Department of Chemistry, Physics, and Earth Sciences
... A. Listing and describing the types of glaciers. B. Describing glacial formation and movement. C. Describing glacial erosion and deposition and classifying associated glacial features. D. Predicting evidence of past climates and discussing Ice Ages and their possible causes. E. Discussing wind and i ...
... A. Listing and describing the types of glaciers. B. Describing glacial formation and movement. C. Describing glacial erosion and deposition and classifying associated glacial features. D. Predicting evidence of past climates and discussing Ice Ages and their possible causes. E. Discussing wind and i ...
Do Now - Barren County Schools
... EQ- What are tectonic plates? What causes plate movement? What are the three types of plate boundaries? OBJ- I can demonstrate understanding of plate boundaries by completing a graphic organizer of the boundaries and creating a puzzle of the Earth’s plates with 80% or higher accuracy. Instructional ...
... EQ- What are tectonic plates? What causes plate movement? What are the three types of plate boundaries? OBJ- I can demonstrate understanding of plate boundaries by completing a graphic organizer of the boundaries and creating a puzzle of the Earth’s plates with 80% or higher accuracy. Instructional ...
Name Period
... 4. Wegener hypothesized that the continents formed part of a single land mass, or __________________. a. mid-ocean ridge. b. monocontinent. c. supercontinent. d. world land. 5. When did Wegener think that small continents began forming? ____________________________. a. 25 million years ago. b. 2.5 b ...
... 4. Wegener hypothesized that the continents formed part of a single land mass, or __________________. a. mid-ocean ridge. b. monocontinent. c. supercontinent. d. world land. 5. When did Wegener think that small continents began forming? ____________________________. a. 25 million years ago. b. 2.5 b ...
What brought them up? Exhumation of the Dabie Shan ultrahigh
... dextral-oblique displacement recorded by subgreenschist facies minerals. In the Dabie Shan the fault does not contain high-temperature ductile structures required by models (Yin and Nie, 1993) that postulate its development as a major transcurrent fault during continental collision. TECTONIC IMPLICA ...
... dextral-oblique displacement recorded by subgreenschist facies minerals. In the Dabie Shan the fault does not contain high-temperature ductile structures required by models (Yin and Nie, 1993) that postulate its development as a major transcurrent fault during continental collision. TECTONIC IMPLICA ...
Chapter 9 Volcanoes
... melting of rock. Increase in temp (DUH!). These are called hot spots. Increase of water in the ...
... melting of rock. Increase in temp (DUH!). These are called hot spots. Increase of water in the ...
Rocks and Glaciers A Story of Sedimentation
... mud cracks & ripple marks, Mt. Reynolds, U-shaped valley and glacial lakes, Blackfoot glacier with crevasses, glacier carved ...
... mud cracks & ripple marks, Mt. Reynolds, U-shaped valley and glacial lakes, Blackfoot glacier with crevasses, glacier carved ...
Subduction zones
... asthenosphere and the materials of the oceanic plate recycle back into the asthenosphere. The ocean plate was originally created at a mid-ocean ridge millions of years before is now recycled back. This process ranges from 150 to 200 million years. Tectonic Processes at Subduction Zones Visit the fol ...
... asthenosphere and the materials of the oceanic plate recycle back into the asthenosphere. The ocean plate was originally created at a mid-ocean ridge millions of years before is now recycled back. This process ranges from 150 to 200 million years. Tectonic Processes at Subduction Zones Visit the fol ...
Freshwater reptile Mesosaurus
... Evidence that supported Wegener’s Theory 1. Change in Climate –Example: Glaciers in Africa Glacial striations, the parallel "scrape" marks on rocks caused by moving glaciers, have been found on rocks in South America, Africa and Australia and are of similar orientation to striations found on Antarc ...
... Evidence that supported Wegener’s Theory 1. Change in Climate –Example: Glaciers in Africa Glacial striations, the parallel "scrape" marks on rocks caused by moving glaciers, have been found on rocks in South America, Africa and Australia and are of similar orientation to striations found on Antarc ...
key - Scioly.org
... 11. What is the east coast of the United States an example of? a. Active continental margin b. Convergent ptate boundary c. Divergent plate boundary d. Passive continental margin e. Transform plate boundary 12. What is the San Andreas Fault in southern California an example of? ...
... 11. What is the east coast of the United States an example of? a. Active continental margin b. Convergent ptate boundary c. Divergent plate boundary d. Passive continental margin e. Transform plate boundary 12. What is the San Andreas Fault in southern California an example of? ...
Plate Boundaries-new
... Presentation Objectives: § Define the theory of plate tectonics. § Explain how the Earth is divided into layers based on chemical and physical properties. § Define the asthenosphere and lithosphere. § Describe the plate motion at each of the three different plate boundaries. § Describe the feat ...
... Presentation Objectives: § Define the theory of plate tectonics. § Explain how the Earth is divided into layers based on chemical and physical properties. § Define the asthenosphere and lithosphere. § Describe the plate motion at each of the three different plate boundaries. § Describe the feat ...
Physical Geology 14e Plummer TB
... 55. Disintegration of rock at Earth's surface may be facilitated by water __. A. flowing on the surface in streams and as runoff B. frozen in a glacier that is flowing over the surface C. moving through near-surface pores and fractures D. present as vapor in the atmosphere E. All of the answers are ...
... 55. Disintegration of rock at Earth's surface may be facilitated by water __. A. flowing on the surface in streams and as runoff B. frozen in a glacier that is flowing over the surface C. moving through near-surface pores and fractures D. present as vapor in the atmosphere E. All of the answers are ...
Return
... a large continent called Pangaea. Wegener suggested they broke apart and made today’s continents. Theory says all continents drifted apart and continue to do so. ...
... a large continent called Pangaea. Wegener suggested they broke apart and made today’s continents. Theory says all continents drifted apart and continue to do so. ...
EGU2012-6051
... thermal state of the mantle. In the present study we will present a number of 3D spherical numerical simulations of mantle convection with self-consistently generated plates and compositionally and rheologically-distinct continents floating at the top of the mantle. We will focus on the question of ...
... thermal state of the mantle. In the present study we will present a number of 3D spherical numerical simulations of mantle convection with self-consistently generated plates and compositionally and rheologically-distinct continents floating at the top of the mantle. We will focus on the question of ...
Section 1 What Are Earthquakes?
... As tectonic plates move, stress on rocks near the edges of the plates increases. In response to this stress, the rock deforms, or changes shape. Rock deforms in mainly two ways. It can deform in a plastic manner, like a piece of clay being molded. Folded rocks, such as the ones shown in Figure 6, ar ...
... As tectonic plates move, stress on rocks near the edges of the plates increases. In response to this stress, the rock deforms, or changes shape. Rock deforms in mainly two ways. It can deform in a plastic manner, like a piece of clay being molded. Folded rocks, such as the ones shown in Figure 6, ar ...
Plate boudaries
... continental plate because it is denser. As the plate descends it starts to melt due to the friction caused by the movement between the plates. This melted plate is now hot, liquid rock (magma). The magma rises through the gaps in the continental plate. If it reaches the surface, the liquid rock form ...
... continental plate because it is denser. As the plate descends it starts to melt due to the friction caused by the movement between the plates. This melted plate is now hot, liquid rock (magma). The magma rises through the gaps in the continental plate. If it reaches the surface, the liquid rock form ...
Key concepts
... -know the difference between oceanic crust & continental crust -know how pressure and temperature change as you move through the layers of the earth and their effects on the behavior of rocks -know the internal source of heat inside the earth and how heat moves by conduction or convection -know how ...
... -know the difference between oceanic crust & continental crust -know how pressure and temperature change as you move through the layers of the earth and their effects on the behavior of rocks -know the internal source of heat inside the earth and how heat moves by conduction or convection -know how ...
Plate Tectonics
... http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html & http://www.geology.com ...
... http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html & http://www.geology.com ...
09_chapter 2
... shield is a mosaic of such cratons and mobile belts. It consists of mainly four Archean ...
... shield is a mosaic of such cratons and mobile belts. It consists of mainly four Archean ...
Inquiry 15.1 - Using a Simple Model of Plate
... 8) Can plates ever move without forming new land? If so, when? ____________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 9) How do you think colliding plates on the earth cause earthquakes? ___________________________ ...
... 8) Can plates ever move without forming new land? If so, when? ____________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 9) How do you think colliding plates on the earth cause earthquakes? ___________________________ ...
Week 2: Huerta Climate PPT
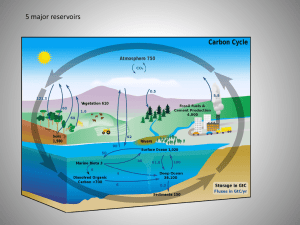
... 5 major reservoirs: atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere, oceans (and ocean critters), sediments, earth’s interior ...
... 5 major reservoirs: atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere, oceans (and ocean critters), sediments, earth’s interior ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.