It`s your fault - Westminster Public Schools Wiki
... 2. If you were standing at point F and looking across the fault, which way did the block on the opposite side move? 3. What happened to rock layers X, Y, and Z? 4. Are the rock layers still continuous? 5. What likely happened to the river? the road? the railroad tracks? 6. If the scale used in this ...
... 2. If you were standing at point F and looking across the fault, which way did the block on the opposite side move? 3. What happened to rock layers X, Y, and Z? 4. Are the rock layers still continuous? 5. What likely happened to the river? the road? the railroad tracks? 6. If the scale used in this ...
Handout 1 (2-3) pink Chapter 10 Section 2 Directed Reading Pages
... 9. In addition to volcanoes, what also occurs frequently in the Pacific Ring of Fire? TYPES OF PLATE BOUNDARIES (page 249-251) 10. What happens to magma at divergent boundaries? ...
... 9. In addition to volcanoes, what also occurs frequently in the Pacific Ring of Fire? TYPES OF PLATE BOUNDARIES (page 249-251) 10. What happens to magma at divergent boundaries? ...
Plate Tectonics Unit Test Study Guide
... 3. Stratovolcano – Have explosive eruptions because of more gassy magma; formed by layers of ash and lava ...
... 3. Stratovolcano – Have explosive eruptions because of more gassy magma; formed by layers of ash and lava ...
Crowded Coasts - SLC Geog A Level Blog
... the softer rocks from erosion. • (If there is local tectonic movements or sea level change (eustatic) then islands may form when separated from the mainland by drowned valleys eg Croatia’s Dalmation Coast) ...
... the softer rocks from erosion. • (If there is local tectonic movements or sea level change (eustatic) then islands may form when separated from the mainland by drowned valleys eg Croatia’s Dalmation Coast) ...
Chapter 6 - SchoolRack
... Wegener Theory of Continental Drift In the early 1900’s Alfred Wegener wrote a book about his theory of continental drift Continental drift - is the theory that continents can drift apart from one another and have done so in the past Does this help explain why the continents could fit togethe ...
... Wegener Theory of Continental Drift In the early 1900’s Alfred Wegener wrote a book about his theory of continental drift Continental drift - is the theory that continents can drift apart from one another and have done so in the past Does this help explain why the continents could fit togethe ...
Plate Tectonics Webquest - Ms. Murray`s Class Website
... How long ago did the Earths crust solidify?_______________________ Is the crust a solid shell? No Yes ...
... How long ago did the Earths crust solidify?_______________________ Is the crust a solid shell? No Yes ...
ANSWER KEY Lesson One: Layers of the Earth Vocabulary Station
... - below lithosphere - asphalt-like consistency - as it flows, it moves the plates of the Earth ...
... - below lithosphere - asphalt-like consistency - as it flows, it moves the plates of the Earth ...
MovingPlates
... 2 or more plates slide past each other slowly at a fault. Stress builds up in the rocks over time and slippage occurs abruptly. The energy released causes an earthquake. Features: fault, shallow hypocenter earthquakes Ex. = San Andreas Fault, California (N. Am plate + Pacific plate) ...
... 2 or more plates slide past each other slowly at a fault. Stress builds up in the rocks over time and slippage occurs abruptly. The energy released causes an earthquake. Features: fault, shallow hypocenter earthquakes Ex. = San Andreas Fault, California (N. Am plate + Pacific plate) ...
Stress and Strain - El Molino High School
... critical point. At these breaks, rocks can move, releasing the energy built up as a result of stress. Earthquakes are the result of this movement and release of energy. ...
... critical point. At these breaks, rocks can move, releasing the energy built up as a result of stress. Earthquakes are the result of this movement and release of energy. ...
How Plates Create
... Lava erupts through narrow cracks along the ridge, adding new rock to the ocean floor. ...
... Lava erupts through narrow cracks along the ridge, adding new rock to the ocean floor. ...
Study Guide Key-Layers of the Earth Continental Drift
... b) Fossil Evidence-similar plants & animals are found on different continents i.e. the Mesosaurus was found on both Africa and South America c) Mountain Ranges and coal beds -Mountain ranges of similar size and rock content are found on different continents (sometimes coal beds match) d) Paleoclimat ...
... b) Fossil Evidence-similar plants & animals are found on different continents i.e. the Mesosaurus was found on both Africa and South America c) Mountain Ranges and coal beds -Mountain ranges of similar size and rock content are found on different continents (sometimes coal beds match) d) Paleoclimat ...
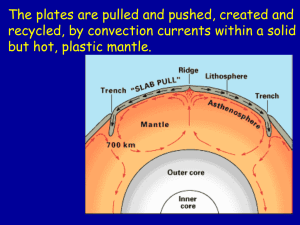
Part IV: Plate Tectonics, Topography and Ecology Due: 5/23 1. What
... Continental Drift – idea that continents have slowly moved to their current locations over time Alfred Wegner. Seafloor Spreading – theory that new seafloor is formed when hot magma is forced upward toward the surface at a mid-ocean ridge Harry Hess. Plate Tectonics - theory that Earth’s crust ...
... Continental Drift – idea that continents have slowly moved to their current locations over time Alfred Wegner. Seafloor Spreading – theory that new seafloor is formed when hot magma is forced upward toward the surface at a mid-ocean ridge Harry Hess. Plate Tectonics - theory that Earth’s crust ...
8-Plate_Tectonics short
... creating new crust or destroying old crust (no rock melts), so no mountains or volcanoes; grinding two blocks of crust past each other, so lots of EQ's (major + minor). ...
... creating new crust or destroying old crust (no rock melts), so no mountains or volcanoes; grinding two blocks of crust past each other, so lots of EQ's (major + minor). ...
Physical Processes WG2b
... • Scientists cannot predict when volcanoes will erupt. • People live near volcanoes because volcanic ash is extremely fertile and good for farming. ...
... • Scientists cannot predict when volcanoes will erupt. • People live near volcanoes because volcanic ash is extremely fertile and good for farming. ...
Chapter 10: Section 1 Continental Drift
... • Over time, all of the continents collide to form a supercontinent. • Then, heat from Earth’s interior builds up under the supercontinent, and rifts form in the supercontinent. The supercontinent breaks apart, and plates carrying separate continents move around the globe. Formation of Pangaea • The ...
... • Over time, all of the continents collide to form a supercontinent. • Then, heat from Earth’s interior builds up under the supercontinent, and rifts form in the supercontinent. The supercontinent breaks apart, and plates carrying separate continents move around the globe. Formation of Pangaea • The ...
Classification and Occurrence of Igneous Rocks
... Mode – mineral content of rock on a volume basis. Either visually estimated or determined by point counting Norm – calculated mineral content of a rock on a weight percent basis. Chemistry of the rock is converted to ideal minerals. ...
... Mode – mineral content of rock on a volume basis. Either visually estimated or determined by point counting Norm – calculated mineral content of a rock on a weight percent basis. Chemistry of the rock is converted to ideal minerals. ...
Discovering Plate Boundaries
... Goal: Students will be able to explain and justify conclusions based on data, maps, and diagrams about the formation and boundaries of geologic features due to tectonic plate movement. Background: The Earth’s outermost layer is fragmented into plates that are moving relative to one another as they s ...
... Goal: Students will be able to explain and justify conclusions based on data, maps, and diagrams about the formation and boundaries of geologic features due to tectonic plate movement. Background: The Earth’s outermost layer is fragmented into plates that are moving relative to one another as they s ...
Earthquake destruction and seismic waves Page 1 of 3 I. Factors
... a. due to increased pressure enhancing elastic properties of rock b. results in curved paths of seismic waves through Earth 2.abrupt velocity changes of waves at particular depths—causes refraction of waves a. S waves travel only through solids b. allows us to model Earth’s interior based on seismic ...
... a. due to increased pressure enhancing elastic properties of rock b. results in curved paths of seismic waves through Earth 2.abrupt velocity changes of waves at particular depths—causes refraction of waves a. S waves travel only through solids b. allows us to model Earth’s interior based on seismic ...
Geology Lab: "Edible Tectonics"
... BACKGROUND INFORMATION (Must be read before performing lab!) Plate Tectonics is Geology’s most important theory – it explains so much about our planet! Most volcanoes and earthquakes occur along the boundaries of tectonic plates. This theory also explains how certain surface features such as mou ...
... BACKGROUND INFORMATION (Must be read before performing lab!) Plate Tectonics is Geology’s most important theory – it explains so much about our planet! Most volcanoes and earthquakes occur along the boundaries of tectonic plates. This theory also explains how certain surface features such as mou ...
White et al Nice abstract
... new acquisition on the Atlantic volcanic margins with new techniques for modelling their evolution. We discuss the distribution of igneous rocks along the North Atlantic margins and discuss the temporal and spatial variations in the Iceland mantle plume in the early Tertiary, which have largely cont ...
... new acquisition on the Atlantic volcanic margins with new techniques for modelling their evolution. We discuss the distribution of igneous rocks along the North Atlantic margins and discuss the temporal and spatial variations in the Iceland mantle plume in the early Tertiary, which have largely cont ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.