Review for CFE-answers
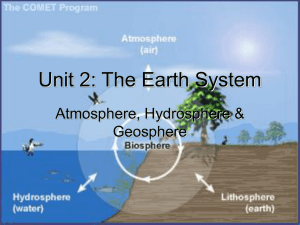
... 39. Describe and compare and contrast Earth systems, atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, geosphere, biosphere pg NS8-NS10 Atmosphere- gaseous envelope that surrounds the earth made mainly of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapor Hydrosphere- water on/in the earth and in the atmosphere. ...
... 39. Describe and compare and contrast Earth systems, atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, geosphere, biosphere pg NS8-NS10 Atmosphere- gaseous envelope that surrounds the earth made mainly of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapor Hydrosphere- water on/in the earth and in the atmosphere. ...
Earth System PP slides
... oxide) and silica-rich minerals • Struggle between oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor environment ...
... oxide) and silica-rich minerals • Struggle between oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor environment ...
Human Population
... Environmental science has so many interacting parts, it is not easy to apply one system to another. Human well-being is a concern because people that are unable to meet their basic needs are less likely to be interested in saving the environment. ...
... Environmental science has so many interacting parts, it is not easy to apply one system to another. Human well-being is a concern because people that are unable to meet their basic needs are less likely to be interested in saving the environment. ...
Reading Record Assessment
... (Earth is made up of layers called the core, mantle, and crust. The core is the centre of Earth and is surrounded by the mantle. The top layer of Earth is the crust.) ...
... (Earth is made up of layers called the core, mantle, and crust. The core is the centre of Earth and is surrounded by the mantle. The top layer of Earth is the crust.) ...
PHSC 4013 Course Outline—Fall 2008
... simulation to check for consistency: do the actual results match the expected results in a reasonable manner? o If the hypothesis passes the tests over time, it is upgraded to a theory, which continues to be tested as our realm of knowledge continues to grow. o A Scientific Law is a description or t ...
... simulation to check for consistency: do the actual results match the expected results in a reasonable manner? o If the hypothesis passes the tests over time, it is upgraded to a theory, which continues to be tested as our realm of knowledge continues to grow. o A Scientific Law is a description or t ...
OUTLINE (GEOS 418)
... MATH F200X; PHYS F104X; or permission of instructor. Professor: Douglas Christensen Office: Rm 413C Geophysical Institute - Phone 474-7426 Rm 341 Natural Science Building E-mail: [email protected] Office Hours By appointment Grading: On a curve Mid Term, ~October 19, 2012 (30%) Final, December ...
... MATH F200X; PHYS F104X; or permission of instructor. Professor: Douglas Christensen Office: Rm 413C Geophysical Institute - Phone 474-7426 Rm 341 Natural Science Building E-mail: [email protected] Office Hours By appointment Grading: On a curve Mid Term, ~October 19, 2012 (30%) Final, December ...
Landform Processes Hasse`s Geomorphology Rule #1
... Hasse’s Rule #2 : “All Earth land features that are not flat are due to active geologic processes” ...
... Hasse’s Rule #2 : “All Earth land features that are not flat are due to active geologic processes” ...
Earth`s Landforms
... • Plate tectonics – Large, slow moving plates that make up Earth’s surface. When moved, they carry continents and the ocean floors! ...
... • Plate tectonics – Large, slow moving plates that make up Earth’s surface. When moved, they carry continents and the ocean floors! ...
Extreme Earth - Introduction
... Formation of the Earth’s core and crust. The Earth’s atmosphere and the evolution of early life. ...
... Formation of the Earth’s core and crust. The Earth’s atmosphere and the evolution of early life. ...
Document
... 1. The process of rocks changing from one rock into another is the __________________________. 2. __________________________ are continent sized blocks of land that move slowly about the Earth’s surface, driven by heat. 3. A _________________________is a crack in the crust (or where two plates meet) ...
... 1. The process of rocks changing from one rock into another is the __________________________. 2. __________________________ are continent sized blocks of land that move slowly about the Earth’s surface, driven by heat. 3. A _________________________is a crack in the crust (or where two plates meet) ...
Color and Lenses - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... 7. _____________ and temperature increase as you travel from the outside of Earth to the inner core. ...
... 7. _____________ and temperature increase as you travel from the outside of Earth to the inner core. ...
Science Test Study Guide
... The solar system is made up of the Sun and all the objects that orbit it. Our Sun is a star. The Moon is a satellite of the Earth. There are eight planets that circle the sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. All the planets orbit the Sun. The inner planets are the ...
... The solar system is made up of the Sun and all the objects that orbit it. Our Sun is a star. The Moon is a satellite of the Earth. There are eight planets that circle the sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. All the planets orbit the Sun. The inner planets are the ...
1 - Net Start Class
... combination of convection and the earth’s rotation 45. Permafrost-Permanently frozen soil found in Tundra 46. Taiga- Forests made up of coniferous trees that stretch around the higher latitudes 47. Tornado Alley- Highest concentration of tornadoes in the world. In the southern great plains of the US ...
... combination of convection and the earth’s rotation 45. Permafrost-Permanently frozen soil found in Tundra 46. Taiga- Forests made up of coniferous trees that stretch around the higher latitudes 47. Tornado Alley- Highest concentration of tornadoes in the world. In the southern great plains of the US ...
Landforms - Rankin County School District / Homepage
... member must present. Turn in song! – Skit- Must be informational yet entertaining. Every group member must have a part. CAN NOT HAVE a Narrator!! Turn in script! ...
... member must present. Turn in song! – Skit- Must be informational yet entertaining. Every group member must have a part. CAN NOT HAVE a Narrator!! Turn in script! ...
study guide - Hull Lessons
... Water causes physical weathering when it breaks a rock into pieces by expanding when it freezes. Water causes chemical weathering when it mixes with air pollutants (carbon dioxide) to form weak acids that change what rocks are made of (dissoves limestone). Weathered rock and soil are moved by the pr ...
... Water causes physical weathering when it breaks a rock into pieces by expanding when it freezes. Water causes chemical weathering when it mixes with air pollutants (carbon dioxide) to form weak acids that change what rocks are made of (dissoves limestone). Weathered rock and soil are moved by the pr ...
(C/1861 G1) which produces the Lyrids meteor showers
... generated by comets intersecting its orbit. While entering into the Earth’s atmosphere, the debris burn up and produce streaks of lights which can be viewed from Earth. During April 16-25, the Earth passes through the debris of Comet Thatcher (C/1861 G1) which produces the Lyrids meteor showers. Abo ...
... generated by comets intersecting its orbit. While entering into the Earth’s atmosphere, the debris burn up and produce streaks of lights which can be viewed from Earth. During April 16-25, the Earth passes through the debris of Comet Thatcher (C/1861 G1) which produces the Lyrids meteor showers. Abo ...
Layers of the Earth
... Layers of the Earth Composition (What it is made of) • _________________ • _________________ • _________________ The Crust • The _________________ is the _______________________ layer • It is ___________________________ km thick. • There are ________ types of ___________________. • One is __________ ...
... Layers of the Earth Composition (What it is made of) • _________________ • _________________ • _________________ The Crust • The _________________ is the _______________________ layer • It is ___________________________ km thick. • There are ________ types of ___________________. • One is __________ ...
Lecture 3 Review Sheet
... Lecture 3: Earth from Core to Crust Terminology: Magnetic field, magnetic field lines, geodynamo, solenoid, solar wind, magnetosphere, inner core, outer core, mantle, crust, asthenosphere, asthenospheric mantle, lithosphere, lithospheric mantle, continental crust, oceanic crust, the Moho, seismic an ...
... Lecture 3: Earth from Core to Crust Terminology: Magnetic field, magnetic field lines, geodynamo, solenoid, solar wind, magnetosphere, inner core, outer core, mantle, crust, asthenosphere, asthenospheric mantle, lithosphere, lithospheric mantle, continental crust, oceanic crust, the Moho, seismic an ...
Turtle
... releasing energy that spreads out like the powerful sound waves from the drum…Her Heart and the fiery Hearth of molten iron that beats beneath her shell. **Which of the 5 “Platonic” mathematical shapes has 12 equal pentagonal faces? What shape is the earth? [Dodecahedron…Oblate spheroid] *See poster ...
... releasing energy that spreads out like the powerful sound waves from the drum…Her Heart and the fiery Hearth of molten iron that beats beneath her shell. **Which of the 5 “Platonic” mathematical shapes has 12 equal pentagonal faces? What shape is the earth? [Dodecahedron…Oblate spheroid] *See poster ...
Ch 3, part 1
... up the air we breathe. Nearly all of these gases are found in the first 30 km above the Earth’s surface. ...
... up the air we breathe. Nearly all of these gases are found in the first 30 km above the Earth’s surface. ...
the junior version pdf file
... Do we want to discover the characteristics of the Earth’s surface and its internal structure? The planet we live on is the Earth and it is shaped like a large ball floating in Space. The Earth has a particular structure consisting of three parts: an external part known as the crust, a central part k ...
... Do we want to discover the characteristics of the Earth’s surface and its internal structure? The planet we live on is the Earth and it is shaped like a large ball floating in Space. The Earth has a particular structure consisting of three parts: an external part known as the crust, a central part k ...
File
... closer you get to the Earth’s surface, because there is more air above you. Measured with a barometer. • Air temperature changes depending on the composition of gasses in the area. ...
... closer you get to the Earth’s surface, because there is more air above you. Measured with a barometer. • Air temperature changes depending on the composition of gasses in the area. ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.