with cold, brittle lithosphere; hot, convecting mantle; and dense, metallic core. c. lithospheric plates that are the size of continents and oceans move ...
... ridges, and the distribution of fossils, rock types, and ancient climatic zones provide evidence for plate tectonics. b. the solid Earth is layered with cold, brittle lithosphere; hot, convecting mantle; and dense, metallic core. c. lithospheric plates that are the size of continents and oceans move ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.