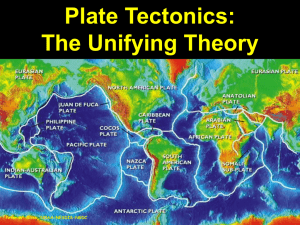
Chapter 6
... • The process of subduction is the movement of one tectonic plate underneath another • Subduction causes an increase in temperature and pressure causing the water in the oceanic crust to be released; it mixes with the mantle rock, which lowers the rock’s melting point, causing it to melt. This body ...
... • The process of subduction is the movement of one tectonic plate underneath another • Subduction causes an increase in temperature and pressure causing the water in the oceanic crust to be released; it mixes with the mantle rock, which lowers the rock’s melting point, causing it to melt. This body ...
APES Chapter 10
... (iron) which gives the Earth its magnetic poles. Mantle—thick solid zone consisting of iron, silicon, oxygen, and magnesium. The outermost layer of the mantle is a thin plastic layer of partially molten rock— the asthenosphere Crust—outermost and thinnest zone of the Earth ...
... (iron) which gives the Earth its magnetic poles. Mantle—thick solid zone consisting of iron, silicon, oxygen, and magnesium. The outermost layer of the mantle is a thin plastic layer of partially molten rock— the asthenosphere Crust—outermost and thinnest zone of the Earth ...
Geology/hydrology of the Chehalis River
... • This is where the Juan de Fuca oceanic plate dives beneath North America and sinks into the earth’s deep mantle. • This zone of plate convergence is called the Cascadia subduction zone, and it is the source of our rocks, geologic hazards, and landscape. ...
... • This is where the Juan de Fuca oceanic plate dives beneath North America and sinks into the earth’s deep mantle. • This zone of plate convergence is called the Cascadia subduction zone, and it is the source of our rocks, geologic hazards, and landscape. ...
Plate Tectonics Webquest (9/16) - Liberty Union High School District
... Los Angeles is 630 km (380 miles) southeast of San Francisco. The plate under L.A. is moving northward at about 36 mm per year relative to the plate under San Fran. Given this average rate of plate movement, how long will take for L.A. to be located next to San Fran? The distance traveled is 630 km, ...
... Los Angeles is 630 km (380 miles) southeast of San Francisco. The plate under L.A. is moving northward at about 36 mm per year relative to the plate under San Fran. Given this average rate of plate movement, how long will take for L.A. to be located next to San Fran? The distance traveled is 630 km, ...
3.1 Notes
... • The smallest magnitude that can be felt is 2.0, and the largest magnitude ever recorded is 9.5. Magnitudes greater than 7.0 cause widespread damage. • Each increase of magnitude by one whole number indicates the release of 31.7 times more energy than the whole number below it. ...
... • The smallest magnitude that can be felt is 2.0, and the largest magnitude ever recorded is 9.5. Magnitudes greater than 7.0 cause widespread damage. • Each increase of magnitude by one whole number indicates the release of 31.7 times more energy than the whole number below it. ...
The evolution of circum-Antarctic oceanic crust since cretaceous
... palaeo-oceanography and marine sedimentation are controlled by plate tectonics through the distribution of land masses and ocean basins (geometry and geography), the opening and closing of oceanic gateways, and changes in topography both on land and at sea. New geological and geophysical datasets an ...
... palaeo-oceanography and marine sedimentation are controlled by plate tectonics through the distribution of land masses and ocean basins (geometry and geography), the opening and closing of oceanic gateways, and changes in topography both on land and at sea. New geological and geophysical datasets an ...
Unit 1
... 1. Where two continental plates meet, there is a build-up of crust into mountain ranges such as the Himalayan Mountains in Asia. 2. Where a thicker continental plate meets a thinner oceanic plate, a subduction zone exists. This subduction zone creates massive volcanic activity. The Japan Islands wer ...
... 1. Where two continental plates meet, there is a build-up of crust into mountain ranges such as the Himalayan Mountains in Asia. 2. Where a thicker continental plate meets a thinner oceanic plate, a subduction zone exists. This subduction zone creates massive volcanic activity. The Japan Islands wer ...
Student Notes - Herzog
... This disappearance of S-waves has allowed seismologists to reason that Earth’s outer core must be liquid. Detailed studies of how other seismic waves reflect deep within Earth show that Earth’s inner core is solid. The travel times and behavior of seismic waves provide a detailed picture of Earth’s ...
... This disappearance of S-waves has allowed seismologists to reason that Earth’s outer core must be liquid. Detailed studies of how other seismic waves reflect deep within Earth show that Earth’s inner core is solid. The travel times and behavior of seismic waves provide a detailed picture of Earth’s ...
Oceanic Crust
... • The subducting plate is bent downward to form a very deep depression in the ocean floor called a trench. • The worlds deepest parts of the ocean are found along ...
... • The subducting plate is bent downward to form a very deep depression in the ocean floor called a trench. • The worlds deepest parts of the ocean are found along ...
P waves
... • Strike-slip Faults – When shear forces cause rocks to move past one another in opposite directions on Earth’s surface Rocks do not move up or down, but rather move side by side ...
... • Strike-slip Faults – When shear forces cause rocks to move past one another in opposite directions on Earth’s surface Rocks do not move up or down, but rather move side by side ...
Earth`s Magnetic Field, Atmosphere and Geology
... • Earth also has larger-scale processes that other planets don’t have: plate tectonics. • Earth’s crust is divided up into about 20 large pieces or plates of rigid crust that float on top of flowing mantle. • Where these plates come together or pull apart is where we get mid-ocean ridges, chains of ...
... • Earth also has larger-scale processes that other planets don’t have: plate tectonics. • Earth’s crust is divided up into about 20 large pieces or plates of rigid crust that float on top of flowing mantle. • Where these plates come together or pull apart is where we get mid-ocean ridges, chains of ...
continental-drift-and-the-theory-of-plate-tectonics-fran-et-al
... The size of the earth was much smaller than it is today and so all continents were together as a single huge land mass (called Pangea) then and as earth continued grow in size all these continents looked like as if they are moving apart whereas they actually have just reached their current positions ...
... The size of the earth was much smaller than it is today and so all continents were together as a single huge land mass (called Pangea) then and as earth continued grow in size all these continents looked like as if they are moving apart whereas they actually have just reached their current positions ...
Continental Drift
... Oldest land - billions of years With seafloor spreading, is the earth expanding? Why is seafloor so young relative to continents? SUBDUCTION “law of conservation of ocean floor” ...
... Oldest land - billions of years With seafloor spreading, is the earth expanding? Why is seafloor so young relative to continents? SUBDUCTION “law of conservation of ocean floor” ...
Edible Tectonics
... 3. Hold the candy bar over the paper towel, and with one hand holding each end of the candy bar, gently pull in opposite directions. The candy bar should stretch slowly and pull apart at the center. ...
... 3. Hold the candy bar over the paper towel, and with one hand holding each end of the candy bar, gently pull in opposite directions. The candy bar should stretch slowly and pull apart at the center. ...
Footwall uplift during normal faulting
... Abstract: In recent years, studies of major normal faults in actively extending regions (Aegean, Basin and Range) have documented the vertical motions associated with normal faulting. In addition to the expected subsidence of the hanging wall, it has been found that uplift of the footwall occurs dur ...
... Abstract: In recent years, studies of major normal faults in actively extending regions (Aegean, Basin and Range) have documented the vertical motions associated with normal faulting. In addition to the expected subsidence of the hanging wall, it has been found that uplift of the footwall occurs dur ...
Evidence for Sea-Floor Spreading
... Guide For Reading: What is the process of sea-floor spreading? • At the mid-ocean ridge, molten material rises from the mantle and erupts. The molten material then spreads out, pushing older rock to both sides of the ridge. • Over tens of millions of years, the process continues until the oldest oc ...
... Guide For Reading: What is the process of sea-floor spreading? • At the mid-ocean ridge, molten material rises from the mantle and erupts. The molten material then spreads out, pushing older rock to both sides of the ridge. • Over tens of millions of years, the process continues until the oldest oc ...
Chapter 4
... geoscience • Integrates from many branches • First suggested based on geology and paleontology • Fully embraced after evidence from geophysics ...
... geoscience • Integrates from many branches • First suggested based on geology and paleontology • Fully embraced after evidence from geophysics ...
Earth Science Questions and Answers for Teachers Teaching Grade 6
... When the continental plates of today are returned to their super-continent positions (through computer modeling), the fossil and sedimentary evidence of ancient life distributions and climate becomes coherent, providing strong support for the existence of Pangaea. As plates move in relation to one a ...
... When the continental plates of today are returned to their super-continent positions (through computer modeling), the fossil and sedimentary evidence of ancient life distributions and climate becomes coherent, providing strong support for the existence of Pangaea. As plates move in relation to one a ...
The structure of the earth – a plenary
... This liquid layer is made of iron and nickel. It is extremely hot in this layer. ...
... This liquid layer is made of iron and nickel. It is extremely hot in this layer. ...
Story of the Red Centre
... Continental crust, being lighter than oceanic crust, tends to float above subduction zones, so two continental blocks interacting at a subduction zone get pushed together rather than being drawn down with the oceanic crust. Subduction zones, or convergent margins, are one of the three types of plate ...
... Continental crust, being lighter than oceanic crust, tends to float above subduction zones, so two continental blocks interacting at a subduction zone get pushed together rather than being drawn down with the oceanic crust. Subduction zones, or convergent margins, are one of the three types of plate ...
Climate Change
... involved have low incomes and depend on the land for their sustenance. If a country compels people to leave when no disaster ensues, the authorities can appear heavy handed. If they fail to evacuate then they appear to have not been taking due care. ...
... involved have low incomes and depend on the land for their sustenance. If a country compels people to leave when no disaster ensues, the authorities can appear heavy handed. If they fail to evacuate then they appear to have not been taking due care. ...
Department of Chemistry, Physics, and Earth Sciences
... A. Listing and describing the types of glaciers. B. Describing glacial formation and movement. C. Describing glacial erosion and deposition and classifying associated glacial features. D. Predicting evidence of past climates and discussing Ice Ages and their possible causes. E. Discussing wind and i ...
... A. Listing and describing the types of glaciers. B. Describing glacial formation and movement. C. Describing glacial erosion and deposition and classifying associated glacial features. D. Predicting evidence of past climates and discussing Ice Ages and their possible causes. E. Discussing wind and i ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.